Page 2190 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 2190
2164 Part XII: Hemostasis and Thrombosis Chapter 126: von Willebrand Disease 2165
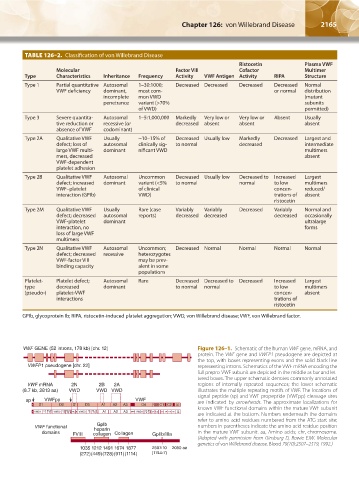
TABLE 126–2. Classification of von Willebrand Disease
Ristocetin Plasma VWF
Molecular Factor VIII Cofactor Multimer
Type Characteristics Inheritance Frequency Activity VWF Antigen Activity RIPA Structure
Type 1 Partial quantitative Autosomal 1–30:1000; Decreased Decreased Decreased Decreased Normal
VWF deficiency dominant, most com- or normal distribution
incomplete mon VWD (mutant
penetrance variant (>70% subunits
of VWD) permitted)
Type 3 Severe quantita- Autosomal 1–5:1,000,000 Markedly Very low or Very low or Absent Usually
tive reduction or recessive (or decreased absent absent absent
absence of VWF codominant)
Type 2A Qualitative VWF Usually ~10–15% of Decreased Usually low Markedly Decreased Largest and
defect; loss of autosomal clinically sig- to normal decreased intermediate
large VWF multi- dominant nificant VWD multimers
mers, decreased absent
VWF-dependent
platelet adhesion
Type 2B Qualitative VWF Autosomal Uncommon Decreased Usually low Decreased to Increased Largest
defect; increased dominant variant (<5% to normal normal to low multimers
VWF–platelet of clinical concen- reduced/
interaction (GPIb) VWD) trations of absent
ristocetin
Type 2M Qualitative VWF Usually Rare (case Variably Variably Decreased Variably Normal and
defect; decreased autosomal reports) decreased decreased decreased occasionally
VWF-platelet dominant ultralarge
interaction, no forms
loss of large VWF
multimers
Type 2N Qualitative VWF Autosomal Uncommon; Decreased Normal Normal Normal Normal
defect; decreased recessive heterozygotes
VWF-factor VIII may be prev-
binding capacity alent in some
populations
Platelet- Platelet defect; Autosomal Rare Decreased Decreased to Decreased Increased Largest
type decreased dominant to normal normal to low multimers
(pseudo-) platelet-VWF concen- absent
interactions trations of
ristocetin
GPIb, glycoprotein Ib; RIPA, ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation; VWD, von Willebrand disease; VWF, von Willebrand factor.
VWF GENE (52 introns, 178 kb) [chr. 12] Figure 126–1. Schematic of the human VWF gene, mRNA, and
protein. The VWF gene and VWFP1 pseudogene are depicted at
the top, with boxes representing exons and the solid black line
VWFP1 pseudogene [chr. 22] representing introns. Schematics of the VWF mRNA encoding the
full prepro-VWF subunit are depicted in the middle as bar and let-
tered boxes. The upper schematic denotes commonly annotated
VWF mRNA 2N 2B 2A regions of internally repeated sequences; the lower schematic
(8.7 kb, 2813 aa) VWD VWD VWD illustrates the multiple repeating motifs of VWF. The locations of
signal peptide (sp) and VWF propeptide (VWFpp) cleavage sites
sp VWFpp VWF are indicated by arrowheads. The approximate localizations for
S D1 D2 D′ D3 A1 A2 A3 D4 B B B C1 C2 CK CI
1 2 3
known VWF functional domains within the mature VWF subunit
S VWD1 C8 TIL –1 E VWD2 C8 TIL –2 E TIL′ E VWD3 C8 TIL –3 –3 E A1 A2 A3 D4N VWD4 C8 –4 TIL -4 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 CK CI
–1
are indicated at the bottom. Numbers underneath the domains
–1
–3
–2 –2
refer to amino acid residues numbered from the ATG start site;
GpIb
VWF functional heparin numbers in parentheses indicate the amino acid residue position
domains FVIII collagen Collagen GpIIb/IIIa in the mature VWF subunit. aa, Amino acids; chr, chromosome.
(Adapted with permission from Ginsburg D, Bowie EJW. Molecular
genetics of von Willebrand disease. Blood 79(10):2507–2519, 1992.)
1035 1212 1491 1674 1877 2507-10 2050 aa
(272)(449)(728)(911)(1114) (1744-7)
Kaushansky_chapter 126_p2163-2182.indd 2165 9/21/15 3:14 PM