Page 116 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 116
92 Part II: The Organization of the Lymphohematopoietic Tissues Chapter 6: The Organization and Structure of Lymphoid Tissues 93
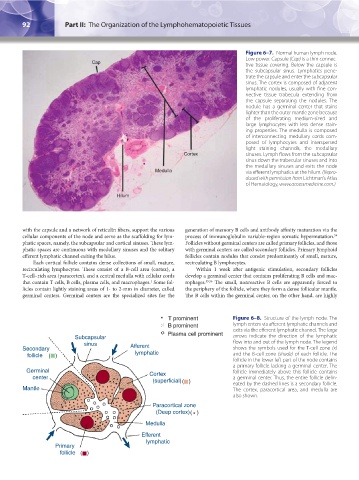
Figure 6–7. Normal human lymph node.
Low power. Capsule (Cap) is a thin connec-
Cap tive tissue covering. Below the capsule is
the subcapsular sinus. Lymphatics pene-
trate the capsule and enter the subcapsular
sinus. The cortex is composed of adjacent
lymphatic nodules, usually with fine con-
nective tissue trabecula extending from
the capsule separating the nodules. The
nodule has a germinal center that stains
lighter than the outer mantle zone because
of the proliferating medium-sized and
large lymphocytes with less dense stain-
ing properties. The medulla is composed
of interconnecting medullary cords com-
posed of lymphocytes and interspersed
light staining channels, the medullary
Cortex sinuses. Lymph flows from the subcapsular
sinus down the trabecular sinuses and into
the medullary sinuses and exits the node
Medulla via efferent lymphatics at the hilum. (Repro-
duced with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas
of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
Hilum
with the capsule and a network of reticulin fibers, support the various generation of memory B cells and antibody affinity maturation via the
cellular components of the node and serve as the scaffolding for lym- process of immunoglobulin variable-region somatic hypermutation.
54
phatic spaces, namely, the subcapsular and cortical sinuses. These lym- Follicles without germinal centers are called primary follicles, and those
phatic spaces are continuous with medullary sinuses and the solitary with germinal centers are called secondary follicles. Primary lymphoid
efferent lymphatic channel exiting the hilus. follicles contain nodules that consist predominantly of small, mature,
Each cortical follicle contains dense collections of small, mature, recirculating B lymphocytes.
recirculating lymphocytes. These consist of a B-cell area (cortex), a Within 1 week after antigenic stimulation, secondary follicles
T-cell–rich area (paracortex), and a central medulla with cellular cords develop a germinal center that contains proliferating B cells and mac-
that contain T cells, B cells, plasma cells, and macrophages. Some fol- rophages. 55,56 The small, nonreactive B cells are apparently forced to
1
licles contain lightly staining areas of 1- to 2-mm in diameter, called the periphery of the follicle, where they form a dense follicular mantle.
germinal centers. Germinal centers are the specialized sites for the The B cells within the germinal center, on the other hand, are highly
T prominent Figure 6–8. Structure of the lymph node. The
B prominent lymph enters via afferent lymphatic channels and
exits via the efferent lymphatic channel. The large
Plasma cell prominent
Subcapsular arrows indicate the direction of the lymphatic
sinus Afferent flow into and out of the lymph node. The legend
Secondary shows the symbols used for the T-cell zone (x)
follicle () lymphatic and the B-cell zone (shade) of each follicle. The
follicle in the lower left part of the node contains
a primary follicle lacking a germinal center. The
Germinal Cortex follicle immediately above this follicle contains
center a germinal center. Thus, the entire follicle delin-
(superficial)() eated by the dashed lines is a secondary follicle.
Mantle The cortex, paracortical area, and medulla are
also shown.
Paracortical zone
(Deep cortex)()
Medulla
Efferent
lymphatic
Primary
follicle ()
Kaushansky_chapter 06_p0085-0096.indd 92 17/09/15 5:53 pm