Page 2055 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2055
2030 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 118: Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia 2031
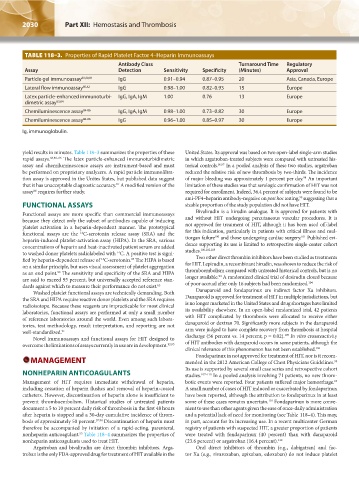
TABLE 118–3. Properties of Rapid Platelet Factor 4–Heparin Immunoassays
Antibody Class Turnaround Time Regulatory
Assay Detection Sensitivity Specificity (Minutes) Approval
Particle gel immunoassay 68,80,81 IgG 0.91–0.94 0.87–0.95 20 Asia, Canada, Europe
Lateral flow immunoassay 80,82 IgG 0.98–1.00 0.82–0.93 15 Europe
Latex particle-enhanced immunoturbi- IgG, IgA, IgM 1.00 0.76 13 Europe
dimetric assay 83,84
Chemiluminescence assay 84-86 IgG, IgA, IgM 0.98–1.00 0.73–0.82 30 Europe
Chemiluminescence assay 84-86 IgG 0.96–1.00 0.85–0.97 30 Europe
Ig, immunoglobulin.
yield results in minutes. Table 118–3 summarizes the properties of these United States. Its approval was based on two open-label single-arm studies
rapid assays. 68,80–86 The latex particle-enhanced immunoturbidimetric in which argatroban-treated subjects were compared with untreated his-
assay and chemiluminescence assays are instrument-based and must torical controls. 96,97 In a pooled analysis of these two studies, argatroban
be performed on proprietary analyzers. A rapid particle immunofiltra- reduced the relative risk of new thrombosis by two-thirds. The incidence
tion assay is approved in the Unites States, but published data suggest of major bleeding was approximately 1 percent per day. An important
98
that it has unacceptable diagnostic accuracy. A modified version of the limitation of these studies was that serologic confirmation of HIT was not
87
assay requires further study. required for enrollment. Indeed, 36.4 percent of subjects were found to be
88
anti-PF4–heparin antibody-negative on post hoc testing, suggesting that a
99
FUNCTIONAL ASSAYS sizable proportion of the study population did not have HIT.
Functional assays are more specific than commercial immunoassays Bivalirudin is a hirudin analogue. It is approved for patients with
because they detect only the subset of antibodies capable of inducing and without HIT undergoing percutaneous vascular procedures. It is
platelet activation in a heparin-dependent manner. The prototypical not approved for treatment of HIT, although it has been used off-label
functional assays are the C-serotonin release assay (SRA) and the for this indication, particularly in patients with critical illness and mul-
14
100
101
heparin-induced platelet-activation assay (HIPA). In the SRA, various tiorgan failure and those undergoing cardiac surgery. Published evi-
concentrations of heparin and heat-inactivated patient serum are added dence supporting its use is limited to retrospective single-center cohort
100,102,103
14
to washed donor platelets radiolabeled with C. A positive test is signi- studies.
14
fied by heparin-dependent release of C-serotonin. The HIPA is based Two other direct thrombin inhibitors have been studied as treatments
89
on a similar principle, but uses visual assessment of platelet aggregation for HIT. Lepirudin, a recombinant hirudin, was shown to reduce the risk of
as an end point. The sensitivity and specificity of the SRA and HIPA thromboembolism compared with untreated historical controls, but is no
90
94
are said to exceed 95 percent, but universally accepted reference stan- longer available. A randomized clinical trial of desirudin closed because
104
dards against which to measure their performance do not exist. 63 of poor accrual after only 16 subjects had been randomized.
Washed platelet functional assays are technically demanding. Both Danaparoid and fondaparinux are indirect factor Xa inhibitors.
the SRA and HIPA require reactive donor platelets and the SRA requires Danaparoid is approved for treatment of HIT in multiple jurisdictions, but
radioisotope. Because these reagents are impracticable for most clinical is no longer marketed in the United States and drug shortages have limited
laboratories, functional assays are performed at only a small number its availability elsewhere. In an open-label randomized trial, 42 patients
of reference laboratories around the world. Even among such labora- with HIT complicated by thrombosis were allocated to receive either
tories, test methodology, result interpretation, and reporting are not danaparoid or dextran 70. Significantly more subjects in the danaparoid
well-standardized. 91 arm were judged to have complete recovery from thrombosis at hospital
105
Novel immunoassays and functional assays for HIT designed to discharge (56 percent vs. 14 percent; p = 0.02). In vitro crossreactivity
overcome the limitations of assays currently in use are in development. 92,93 of HIT antibodies with danaparoid occurs in some patients, although the
clinical relevance of this phenomenon has not been established. 106
Fondaparinux in not approved for treatment of HIT, nor is it recom-
MANAGEMENT mended in the 2012 American College of Chest Physicians Guidelines.
95
Its use is supported by several small case series and retrospective cohort
NONHEPARIN ANTICOAGULANTS studies. 107–110 In a pooled analysis involving 71 patients, no new throm-
Management of HIT requires immediate withdrawal of heparin, botic events were reported. Four patients suffered major hemorrhage.
63
including cessation of heparin flushes and removal of heparin-coated A small number of cases of HIT induced or exacerbated by fondaparinux
catheters. However, discontinuation of heparin alone is insufficient to have been reported, although the attribution to fondaparinux in at least
prevent thromboembolism. Historical studies of untreated patients some of these cases remains uncertain. Fondaparinux is more conve-
111
document a 5 to 10 percent daily risk of thrombosis in the first 48 hours nient to use than other agents given the ease of once-daily administration
after heparin is stopped and a 30-day cumulative incidence of throm- and a potential lack of need for monitoring (see Table 118–4). This may,
bosis of approximately 50 percent. 57,94 Discontinuation of heparin must in part, account for its increasing use. In a recent multicenter German
therefore be accompanied by initiation of a rapid-acting, parenteral, registry of patients with suspected HIT, a greater proportion of patients
nonheparin anticoagulant. Table 118–4 summarizes the properties of were treated with fondaparinux (40 percent) than with danaparoid
95
nonheparin anticoagulants used to treat HIT. (23.6 percent) or argatroban (16.4 percent). 112
Argatroban and bivalirudin are direct thrombin inhibitors. Arga- Oral direct inhibitors of thrombin (e.g., dabigatran) and fac-
troban is the only FDA-approved drug for treatment of HIT available in the tor Xa (e.g., rivaroxaban, apixaban, edoxaban) do not induce platelet
Kaushansky_chapter 118_p2025-2034.indd 2030 9/18/15 5:43 PM