Page 821 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 821
796 Part VI: The Erythrocyte Chapter 50: Methemoglobinemia and Other Dyshemoglobinemias 797
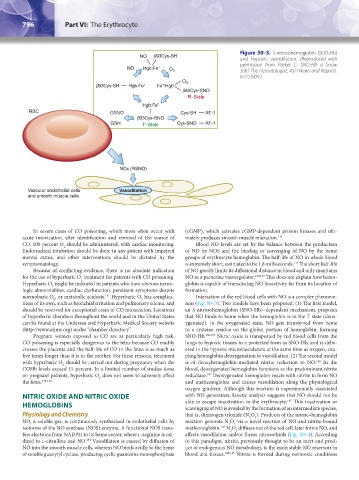
Figure 50–3. S-nitrosohemoglobin (SNO-Hb)
NO b93Cys-SH and hypoxic vasodilation. (Reproduced with
permission from Parker C: SNO-HB a Snow
NO Hgb:Fe" O 2 Job? The Hematologist: ASH News and Reports.
6:12;2009.)
O 2
b93Cys-SH Hgb:Fe" Fe":Hgb
b93Cys-SNO
R–State
Hgb:Fe"
RBC GSNO Cys-SH AE-1
b93Cys-SNO
GSH T–State Cys-SNO AE-1
NOx (RSNO)
Vascular endothelial cells Vasodilation
and smooth muscle cells
In severe cases of CO poisoning, which more often occur with (cGMP), which activates cGMP-dependent protein kinases and ulti-
acute intoxication, after identification and removal of the source of mately produces smooth muscle relaxation. 134
CO, 100 percent O should be administered, with cardiac monitoring. Blood NO levels are set by the balance between the production
2
Endotracheal intubation should be done in any patient with impaired of NO by NOS and the binding or scavenging of NO by the heme
mental status, and other interventions should be dictated by the groups of erythrocyte hemoglobin. The half-life of NO in whole blood
symptomatology. is extremely short, estimated to be 1.8 milliseconds. The short half-life
135
Because of conflicting evidence, there is no absolute indication of NO greatly limits its diffusional distance in blood and only maintains
for the use of hyperbaric O treatment for patients with CO poisoning. NO as a paracrine vasoregulator. 136,137 This does not explain how hemo-
2
Hyperbaric O might be indicated in patients who have obvious neuro- globin is capable of transducing NO bioactivity far from its location of
2
logic abnormalities, cardiac dysfunction, persistent symptoms despite formation.
normobaric O , or metabolic acidosis. Hyperbaric O has complica- Interaction of the red blood cells with NO is a complex phenome-
131
2
2
tions of its own, such as bronchial irritation and pulmonary edema, and non (Fig. 50–3). Two models have been proposed: (1) The first model,
should be reserved for exceptional cases of CO intoxication. Locations an S-nitrosohemoglobin (SNO-Hb)–dependent mechanism, proposes
of hyperbaric chambers throughout the world and in the United States that NO binds to heme when the hemoglobin is in the T state (deox-
can be found at the Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society website ygenated). In the oxygenated state, NO gets transferred from heme
(http://www.uhms.org) under “chamber directory.” to a cysteine residue on the globin portion of hemoglobin, forming
Pregnant women exposed to CO are at particularly high risk. SNO-Hb. 138,139 Nitric oxide is transported by red blood cells from the
CO poisoning is especially dangerous to the fetus because CO readily lungs to hypoxic tissues in a protected form as SNO-Hb, and is deliv-
crosses the placenta and the half-life of CO in the fetus is as much as ered in the hypoxic microvasculature at the same time as oxygen, cou-
five times longer than it is in the mother. For these reasons, treatment pling hemoglobin deoxygenation to vasodilation. (2) The second model
with hyperbaric O should be carried out during pregnancy when the is of deoxyhemoglobin-mediated nitrite reduction to NO. In the
140
2
COHb levels exceed 15 percent. In a limited number of studies done blood, deoxygenated hemoglobin functions as the predominant nitrite
on pregnant patients, hyperbaric O does not seem to adversely affect reductase. Deoxygenated hemoglobin reacts with nitrite to form NO
141
2
the fetus. 132,133 and methemoglobin and causes vasodilation along the physiological
oxygen gradient. Although this reaction is experimentally associated
NITRIC OXIDE AND NITRIC OXIDE with NO generation, kinetic analysis suggests that NO should not be
142
HEMOGLOBINS able to escape inactivation in the erythrocyte. This inactivation or
scavenging of NO is avoided by the formation of an intermediate species,
Physiology and Chemistry that is, dinitrogen trioxide (N O ). Products of the nitrite–hemoglobin
2
3
NO, a soluble gas, is continuously synthesized in endothelial cells by reaction generate N O via a novel reaction of NO and nitrite-bound
2
3
isoforms of the NO synthase (NOS) enzyme. A functional NOS trans- methemoglobin. N O diffuses out of the red cell, later forms NO, and
143
2
3
fers electrons from NADPH to its heme center, where l-arginine is oxi- affects vasodilation and/or forms nitrosothiols (Fig. 50–4). According
dized to l-citrulline and NO. Vasodilation is caused by diffusion of to this paradigm, nitrite, previously thought to be an inert end prod-
134
NO into the smooth muscle cells, wherein NO binds avidly to the heme uct of endogenous NO metabolism, is the main stable NO reservoir in
of soluble guanylyl cyclase, producing cyclic guanosine monophosphate blood and tissues. 144,145 Nitrite is formed during normoxic conditions
Kaushansky_chapter 50_p0789-0800.indd 796 9/17/15 2:39 PM