Page 113 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 113
88 Part II: The Organization of the Lymphohematopoietic Tissues Chapter 6: The Organization and Structure of Lymphoid Tissues 89
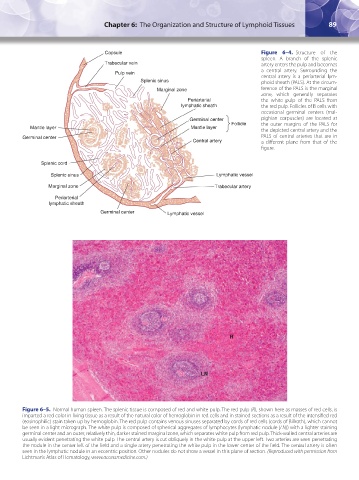
Capsule Figure 6–4. Structure of the
spleen. A branch of the splenic
Trabecular vein artery enters the pulp and becomes
a central artery. Surrounding the
Pulp vein central artery is a periarterial lym-
Splenic sinus phoid sheath (PALS). At the circum-
Marginal zone ference of the PALS is the marginal
zone, which generally separates
Periarterial the white pulp of the PALS from
lymphatic sheath the red pulp. Follicles of B cells with
occasional germinal centers (mal-
Germinal center pighian corpuscles) are located at
Follicle the outer margins of the PALS for
Mantle layer Mantle layer
the depicted central artery and the
Germinal center PALS of central arteries that are in
Central artery a different plane from that of the
figure.
Splenic cord
Splenic sinus Lymphatic vessel
Marginal zone Trabecular artery
Periarterial
lymphatic sheath
Germinal center Lymphatic vessel
R
LN
Figure 6–5. Normal human spleen. The splenic tissue is composed of red and white pulp. The red pulp (R), shown here as masses of red cells, is
imparted a red color in living tissue as a result of the natural color of hemoglobin in red cells and in stained sections as a result of the intensified red
(eosinophilic) stain taken up by hemoglobin. The red pulp contains venous sinuses separated by cords of red cells (cords of Billroth), which cannot
be seen in a light micrograph. The white pulp is composed of spherical aggregates of lymphocytes (lymphatic nodule [LN]) with a lighter staining
germinal center and an outer, relatively thin, darker stained marginal zone, which separates white pulp from red pulp. Thick-walled central arteries are
usually evident penetrating the white pulp. The central artery is cut obliquely in the white pulp at the upper left. Two arteries are seen penetrating
the nodule in the center-left of the field and a single artery penetrating the white pulp in the lower-center of the field. The central artery is often
seen in the lymphatic nodule in an eccentric position. Other nodules do not show a vessel in this plane of section. (Reproduced with permission from
Lichtman’s Atlas of Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
Kaushansky_chapter 06_p0085-0096.indd 89 17/09/15 5:53 pm