Page 802 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 802
776 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 49: Disorders of Hemoglobin Structure: Sickle Cell Anemia and Related Abnormalities 777
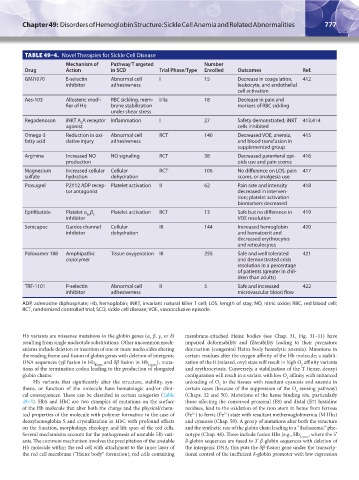
TABLE 49–4. Novel Therapies for Sickle Cell Disease
Mechanism of Pathway T argeted Number
Drug Action in SCD Trial Phase/Type Enrolled Outcomes Ref.
GMI1070 E-selectin Abnormal cell I 15 Decrease in coagulation, 412
inhibitor adhesiveness leukocyte, and endothelial
cell activation
Aes-103 Allosteric modi- RBC sickling, mem- I/IIa 18 Decrease in pain and
fier of Hb brane stabilization markers of RBC sickling
under shear stress
Regadenoson iNKT A A receptor Inflammation I 27 Safety demonstrated; iNKT 413,414
2
agonist cells inhibited
Omega-3 Reduction in oxi- Abnormal cell RCT 140 Decreased VOE, anemia, 415
fatty acid dative injury adhesiveness and blood transfusion in
supplemented group
Arginine Increased NO NO signaling RCT 38 Decreased parenteral opi- 416
production oids use and pain scores
Magnesium Increased cellular Cellular RCT 106 No difference on LOS, pain 417
sulfate hydration dehydration scores, or analgesia use
Prasugrel P2Y12 ADP recep- Platelet activation II 62 Pain rate and intensity 418
tor antagonist decreased in interven-
tion; platelet activation
biomarkers decreased
Eptifibatide Platelet α β Platelet activation RCT 13 Safe but no difference in 419
IIb 3
inhibitor VOE resolution
Senicapoc Gardos channel Cellular III 144 Increased hemoglobin 420
inhibitor dehydration and hematocrit and
decreased erythrocytes
and reticulocytes
Poloxamer 188 Amphipathic Tissue oxygenation III 255 Safe and well tolerated 421
copolymer and demonstrated crisis
resolution in a percentage
of patients (greater in chil-
dren than adults)
TRF-1101 P-selectin Abnormal cell II 5 Safe and increased 422
inhibitor adhesiveness microvascular blood flow
ADP, adenosine diphosphate; Hb, hemoglobin; iNKT, invariant natural killer T cell; LOS, length of stay; NO, nitric oxide; RBC, red blood cell;
RCT, randomized controlled trial; SCD, sickle cell disease; VOE, vasoocclusive episode.
Hb variants are missense mutations in the globin genes (α, β, γ, or δ) membrane-attached Heinz bodies (see Chap. 31, Fig. 31–11) have
resulting from single nucleotide substitutions. Other uncommon mech- impaired deformability and filterability leading to their premature
anisms include deletion or insertion of one or more nucleotides altering destruction (congenital Heinz body hemolytic anemia). Mutations in
the reading frame and fusion of globin genes with deletion of intergenic certain residues alter the oxygen affinity of the Hb molecule; a stabili-
DNA sequences (γβ fusion in Hb Kenya and δβ fusion in Hb Lepore ), muta- zation of the R (relaxed, oxy) state will result in high O affinity variants
2
tions of the termination codon leading to the production of elongated and erythrocytosis. Conversely, a stabilization of the T (tense, deoxy)
globin chains. configuration will result in a variant with low O affinity with enhanced
2
Hb variants that significantly alter the structure, stability, syn- unloading of O to the tissues with resultant cyanosis and anemia in
2
thesis, or function of the molecule have hematologic and/or clini- certain cases (because of the suppression of the O sensing pathway)
2
cal consequences. These can be classified in certain categories (Table (Chaps. 32 and 50). Mutations of the heme binding site, particularly
49–5). HbS and HbC are two examples of mutations on the surface those affecting the conserved proximal (F8) and distal (E7) histidine
of the Hb molecule that alter both the charge and the physical/chem- residues, lead to the oxidation of the iron atom in heme from ferrous
ical properties of the molecule with polymer formation in the case of (Fe ) to ferric (Fe ) state with resultant methemoglobinemia (M Hbs)
2+
3+
deoxyhemoglobin S and crystallization in HbC with profound effects and cyanosis (Chap. 50). A group of mutations alter both the structure
on the function, morphology, rheology, and life span of the red cells. and the synthetic rate of the globin chain leading to a “thalassemic” phe-
Several mechanisms account for the pathogenesis of unstable Hb vari- notype (Chap. 48). These include fusion Hbs (e.g., Hb Lepore , where the 5′
ants. The common mechanism involves the precipitation of the unstable δ-globin sequences are fused to 3′ β-globin sequences with deletion of
Hb molecule within the red cell with attachment to the inner layer of the intergenic DNA; this puts the δβ-fusion gene under the transcrip-
the red cell membrane (“Heinz body” formation); red cells containing tional control of the inefficient δ-globin promoter with low expression
Kaushansky_chapter 49_p0759-0788.indd 777 9/18/15 3:01 PM