Page 1863 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1863
1838 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 112: Platelet Morphology, Biochemistry, and Function 1839
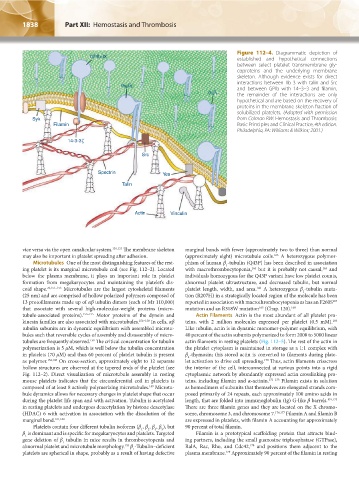
Figure 112–4. Diagrammatic depiction of
established and hypothetical connections
between select platelet transmembrane gly-
coproteins and the underlying membrane
skeleton. Although evidence exists for direct
a b interactions between IIb 3 with talin and Src
IIb 3
and between GPIb with 14–3–3 and filamin,
a b the remainder of the interactions are only
2 1
hypothetical and are based on the recovery of
proteins in the membrane skeleton fraction of
solubilized platelets. (Adapted with permission
from Colman RW: Hemostasis and Thrombosis:
Basic Principles and Clinical Practice, 4th edition.
Philadelphia, PA: Williams & Wilkins; 2001.)
vice versa via the open canalicular system. 101,133 The membrane skeleton marginal bands with fewer (approximately two to three) than normal
may also be important in platelet spreading after adhesion. (approximately eight) microtubule coils. A heterozygous polymor-
163
Microtubules One of the most distinguishing features of the rest- phism of human β -tubulin (Q43P) has been described in association
1
ing platelet is its marginal microtubule coil (see Fig. 112–2). Located with macrothrombocytopenia, but it is probably not causal, and
165
164
below the plasma membrane, it plays an important role in platelet individuals homozygous for the Q43P variant have low platelet counts,
formation from megakaryocytes and maintaining the platelet’s dis- abnormal platelet ultrastructure, and decreased tubulin, but normal
coid shape. 76,151–153 Microtubules are the largest cytoskeletal filaments platelet length, width, and area. A heterozygous β -tubulin muta-
166
1
(25 nm) and are comprised of hollow polarized polymers composed of tion (R207H) in a strategically located region of the molecule has been
13 protofilaments made up of αβ tubulin dimers (each of Mr 110,000) reported in association with macrothrombocytopenia as has an F260S
167
that associate with several high-molecular-weight proteins (micro- mutation and an R318W mutation (Chap. 120). 168
165
tubule-associated proteins). 153–155 Motor proteins of the dynein and Actin Filaments Actin is the most abundant of all platelet pro-
kinesin families are also associated with microtubules. 156–158 In cells, αβ teins, with 2 million molecules expressed per platelet (0.5 mM).
169
tubulin subunits are in dynamic equilibrium with assembled microtu- Like tubulin, actin is in dynamic monomer-polymer equilibrium, with
bules such that reversible cycles of assembly and disassembly of micro- 40 percent of the actin subunits polymerized to form 2000 to 5000 linear
tubules are frequently observed. The critical concentration for tubulin actin filaments in resting platelets (Fig. 112–5). The rest of the actin in
159
polymerization is 5 μM, which is well below the tubulin concentration the platelet cytoplasm is maintained in storage as a 1:1 complex with
in platelets (70 μM) and thus 60 percent of platelet tubulin is present β -thymosin; this stored actin is converted to filaments during plate-
4
as polymer. 154,160 On cross-section, approximately eight to 12 separate let activation to drive cell spreading. Thus, actin filaments crisscross
170
hollow structures are observed at the tapered ends of the platelet (see the interior of the cell, interconnected at various points into a rigid
Fig. 112–2). Direct visualization of microtubule assembly in resting cytoplasmic network by abundantly expressed actin crosslinking pro-
mouse platelets indicates that the circumferential coil in platelets is teins, including filamin and α-actinin. 171–173 Filamin exists in solution
composed of at least 8 actively polymerizing microtubules. Microtu- as homodimers of subunits that themselves are elongated strands com-
159
bule dynamics allows for necessary changes in platelet shape that occur posed primarily of 24 repeats, each approximately 100 amino acids in
during the platelet life span and with activation. Tubulin is acetylated length, that are folded into immunoglobulin (Ig) G-like β barrels. 174,175
in resting platelets and undergoes deacetylation by histone deacetylase There are three filamin genes and they are located on the X chromo-
(HDAC) 6 with activation in association with the dissolution of the some, chromosome 3, and chromosome 7. 176,177 Filamin A and filamin B
marginal band. 161,162 are expressed in platelets, with filamin A accounting for approximately
Platelets contain four different tubulin isoforms (β , β , β , β ), but 90 percent of total filamin.
4
1
2
5
β is dominant and is specific for megakaryocytes and platelets. Targeted Filamin is a prototypical scaffolding protein that attracts bind-
1
gene deletion of β tubulin in mice results in thrombocytopenia and ing partners, including the small guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase),
1
abnormal platelet and microtubule morphology. β -Tubulin–deficient RalA, Rac, Rho, and Cdc42, and positions them adjacent to the
153
178
1
platelets are spherical in shape, probably as a result of having defective plasma membrane. Approximately 90 percent of the filamin in resting
179
Kaushansky_chapter 112_p1829-1914.indd 1838 17/09/15 3:26 pm