Page 1858 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1858
1832 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 112: Platelet Morphology, Biochemistry, and Function 1833
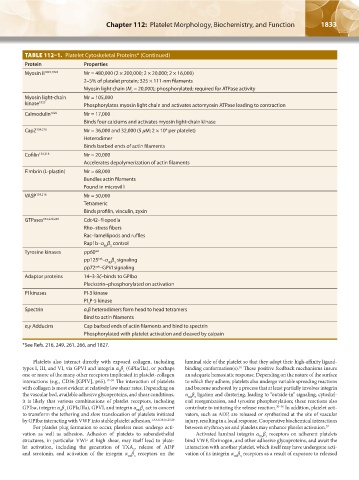
TABLE 112–1. Platelet Cytoskeletal Proteins* (Continued)
Protein Properties
Myosin II 1823,1824 Mr = 480,000 (2 × 200,000; 2 × 20,000; 2 × 16,000)
2–5% of platelet protein; 325 × 111-nm filaments
Myosin light chain (M = 20,000); phosphorylated; required for ATPase activity
r
Myosin light-chain Mr = 105,000
kinase 1825 Phosphorylates myosin light chain and activates actomyosin ATPase leading to contraction
Calmodulin 1826 Mr = 17,000
Binds four calciums and activates myosin light-chain kinase
CapZ 154,216 Mr = 36,000 and 32,000 (5 μM; 2 × 10 per platelet)
4
Heterodimer
Binds barbed ends of actin filaments
Cofilin 154,216 Mr = 20,000
Accelerates depolymerization of actin filaments
Fimbrin (L-plastin) Mr = 68,000
Bundles actin filaments
Found in microvilli
VASP 154,216 Mr = 50,000
Tetrameric
Binds profilin, vinculin, zyxin
GTPases 154,229,249 Cdc42–filopodia
Rho–stress fibers
Rac–lamellipods and ruffles
Rap1b–α β control
IIb 3
Tyrosine kinases pp60 src
Fak
pp125 –α β signaling
IIb 3
syk
pp72 –GPVI signaling
Adaptor proteins 14–3-3ζ–binds to GPIbα
Pleckstrin–phosphorylated on activation
PI kinases PI-3 kinase
PI P-5 kinase
4
Spectrin α,β heterodimers form head to head tetramers
Bind to actin filaments
α,γ Adducins Cap barbed ends of actin filaments and bind to spectrin
Phosphorylated with platelet activation and cleaved by calpain
*See Refs. 216, 249, 261, 266, and 1827.
Platelets also interact directly with exposed collagen, including luminal side of the platelet so that they adopt their high-affinity ligand-
types I, III, and VI, via GPVI and integrin α β (GPIa/IIa), or perhaps binding conformation(s). These positive feedback mechanisms insure
10
2 1
one or more of the many other receptors implicated in platelet-collagen an adequate hemostatic response. Depending on the nature of the surface
interactions (e.g., CD36 [GPIV], p65). 17–29 The interaction of platelets to which they adhere, platelets also undergo variable spreading reactions
with collagen is most evident at relatively low shear rates. Depending on and become anchored by a process that at least partially involves integrin
the vascular bed, available adhesive glycoproteins, and shear conditions, α β ligation and clustering, leading to “outside-in” signaling, cytoskel-
IIb 3
it is likely that various combinations of platelet receptors, including etal reorganization, and tyrosine phosphorylation; these reactions also
GPIbα, integrin α β (GPIa/IIa), GPVI, and integrin α β act in concert contribute to initiating the release reaction. 30–36 In addition, platelet acti-
IIb 3
2 1
to transform the tethering and slow translocation of platelets initiated vators, such as ADP, are released or synthesized at the site of vascular
by GPIbα interacting with VWF into stable platelet adhesion. 1,3,4,8,10,16,25,28 injury, resulting in a local response. Cooperative biochemical interactions
For platelet plug formation to occur, platelets must undergo acti- between erythrocytes and platelets may enhance platelet activation. 37
vation as well as adhesion. Adhesion of platelets to subendothelial Activated luminal integrin α β receptors on adherent platelets
IIb 3
structures, in particular VWF at high shear, may itself lead to plate- bind VWF, fibrinogen, and other adhesive glycoproteins, and await the
let activation, including the generation of TXA , release of ADP interaction with another platelet, which itself may have undergone acti-
2
and serotonin, and activation of the integrin α β receptors on the vation of its integrin α β receptors as a result of exposure to released
IIb 3 IIb 3
Kaushansky_chapter 112_p1829-1914.indd 1833 17/09/15 3:25 pm