Page 2066 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2066
2040 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 120: Hereditary Qualitative Platelet Disorders 2041
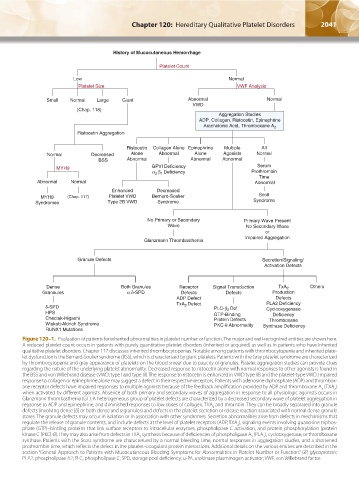
History of Mucocutaneous Hemorrhage
Platelet Count
Low Normal
Platelet Size VWF Analysis
Small Normal Large Giant Abnormal Normal
VWD
(Chap. 118)
Aggregation Studies
ADP, Collagen, Ristocetin, Epinephrine
Arachidonic Acid, Thromboxane A 2
Ristocetin Aggregation
Ristocetin Collagen Alone Epinephrine Multiple All
Normal Decreased Alone Abnormal Alone Agonists Normal
BSS Abnormal Abnormal Abnormal
Serum
MYH9
Prothrombin
Time
Abnormal Normal Abnormal
Enhanced Decreased
MYH9 (Chap. 117) Platelet VWD Bernard-Soulier Scott
Syndromes Type 2B VWD Syndrome Syndrome
No Primary or Secondary Primary Wave Present
Wave No Secondary Wave
or
Impaired Aggregation
Glanzmann Thrombasthenia
Granule Defects Secretion/Signaling/
Activation Defects
Dense Receptor Signal Transduction TxA 2 Others
Grannules Defects Defects Production
ADP Defect Defects
TxA 2 Defect PLA2 Deficiency
Cyclooxygenase
GTP-Binding Deficiency
Thromboxane
- Synthase Deficiency
Figure 120–1. Evaluation of patients for inherited abnormalities in platelet number or function. The major and well-recognized entities are shown here.
A reduced platelet count occurs in patients with purely quantitative platelet disorders (inherited or acquired) as well as in patients who have inherited
qualitative platelet disorders. Chapter 117 discusses inherited thrombocytopenias. Notable among patients with thrombocytopenia and inherited plate-
let dysfunction is the Bernard-Soulier syndrome (BSS), which is characterized by giant platelets. Patients with the Gray platelet syndrome are characterized
by thrombocytopenia and gray appearance of platelets on the blood smear due to paucity of granules. Platelet aggregation studies can provide clues
regarding the nature of the underlying platelet abnormality. Decreased response to ristocetin alone with normal responses to other agonists is found in
the BSS and von Willebrand disease (VWD; type I and type III). The response to ristocetin is enhanced in VWD type IIB and the platelet-type VWD. Impaired
response to collagen or epinephrine alone may suggest a defect in their respective receptors. Patients with adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and thrombox-
ane receptor defects have impaired responses to multiple agonists because of the feedback amplification provided by ADP and thromboxane A (TXA )
2
2
when activated by different agonists. Absence of both primary and secondary waves of aggregation in response to all physiologic agonists occurs in
Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GT). A heterogeneous group of platelet defects are characterized by a decreased secondary wave of platelet aggregation in
response to ADP and epinephrine, and diminished responses to low doses of collagen, TXA and thrombin. They can be broadly separated into granule
2
defects (involving dense [δ] or both dense and α granules) and defects in the platelet secretion or release reaction associated with normal dense granule
stores. The granule defects may occur in isolation or in association with other syndromes. Secretion abnormalities arise from defects in mechanisms that
regulate the release of granule contents, and include defects at the level of platelet receptors (ADP, TXA ), signaling events involving guanosine triphos-
2
phate (GTP)–binding proteins that link surface receptors to intracellular enzymes, phospholipase C activation, and protein phosphorylation (protein
kinase C [PKC]-θ). They may also arise from defects in TXA synthesis because of deficiencies of phospholipase A (PLA ), cyclooxygenase, or thromboxane
2
2
2
synthase. Patients with the Scott syndrome are characterized by a normal bleeding time, normal responses in aggregation studies, and a shortened
prothrombin time, which reflects the defect in the platelet–coagulant protein interactions. Additional details on the various entities are described in the
section “General Approach to Patients with Mucocutaneous Bleeding Symptoms for Abnormalities in Platelet Number or Function.” GP, glycoprotein;
PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C; SPD, storage pool deficiency; u-PA, urokinase plasminogen activator; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
Kaushansky_chapter 120_p2039-2072.indd 2041 9/21/15 2:20 PM