Page 1860 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1860
1834 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 112: Platelet Morphology, Biochemistry, and Function 1835
SMF
C.S.
E.C.
C.M. M.
M.T. D.T.S.
Gly.
D.B.
D.B.
G.
A D
G.
GZ M.
D.B.
C.M.
M.T.
D.T.S.
B
C.S. E.C.
Gly.
G+D.B. G.T.
E
MT
Gly.
M
DB
DTS
OCS
G
C F
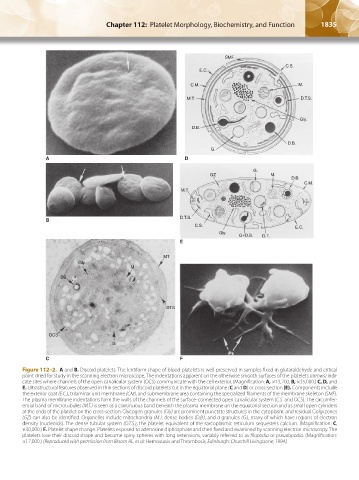
Figure 112–2. A and B. Discoid platelets. The lentiform shape of blood platelets is well preserved in samples fixed in glutaraldehyde and critical
point dried for study in the scanning electron microscope. The indentations apparent on the otherwise smooth surfaces of the platelets (arrows) indi-
cate sites where channels of the open canalicular system (OCS) communicate with the cell exterior. (Magnification: A, ×13,200; B, ×35,000.) C, D, and
E. Ultrastructural features observed in thin sections of discoid platelets cut in the equatorial plane (C and D) or cross-section (E). Components include
the exterior coat (E.C.), trilaminar unit membrane (CM), and submembrane area containing the specialized filaments of the membrane skeleton (SMF).
The plasma membrane indentations form the walls of the channels of the surface-connected open canalicular system (C.S. and OCS). The circumfer-
ential band of microtubules (M.T.) is seen as a continuous band beneath the plasma membrane on the equatorial section and as small open cylinders
at the ends of the platelet on the cross-section. Glycogen granules (Gly) are prominent punctate structures in the cytoplasm, and residual Golgi zones
(GZ) can also be identified. Organelles include mitochondria (M.), dense bodies (D.B.), and α granules (G.), many of which have regions of electron
density (nucleoids). The dense tubular system (D.T.S.), the platelet equivalent of the sarcoplasmic reticulum sequesters calcium. (Magnification: C,
×30,000.) F. Platelet shape change. Platelets exposed to adenosine diphosphate and then fixed and examined by scanning electron microscopy. The
platelets lose their discoid shape and become spiny spheres with long extensions, variably referred to as filopodia or pseudopodia. (Magnification:
×17,000.) (Reproduced with permission from Bloom AL, et al: Hemostasis and Thrombosis, Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 1994.)
Kaushansky_chapter 112_p1829-1914.indd 1835 17/09/15 3:26 pm