Page 114 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 114
90 Part II: The Organization of the Lymphohematopoietic Tissues Chapter 6: The Organization and Structure of Lymphoid Tissues 91
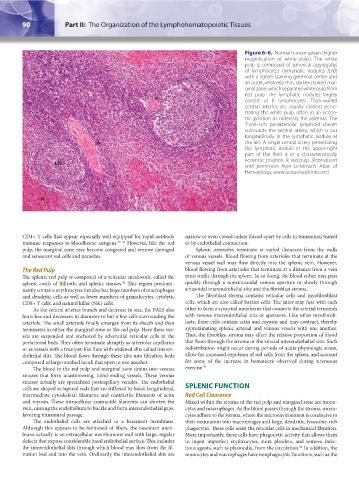
Figure 6–6. Normal human spleen (higher
magnification of white pulp). The white
pulp is composed of spherical aggregates
of lymphocytes (lymphatic nodules [LN])
with a lighter staining germinal center and
an outer, relatively thin, darker stained mar-
ginal zone, which separates white pulp from
red pulp. The lymphatic nodules largely
consist of B lymphocytes. Thick-walled
central arteries are usually evident pene-
trating the white pulp, often in an eccen-
tric position as noted by the asterisks. The
T-cell–rich periarteriolar lymphoid sheath
surrounds the central artery, which is cut
longitudinally in the lymphatic nodule at
the left. A single central artery penetrating
the lymphatic nodule in the upper-right
part of the field is in a characteristically
eccentric position. R, red pulp. (Reproduced
LN
with permission from Lichtman’s Atlas of
Hematology, www.accessmedicine.com.)
R
CD4+ T cells that appear especially well equipped for rapid antibody narrow or even closed unless forced apart by cells in transmural transit
immune responses to bloodborne antigens. 39–41 However, like the red or by endothelial contraction.
pulp, the marginal zone may become congested and remove damaged Splenic arterioles terminate at varied distances from the walls
and senescent red cells and parasites. of venous vessels. Blood flowing from arterioles that terminate at the
venous vessel wall may flow directly into the splenic vein. However,
The Red Pulp blood flowing from arterioles that terminate at a distance from a vein
The splenic red pulp is composed of a reticular meshwork, called the must traffic through the spleen. In so doing, the blood either may pass
splenic cords of Billroth, and splenic sinuses. This region predomi- quickly through a nonsinusoidal venous aperture or slowly through
42
nantly contains erythrocytes but also has large numbers of macrophages sinusoidal interendothelial slits and the fibroblast stroma.
and dendritic cells as well as fewer numbers of granulocytes, cytolytic The fibroblast stroma contains reticular cells and myofibroblast
CD8+ T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. cells, which are also called barrier cells. The latter may fuse with each
As the central arteries branch and decrease in size, the PALS also other to form a syncytial membrane that connects the arterial terminals
branches and decreases in diameter to but a few cells surrounding the with venous interendothelial slits or apertures. Like other myofibrob-
arteriole. The small arteriole finally emerges from its sheath and then lasts, these cells contain actin and myosin and may contract, thereby
terminates in either the marginal zone or the red pulp. Here these ves- approximating splenic arterial and venous vessels with one another.
sels are suspended and anchored by adventitial reticular cells in the Thus, the fibroblast stroma may affect the relative proportion of blood
periarterial beds. They often terminate abruptly as arteriolar capillaries that flows through the stroma or the sinusal interendothelial slits. Such
or as vessels with a trumpet-like flare with widened slits called interen- redistribution might occur during periods of acute physiologic stress,
dothelial slits. The blood flows through these slits into filtration beds allow for increased expulsion of red cells from the spleen, and account
composed of large-meshed loculi that open to one another. for some of the increase in hematocrit observed during strenuous
The blood in the red pulp and marginal zone drains into venous exercise. 43
sinuses that form anastomosing, blind-ending vessels. These venous
sinuses actually are specialized postcapillary venules. The endothelial
cells are shaped as tapered rods that are stiffened by basal, longitudinal, SPLENIC FUNCTION
intermediate cytoskeletal filaments and contractile filaments of actin Red Cell Clearance
and myosin. These intracellular contractile filaments can shorten the Mixed within the stroma of the red pulp and marginal zone are mono-
vein, causing the endothelium to buckle and form interendothelial gaps, cytes and macrophages. As the blood passes through the stroma, mono-
favoring transmural passage. cytes adhere to the stroma, where the microenvironment is conducive to
The endothelial cells are attached to a basement membrane. their maturation into macrophages and large, dendritic, lysosome-rich
Although this appears to be fashioned of fibers, the basement mem- phagocytes. These cells assist the reticular cells in mechanical filtration.
brane actually is an extracellular membranous wall with large, regular More importantly, these cells have phagocytic activity that allows them
defects that expose considerable basal endothelial surface. This includes to ingest imperfect erythrocytes, store platelets, and remove infec-
the interendothelial slits through which blood may flow from the fil- tious agents, such as plasmodia, from the circulation. In addition, the
44
tration bed and into the vein. Ordinarily the interendothelial slits are monocytes and macrophages have nonphagocytic functions, such as the
Kaushansky_chapter 06_p0085-0096.indd 90 17/09/15 5:53 pm