Page 1993 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1993
1968 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 115: Vascular Function In Hemostasis 1969
TABLE 115–1. Chronology of Endothelial Cell activating guanylate cyclase, the resulting increase in cyclic guanylate
monophosphate (GMP) inhibits platelet function and induces vascu-
Thromboregulators lar relaxation. 10,11 Endothelial cell ecto-ATP/Dase-1/CD39 is a mem-
Early thromboregulators brane-associated apyrase that metabolizes adenosine diphosphate
Nitric oxide (NO) (ADP) in the primary platelet releasate, preventing further platelet acti-
Eicosanoids (prostacyclin and prostaglandin D ) vation and recruitment. 12,13
2
Endothelial cell CD39/ENTPDase1 Late thromboregulators produced by endothelial cells act either
Endothelin to prevent excessive thrombin generation or to promote lysis of intra-
Late thromboregulators vascular thrombi (see Tabl e 115–1). Antithrombin, a natural anticoag-
Endothelin ulant, acts as an inhibitor of thrombin and factor Xa in the circulation.
Endothelial cell heparan proteoglycans act as cofactors for antith-
Antithrombin rombin. The tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) inhibits the com-
Endothelial cell/heparin proteoglycans plex between factor VIIa and tissue factor (TF). The thrombomodulin/
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR)/protein C system in the
Thrombomodulin-protein C-protein S pathway vascular wall regulates hemostasis through inactivation of procoagu-
Fibrinolytic system (plasminogen activators, inhibitors, and lant cofactors, and antiinflammatory activity. The fibrinolytic system
14
receptors) is intimately involved with the vascular endothelium because endo-
Inflammatory thromboregulators thelial cells not only synthesize and secrete tissue plasminogen activa-
Thrombomodulin-protein C-protein S pathway tor (t-PA), but also regulate formation of plasmin from its precursor,
15
Cellular adhesion molecules plasminogen, through the expression of receptors. Impairment of
Selectins fibrinolytic potential can play a central role in the etiology of occlu-
sive vascular disease. Finally, endothelial cell adhesion molecules,
16
including the cell adhesion molecules (CAMs: mucosal addressin cell
t-PA Thr PC adhesion molecule [MAdCAM]-1, intercellular adhesion molecule
AT u-PA PLG VIIa [ICAM]-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule [VCAM]-1, and plate-
A2 TM EPCR TFPI let endothelial cell adhesion molecule [PECAM]-1) and the selectins
HS uPAR p11 TF (P- and E-selectin), are glycoproteins that modulate multiple inter-
CD39 actions between the endothelium and various classes of circulating
17
CAMs leukocytes, thereby modulating vascular patency. Together, these
NO mechanisms define thromboregulation, the processes by which blood
Endothelial cell JAMs cells and cells of the vessel wall, through their close proximity, interact
PGI 2
Selectins to facilitate or inhibit thrombus formation. 18
The physiologic defense systems that render endothelial surfaces
ET CD99 and blood cells antithrombotic can be overwhelmed by excessive shear
stress, increased turbulence, injury, inflammation, and severe athero-
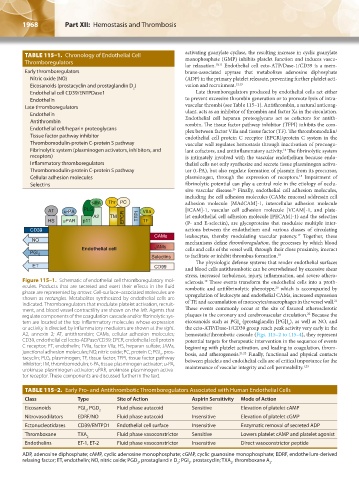
Figure 115–1. Schematic of endothelial cell thromboregulatory mol- sclerosis. These events transform the endothelial cells into a proth-
19
ecules. Products that are secreted and exert their effects in the fluid rombotic and antifibrinolytic phenotype, which is accompanied by
20
phase are represented by arrows. Cell-surface–associated molecules are upregulation of leukocyte and endothelial CAMs, increased expression
shown as rectangles. Metabolites synthesized by endothelial cells are 21
indicated. Thromboregulators that modulate platelet activation, recruit- of TF, and accumulation of monocytes/macrophages in the vessel wall.
ment, and blood vessel contractility are shown on the left. Agents that These events commonly occur at the site of fissured atherosclerotic
22
regulate components of the coagulation cascade and/or fibrinolytic sys- plaques in the coronary and cerebrovascular circulation. Because the
tem are located at the top. Inflammatory molecules whose expression eicosanoids such as PGI (prostaglandin [PG]I ), as well as NO, and
2
2
or activity is directed by inflammatory mediators are shown at the right. the ecto-ATP/Dase-1/CD39 group reach peak activity very early in the
A2, annexin 2; AT, antithrombin; CAMs, cellular adhesion molecules; hemostatic/thrombotic cascade (Figs. 115–2 to 115–4), they represent
CD39, endothelial cell ecto-ADPase/CD39; EPCR, endothelial cell protein potential targets for therapeutic intervention in the sequence of events
C receptor; ET, endothelin; FVIIa, factor VIIa; HS, heparan sulfate; JAMs, beginning with platelet activation, and leading to coagulation, throm-
junctional adhesion molecules; NO, nitric oxide; PC, protein C; PGI , pros- bosis, and atherogenesis. 21,22 Finally, functional and physical contacts
2
tacyclin; PLG, plasminogen; TF, tissue factor; TFPI, tissue factor pathway between platelets and endothelial cells are of critical importance for the
inhibitor; TM, thrombomodulin; t-PA, tissue plasminogen activator; u-PA, 1,23
urokinase plasminogen activator; uPAR, urokinase plasminogen activa- maintenance of vascular integrity and cell permeability.
tor receptor. These components are discussed further in the text.
TABLE 115–2. Early Pro- and Antithrombotic Thromboregulators Associated with Human Endothelial Cells
Class Type Site of Action Aspirin Sensitivity Mode of Action
Eicosanoids PGI , PGD Fluid phase autacoid Sensitive Elevation of platelet cAMP
2 2
Nitrovasodilators EDRF/NO Fluid phase autacoid Insensitive Elevation of platelet cGMP
Ectonucleotidases CD39/ENTPD1 Endothelial cell surface Insensitive Enzymatic removal of secreted ADP
Thromboxane TXA Fluid phase vasoconstrictor Sensitive Lowers platelet cAMP and platelet agonist
2
Endothelins ET-1, ET-2 Fluid phase vasoconstrictor Insensitive Direct vasoconstrictor peptide
ADP, adenosine diphosphate; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; EDRF, endothelium-derived
relaxing factor; ET, endothelin; NO, nitric oxide; PGD , prostaglandin D ; PGI , prostacyclin; TXA , thromboxane A .
2 2 2 2 2
Kaushansky_chapter 115_p1967-1984.indd 1968 9/18/15 10:07 AM