Page 2014 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2014
1988 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 116: Classification, Clinical Manifestations, and Evaluation of Disorders of Hemostasis 1989
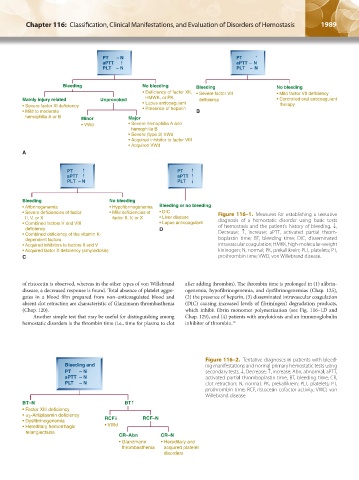
PT – N PT
aPTT aPTT – N
PLT – N PLT – N
Bleeding No bleeding Bleeding No bleeding
• Deficiency of factor XII, • Severe factor VII • Mild factor VII deficiency
Mainly injury related Unprovoked HMWK, or PK deficiency • Controlled oral anticoagulant
• Severe factor Xl deficiency • Lupus anticoagulant therapy
• Presence of heparin
• Mild to moderate B
hemophilia A or B Minor Major
• VWd • Severe hemophilia A and
hemophilia B
• Severe (type 3) VWd
• Acquired inhibitor to factor VIII
• Acquired VWd
A
PT PT
aPTT aPTT
PLT – N PLT
Bleeding No bleeding
• Afibrinogenemia • Hypofibrinogenemia Bleeding or no bleeding
• Severe deficiencies of factor • Mild deficiencies of • DIC Figure 116–1. Measures for establishing a tentative
II, V, or X factor II, V, or X • Liver disease diagnosis of a hemostatic disorder using basic tests
• Combined factors V and VIII • Lupus anticoagulant of hemostasis and the patient’s history of bleeding. ↓,
deficiency D Decrease; ↑, increase; aPTT, activated partial throm-
• Combined deficiency of the vitamin K-
dependent factors boplastin time; BT, bleeding time; DIC, disseminated
• Acquired inhibitors to factors II and V intravascular coagulation; HMKK, high-molecular-weight
• Acquired factor X deficiency (amyloidosis) kininogen; N, normal; PK, prekallikrein; PLT, platelets; PT,
C prothrombin time; VWD, von Willebrand disease.
of ristocetin is observed, whereas in the other types of von Willebrand after adding thrombin). The thrombin time is prolonged in (1) afibrin-
disease, a decreased response is found. Total absence of platelet aggre- ogenemia, hypofibrinogenemia, and dysfibrinogenemias (Chap. 125),
gates in a blood film prepared from non–anticoagulated blood and (2) the presence of heparin, (3) disseminated intravascular coagulation
absent clot retraction are characteristic of Glanzmann thrombasthenia (DIC) causing increased levels of fibrin(ogen) degradation products,
(Chap. 120). which inhibit fibrin monomer polymerization (see Fig. 116–1D and
Another simple test that may be useful for distinguishing among Chap. 129), and (4) patients with amyloidosis and an immunoglobulin
hemostatic disorders is the thrombin time (i.e., time for plasma to clot inhibitor of thrombin. 12
Figure 116–2. Tentative diagnoses in patients with bleed-
Bleeding and ing manifestations and normal primary hemostatic tests using
PT – N secondary tests. ↓, Decrease; ↑, increase; Abn, abnormal; aPTT,
aPTT – N activated partial thromboplastin time; BT, bleeding time; CR,
PLT – N clot retraction; N, normal; PK, prekallikrein; PLT, platelets; PT,
prothrombin time; RCF, ristocetin cofactor activity; VWD, von
Willebrand disease.
BT–N BT
• Factor XIII deficiency
α -Antiplasmin deficiency
• 2 RCF RCF–N
• Dysfibrinogenemia
• Hereditary hemorrhagic • VWd
telangiectasia
CR–Abn CR–N
• Glanzmann • Hereditary and
thrombasthenia acquired platelet
disorders
Kaushansky_chapter 116_p1985-1992.indd 1989 9/18/15 10:13 AM