Page 521 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 521
496 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 33: Erythrocyte Turnover 497
100 as twice the half-life. If the data indicate exponential disappearance
Cohort labeling and it is necessary to use a semilogarithmic paper in order to depict
the data on a straight line, the destruction is random and the life span is
80 1.44 times the half-life. One objection to this method is that the degree
of chromium elution is not a constant but varies from day to day and is
30
Random labeling influenced by various disease states. Furthermore, the best fit of data is
60 rarely linear or exponential, but somewhere between. Although computer-
assisted methods can resolve ambiguities, the inherent biologic and
% technical variations in measuring red cell life span are such that it is
better to rely on chromium T with intuitive adjustments based on
40 1/2
clinical findings.
51 Cr labeling Biotin Method
20 A nonradioactive label has also been developed to label the RBCs in
humans by covalent attachment of biotin to red cell membrane proteins
and enumerating the survival by flow cytometry. Biotin labeling esti-
36
51
mates RBC survival comparable to that obtained with a concurrent Cr
0 30 60 90 120 label for both normal volunteers and patients with sickle-cell disease.
Days In addition to being a nonradioactive probe, biotin labeling has other
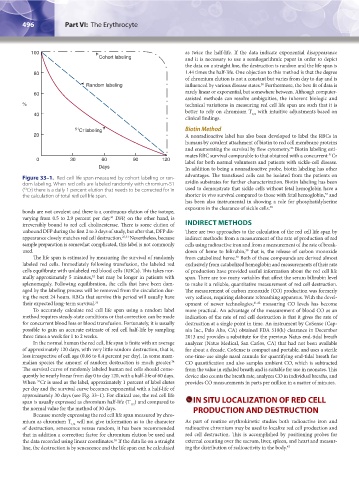
Figure 33–1. Red cell life span measured by cohort labeling or ran- advantages. The transfused cells can be isolated from the patients on
dom labeling. When red cells are labeled randomly with chromium-51 avidin substrates for further characterization. Biotin labeling has been
( Cr) there is a daily 1 percent elution that needs to be corrected for in used to demonstrate that sickle cells without fetal hemoglobin have a
51
37
the calculation of total red cell life span. shorter in vivo survival compared to those with fetal hemoglobin, and
has been also instrumental in showing a role for phosphatidylserine
exposure in the clearance of sickle cells. 38
bonds are not covalent and there is a continuous elution of the isotope,
varying from 0.5 to 2.9 percent per day. DFP, on the other hand, is
30
irreversibly bound to red cell cholinesterase. There is some elution of INDIRECT METHODS
unbound DFP during the first 2 to 3 days of study, but after that, DFP dis- There are two approaches to the calculation of the red cell life span by
appearance closely matches red cell destruction. 23,31 Nevertheless, because indirect methods: from a measurement of the rate of production of red
sample preparation is somewhat complicated, this label is not commonly cells using radioactive iron and from a measurement of the rate of break-
used. down of heme to bilirubin, that is, the release of carbon monoxide
39
The life span is estimated by measuring the survival of randomly from catabolized heme. Both of these compounds are derived almost
40
labeled red cells. Immediately following transfusion, the labeled red exclusively from catabolized hemoglobin and measurements of their rate
cells equilibrate with unlabeled red blood cells (RBCs). This takes nor- of production have provided useful information about the red cell life
32
mally approximately 5 minutes, but may be longer in patients with span. There are too many variables that affect the serum bilirubin level
splenomegaly. Following equilibration, the cells that have been dam- to make it a reliable, quantitative measurement of red cell destruction.
aged by the labeling process will be removed from the circulation dur- The measurement of carbon monoxide (CO) production was formerly
ing the next 24 hours. RBCs that survive this period will usually have very tedious, requiring elaborate rebreathing apparatus. With the devel-
their expected long-term survival. 33 opment of newer technologies, 41,42 measuring CO levels has become
To accurately calculate red cell life span using a random label more practical. An advantage of the measurement of blood CO as an
method requires steady-state conditions or that correction can be made indication of the rate of red cell destruction is that it gives the rate of
for concurrent blood loss or blood transfusion. Fortunately, it is usually destruction at a single point in time. An instrument by CoSense (Cap-
possible to gain an accurate estimate of red cell half-life by sampling nia Inc., Palo Alto, CA) obtained FDA 510(k) clearance in December
three times a week for 1 to 2 weeks. 2013 and provides a substitute for the previous Natus end-tidal breath
In the normal human the red cell, life span is finite with an average analyzer (Natus Medical, San Carlos, CA) that had not been available
of approximately 120 days, with very little random destruction, that is, for about a decade. CoSense is compact and portable, and uses a sterile
loss irrespective of cell age (0.06 to 0.4 percent per day). In some mam- one-time-use single nasal cannula for quantifying end-tidal breath for
34
malian species the amount of random destruction is much greater. CO quantification and also samples ambient CO, which is subtracted
The survival curve of randomly labeled human red cells should conse- from the value in exhaled breath and is suitable for use in neonates. This
quently be nearly linear from day 0 to day 120, with a half-life of 60 days. device also counts the breath rate, analyzes CO in individual breaths, and
51
When Cr is used as the label, approximately 1 percent of label elutes provides CO measurements in parts per million in a matter of minutes.
per day and the survival curve becomes exponential with a half-life of
approximately 30 days (see Fig. 33–1). For clinical use, the red cell life
span is usually expressed as chromium half-life (T ) and compared to IN SITU LOCALIZATION OF RED CELL
1/2
the normal value for the method of 30 days. PRODUCTION AND DESTRUCTION
Because merely expressing the red cell life span measured by chro-
mium as chromium T will not give information as to the character As part of routine erythrokinetic studies both radioactive iron and
1/2
of destruction, senescence versus random, it has been recommended radioactive chromium may be used to localize red cell production and
that in addition a correction factor for chromium elution be used and red cell destruction. This is accomplished by positioning probes for
the data recorded using linear coordinates. If the data lie on a straight external counting over the sacrum, liver, spleen, and heart and measur-
35
line, the destruction is by senescence and the life span can be calculated ing the distribution of radioactivity in the body. 43
Kaushansky_chapter 33_p0495-0502.indd 496 9/17/15 6:10 PM