Page 508 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 508
482 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 32: Erythropoiesis 483
Erythron Erythropoiesis
Stem Progenitor cells Precursor cells Mature Stem cell
cells BFU-E CFU-E Erythroblasts cells
SCF, IL3
CFU-GEMM
Redundant role for
EPO/EPOR
EPO, G-CSF, BFU–E
TPO
CFU–E Obligatory role for
EPO/EPOR
Erythroblast
Reticulocyte
A Erythrocyte
Regulation of erythropoiesis by hypoxia
Oxygen homeostasis
in local tissue oxygen tension
Anaerobic metabolism
Receptors HIF-1 level Angiogenesis
EPO
Erythropoiesis
GM-CSF
IL-3 Glycolytic enzyme genes
Transferrin
VEGF
Fibronectin EPO Kidney (liver)
B erythroid progenitors
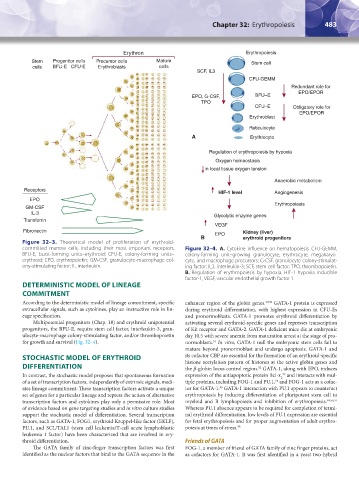
Figure 32–3. Theoretical model of proliferation of erythroid-
committed marrow cells, including their most important receptors. Figure 32–4. A. Cytokine influence on hematopoiesis. CFU-GEMM,
BFU-E, burst-forming units–erythroid; CFU-E, colony-forming units– colony-forming unit–growing granulocyte, erythrocyte, megakaryo-
erythroid; EPO, erythropoietin; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage col- cyte, and macrophage precursors; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulat-
ony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin. ing factor; IL3, interleukin-3; SCF, stem cell factor; TPO, thrombopoietin.
B. Regulation of erythropoiesis by hypoxia. HIF-1 hypoxia inducible
factor-1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor 1.
DETERMINISTIC MODEL OF LINEAGE
COMMITMENT
According to the deterministic model of lineage commitment, specific enhancer region of the globin genes. 49,50 GATA-1 protein is expressed
extracellular signals, such as cytokines, play an instructive role in lin- during erythroid differentiation, with highest expression in CFU-Es
eage specification. and pronormoblasts. GATA-1 promotes erythroid differentiation by
Multipotential progenitors (Chap. 18) and erythroid unipotential activating several erythroid-specific genes and represses transcription
progenitors, the BFU-E, require stem cell factor, interleukin-3, gran- of Kit receptor and GATA-2. GATA-1 deficient mice die at embryonic
ulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and/or thrombopoietin day 10.5 with severe anemia from maturation arrest at the stage of pro-
for growth and survival (Fig. 32–4). normoblasts. In vitro, GATA-1 null the embryonic stem cells fail to
51
mature beyond pronormoblast and undergo apoptosis. GATA-1 and
STOCHASTIC MODEL OF ERYTHROID its cofactor CBP are essential for the formation of an erythroid-specific
histone acetylation pattern of histones at the active globin genes and
DIFFERENTIATION the β-globin locus control region. GATA-1, along with EPO, induces
52
53
In contrast, the stochastic model proposes that spontaneous formation expression of the antiapoptotic protein Bcl-x and interacts with mul-
L
of a set of transcription factors, independently of extrinsic signals, medi- tiple proteins, including FOG-1 and PU.1, and FOG-1 acts as a cofac-
54
55
ates lineage commitment. These transcription factors activate a unique tor for GATA-1. GATA-1 interaction with PU.1 appears to counteract
set of genes for a particular lineage and repress the action of alternative erythropoiesis by inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cell to
transcription factors and cytokines play only a permissive role. Most myeloid and B lymphopoiesis and inhibition of erythropoiesis. 54,56,57
of evidence based on gene targeting studies and in vitro culture studies Whereas PU.1 absence appears to be required for completion of termi-
support the stochastic model of differentiation. Several transcription nal erythroid differentiation, low levels of PU.1 expression are essential
factors, such as GATA-1, FOG1, erythroid Kruppel-like factor (EKLF), for fetal erythropoiesis and for proper augmentation of adult erythro-
PU.1, and SCL/TAL1 (stem cell leukemia/T-cell acute lymphoblastic poiesis at times of stress. 58
leukemia 1 factor) have been characterized that are involved in ery-
throid differentiation. Friends of GATA
The GATA family of zinc-finger transcription factors was first FOG-1, a member of friend of GATA family of zinc finger proteins, act
identified as the nuclear factors that bind to the GATA sequence in the as cofactors for GATA-1. It was first identified in a yeast two-hybrid
Kaushansky_chapter 32_p0479-0494.indd 483 9/17/15 6:10 PM