Page 800 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 800
774 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 49: Disorders of Hemoglobin Structure: Sickle Cell Anemia and Related Abnormalities 775
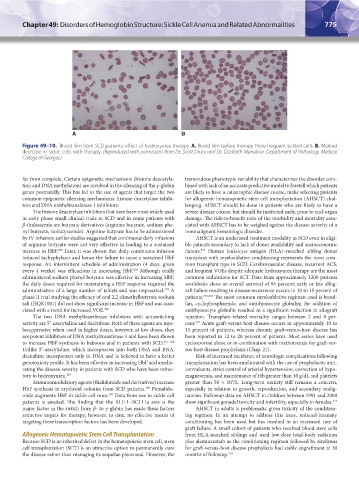
A B
Figure 49–10. Blood film from SCD patients: effect of hydroxyurea therapy. A. Blood film before therapy. Note frequent sickled cells. B. Marked
decrease in sickle cells with therapy. (Reproduced with permission from Dr. Scott Drury and Dr. Elizabeth Manaloor, Department of Pathology, Medical
College of Georgia.)
far from complete. Certain epigenetic mechanisms (histone deacetyla- tremendous phenotypic variability that characterizes the disorder com-
tion and DNA methylation) are involved in the silencing of the γ-globin bined with lack of an accurate predictive model to foretell which patients
genes postnatally. This has led to the use of agents that target the two are likely to have a catastrophic disease course, make selecting patients
common epigenetic silencing mechanisms: histone deacetylase inhibi- for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) chal-
tors and DNA methyltransferase 1 inhibitors. lenging. AHSCT should be done in patients who are likely to have a
The histone deacetylase inhibitors that have been most widely used severe disease course, but should be instituted early, prior to end-organ
in early phase small clinical trials in SCD and in some patients with damage. The risk-to-benefit ratio of the morbidity and mortality asso-
β-thalassemia are butyrate derivatives (arginine butyrate, sodium phe- ciated with AHSCT has to be weighed against the disease severity of a
nyl butyrate, isobutyramide). Arginine butyrate has to be administered nonmalignant hematologic disorder.
by IV infusion; earlier studies suggested that continuous daily infusions AHSCT is an underused treatment modality in SCD even in eligi-
of arginine butyrate were not very effective in leading to a sustained ble patients secondary to lack of donor availability and socioeconomic
258
371
increase in HbF. Later, it was shown that daily continuous infusion factors. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)–matched sibling donor
induced tachyphylaxis and hence the failure to cause a sustained HbF transplant with myeloablative conditioning represents the most com-
response. An intermittent schedule of administration (4 days, given mon transplant type in SCD. Cerebrovascular disease, recurrent ACS,
every 4 weeks) was efficacious in increasing HbF. Although orally and frequent VOEs despite adequate hydroxyurea therapy are the most
358
administered sodium phenyl butyrate was effective in increasing HbF, common indications for SCT. Data from approximately 1200 patients
the daily doses required for maintaining a HbF response required the worldwide show an overall survival of 95 percent; early or late allog-
administration of a large number of tablets and was impractical. A raft failure resulting in disease recurrence occurs in 10 to 15 percent of
359
phase II trial studying the efficacy of oral 2,2-dimethylbutyrate sodium patients. 371,372 The most common myeloablative regimen used is busul-
salt (HQK1001) did not show significant increase in HbF and was asso- fan, cyclophosphamide, and antithymocyte globulin; the addition of
ciated with a trend for increased VOE. 360 antithymocyte globulin resulted in a significant reduction in allograft
The two DNA methyltransferase inhibitors with antiswitching rejection. Transplant-related mortality ranges between 2 and 8 per-
activity are 5′-azacytidine and decitabine. Both of these agents are mye- cent. Acute graft-versus-host disease occurs in approximately 10 to
372
losuppressive when used in higher doses; however, at low doses, they 15 percent of patients, whereas chronic graft-versus-host disease has
are potent inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase 1 and have been shown been reported in 12 to 20 percent of patients. Most series have used
to increase HbF synthesis in baboons and in patients with SCD. 361–368 cyclosporine alone or in combination with methotrexate for graft-ver-
Unlike 5′-azacytidine, which incorporates into both DNA and RNA, sus-host disease prophylaxis (Chap. 21).
decitabine incorporates only in DNA and is believed to have a better Risk of increased incidence of neurologic complications following
genotoxicity profile. It has been effective in increasing HbF and amelio- transplantation has been ameliorated with the use of prophylactic anti-
rating the disease severity in patients with SCD who have been refrac- convulsants, strict control of arterial hypertension, correction of hypo-
tory to hydroxyurea. 363 magnesemia, and maintenance of Hb greater than 10 g/dL and platelets
Immunomodulatory agents (thalidomide and derivatives) increase greater than 50 × 10 /L. Long-term toxicity still remains a concern,
9
369
HbF synthesis in erythroid colonies from SCD patients. Pomalido- especially in relation to growth, reproduction, and secondary malig-
370
mide augments HbF in sickle cell mice. Data from use in sickle cell nancies. Followup data on AHSCT in children between 1991 and 2000
patients is awaited. The finding that the KLF-1–BCL11a axis is the show significant gonadal toxicity and infertility, especially in females. 373
major factor in the switch from β- to γ-globin has made these factors AHSCT in adults is problematic given toxicity of the condition-
attractive targets for therapy; however, to date, no effective means of ing regimen. In an attempt to address this issue, reduced-intensity
targeting these transcription factors has been developed. conditioning has been used but has resulted in an increased rate of
graft failure. A small cohort of patients who received blood stem cells
Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation from HLA-matched siblings and used low-dose total-body radiation
Because SCD is an inherited defect in the hematopoietic stem cell, stem plus alemtuzumab as the conditioning regimen followed by sirolimus
cell transplantation (SCT) is an attractive option to permanently cure for graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis had stable engraftment at 30
the disease rather than managing its sequelae piecemeal. However, the months of followup. 374
Kaushansky_chapter 49_p0759-0788.indd 775 9/18/15 3:01 PM