Page 1476 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1476
1450 Part X: Malignant Myeloid Diseases Chapter 89: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Related Disorders 1451
TKI is initiated, combination with anagrelide is associated with a nor- or blast phase as compared with imatinib. Thus far, an overall survival
malization of platelet counts. 414 advantage of dasatinib or nilotinib compared with imatinib has not
been shown. Third-generation TKIs, bosutinib and ponatinib, are
415
INITIAL THERAPY WITH A TYROSINE KINASE under study. Table 89–2 compares these inhibitors.
Imatinib Patients with newly diagnosed, chronic phase CML can be
INHIBITOR started on imatinib, 400 mg/day by mouth. The goal of imatinib therapy
Imatinib mesylate (imatinib) was the first TKI developed, and it was is to decrease the cells bearing the t(9;22) translocation (leukemic cells)
approved by the FDA for initial therapy of CML in 2002. Subsequently, to the lowest levels possible, during which process normal (polyclonal)
two second-generation TKIs, nilotinib and dasatinib, were approved for hematopoiesis is restored. The efficacy of imatinib is judged by measur-
initial therapy in 2010. This approval was based upon superior cyto- ing three benchmarks: hematologic response, cytogenetic response, and
genetic and molecular response rates with nilotinib and dasatinib at molecular response as defined in Table 89–3. 416,417 These benchmarks are
benchmark time points and lower rates of conversion to accelerated used to determine its maximal therapeutic effect. The time to achieve
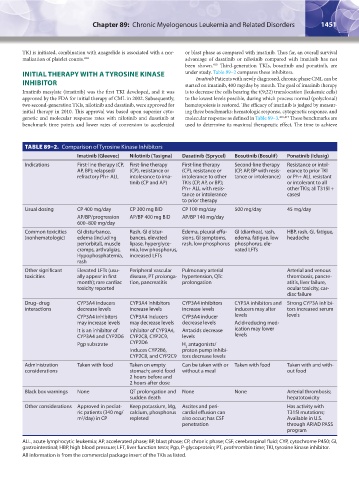
TABLE 89–2. Comparison of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Imatinib (Gleevec) Nilotinib (Tasigna) Dasatinib (Sprycel) Bosutinib (Bosulif) Ponatinib (Iclusig)
Indications First-line therapy (CP, First-line therapy First-line therapy Second-line therapy Resistance or intol-
AP, BP); relapsed/ (CP), resistance or (CP), resistance or (CP, AP, BP with resis- erance to prior TKI
refractory Ph+ ALL intolerance to ima- intolerance to other tance or intolerance) or Ph+ ALL resistant
tinib (CP and AP) TKIs (CP, AP, or BP); or intolerant to all
Ph+ ALL with resis- other TKIs; all T315I +
tance or intolerance casesI
to prior therapy
Usual dosing CP 400 mg/day CP 300 mg BID CP 100 mg/day 500 mg/day 45 mg/day
AP/BP/progression AP/BP 400 mg BID AP/BP 140 mg/day
600–800 mg/day
Common toxicities GI disturbance, Rash, GI distur- Edema, pleural effu- GI (diarrhea), rash, HBP, rash, GI, fatigue,
(nonhematologic) edema (including bances, elevated sions, GI symptoms, edema, fatigue, low headache
periorbital), muscle lipase, hyperglyce- rash, low phosphorus phosphorus, ele-
cramps, arthralgias, mia, low phosphorus, vated LFTs
Hypophosphatemia, increased LFTs
rash
Other significant Elevated LFTs (usu- Peripheral vascular Pulmonary arterial Arterial and venous
toxicities ally appear in first disease, PT prolonga- hypertension, QTc thrombosis, pancre-
month); rare cardiac tion, pancreatitis prolongation atitis, liver failure,
toxicity reported ocular toxicity, car-
diac failure
Drug–drug CYP3A4 inducers CYP3A4 inhibitors CYP3A4 inhibitors CYP3A inhibitors and Strong CYP3A inhibi-
interactions decrease levels increase levels increase levels inducers may alter tors increased serum
CYP3A4 inhibitors CYP3A4 inducers CYP3A4 inducer levels levels
may increase levels may decrease levels decrease levels Acid-reducing med-
It is an inhibitor of Inhibitor of CYP3A4, Antacids decrease ication may lower
CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 CYP2C8, CYP2C9, levels levels
Pgp substrate CYP2D6 H antagonists/
2
Induces CYP2B6, proton pump inhibi-
CYP2C8, and CYP2C9 tors decrease levels
Administration Taken with food Taken on empty Can be taken with or Taken with food Taken with and with-
considerations stomach; avoid food without a meal out food
2 hours before and
2 hours after dose
Black box warnings None QT prolongation and None None Arterial thrombosis;
sudden death hepatotoxicity
Other considerations Approved in pediat- Keep potassium, Mg, Ascites and peri- Has activity with
ric patients (340 mg/ calcium, phosphorus cardial effusion can T315I mutations;
m /day) in CP repleted also occur; has CSF Available in U.S.
2
penetration through ARIAD PASS
program
ALL, acute lymphocytic leukemia; AP, accelerated phase; BP, blast phase; CP, chronic phase; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; CYP, cytochrome P450; GI,
gastrointestinal; HBP, high blood pressure; LFT, liver function tests; Pgp, P-glycoprotein; PT, prothrombin time; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
All information is from the commercial package insert of the TKIs as listed.
Kaushansky_chapter 89_p1437-1490.indd 1451 9/18/15 3:41 PM