Page 1589 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1589
1564 Part XI: Malignant Lymphoid Diseases Chapter 94: Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia 1565
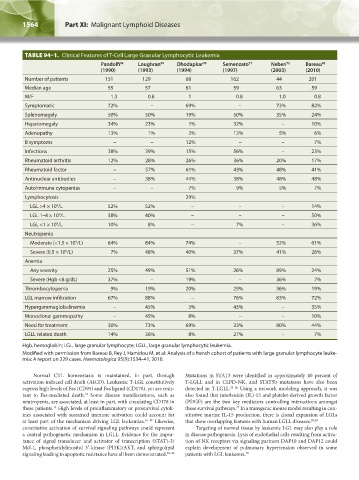
TABLE 94–1. Clinical Features of T-Cell Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia
69
68
Pandolfi Loughran Dhodapkar Semenzato Neben Bareau
72
48
70
71
(1990) (1993) (1994) (1997) (2003) (2010)
Number of patients 151 129 68 162 44 201
Median age 55 57 61 59 63 59
M/F 1.3 0.8 1 0.8 1.0 0.8
Symptomatic 72% – 69% – 73% 82%
Splenomegaly 50% 50% 19% 50% 35% 24%
Hepatomegaly 34% 23% 1% 32% – 10%
Adenopathy 13% 1% 3% 13% 5% 6%
B symptoms – – 12% – – 7%
Infections 38% 39% 15% 56% – 23%
Rheumatoid arthritis 12% 28% 26% 36% 20% 17%
Rheumatoid factor – 57% 61% 43% 48% 41%
Antinuclear antibodies – 38% 44% 38% 48% 48%
Autoimmune cytopenias – – 7% 9% 5% 7%
Lymphocytosis 29%
9
LGL >4 × 10 /L 52% 52% – – – 14%
LGL 1–4 × 10 /L 38% 40% – – – 50%
9
9
LGL <1 × 10 /L 10% 8% – 7% – 36%
Neutropenia
Moderate (<1.5 × 10 /L) 64% 84% 74% – 52% 61%
9
Severe (0.5 × 10 /L) 7% 48% 40% 37% 41% 26%
9
Anemia
Any severity 25% 49% 51% 26% 89% 24%
Severe (Hgb <8 g/dL) 37% – 19% – 36% 7%
Thrombocytopenia 9% 19% 20% 29% 36% 19%
LGL marrow infiltration 67% 88% – 76% 83% 72%
Hypergammaglobulinemia – 45% 5% 43% – 35%
Monoclonal gammopathy – 45% 8% – – 10%
Need for treatment 30% 73% 69% 33% 80% 44%
LGLL related death 14% 36% 8% 27% – 7%
Hgb, hemoglobin; LGL, large granular lymphocyte; LGLL, large granular lymphocytic leukemia.
Modified with permission from Bareau B, Rey J, Hamidou M, et al: Analysis of a french cohort of patients with large granular lymphocyte leuke-
mia: A report on 229 cases. Haematologica 95(9):1534–41, 2010.
Normal CTL homeostasis is maintained, in part, through Mutations in STAT3 were identified in approximately 40 percent of
activation-induced cell death (AICD). Leukemic T-LGL constitutively T-LGLL and in CLPD-NK, and STAT5b mutations have also been
express high levels of Fas (CD95) and Fas ligand (CD178), yet are resis- detected in T-LGLL. 23–26 Using a network modeling approach, it was
tant to Fas-mediated death. Some disease manifestations, such as also found that interleukin (IL)-15 and platelet-derived growth factor
14
neutropenia, are associated, at least in part, with circulating CD178 in (PDGF) are the two key mediators controlling interactions amongst
these patients. High levels of proinflammatory or prosurvival cytok- these survival pathways. In a transgenic mouse model resulting in con-
27
15
ines associated with sustained immune activation could account for stitutive murine IL-15 production, there is clonal expansion of LGLs
at least part of the mechanism driving LGL leukemias. 16–19 Likewise, that show overlapping features with human LGLL diseases. 28,29
constitutive activation of survival signaling pathways could represent Targeting of normal tissue by leukemic LGL may also play a role
a central pathogenetic mechanism in LGLL. Evidence for the impor- in disease pathogenesis. Lysis of endothelial cells resulting from activa-
tance of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)-3/ tion of NK receptors via signaling partners DAP10 and DAP12 could
Mcl-1, phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase (PI3K)/AKT, and sphingolipid explain development of pulmonary hypertension observed in some
signaling leading to apoptotic resistance have all been demonstrated. 20–22 patients with LGL leukemia. 30
Kaushansky_chapter 94_p1563-1568.indd 1564 9/18/15 10:52 AM