Page 86 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 86
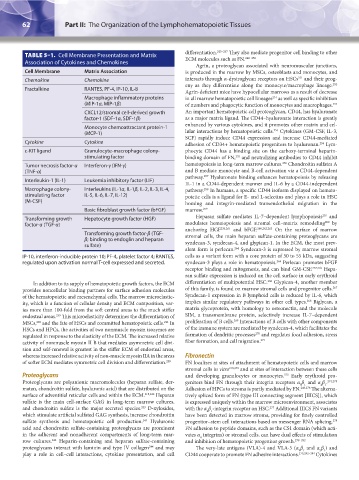
62 Part II: The Organization of the Lymphohematopoietic Tissues Chapter 5: Structure of the Marrow and the Hematopoietic Microenvironment 63
TABLE 5–1. Cell Membrane Presentation and Matrix differentiation. 245–247 They also mediate progenitor cell binding to other
248–250
ECM molecules such as FN.
Association of Cytokines and Chemokines
Agrin, a proteoglycan associated with neuromuscular junctions,
Cell Membrane Matrix Association is produced in the marrow by MSCs, osteoblasts and monocytes, and
251
Chemokine Chemokine interacts through α-dystroglycan receptors on HSCs and their prog-
252
eny as they differentiate along the monocyte/macrophage lineage.
Fractalkine RANTES, PF-4, IP-10, IL-8
Agrin-deficient mice have hypocellular marrows as a result of decrease
Macrophage inflammatory proteins in all marrow hematopoietic cell lineages as well as specific inhibition
251
(MIP-1α, MIP-1β) of numbers and phagocytic function of monocytes and macrophages.
252
CXCL12/stromal cell-derived growth An important hematopoietic cell proteoglycan, CD44, has hyaluronate
factor-1 (SDF-1α, SDF-1β) as a major matrix ligand. The CD44–hyaluronate interaction is greatly
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 enhanced by various cytokines, and it promotes other matrix and cel-
253
(MCP-1) lular interactions by hematopoietic cells. Cytokines (GM-CSF, IL-3,
SCF) rapidly induce CD44 expression and increase CD44-mediated
Cytokine Cytokine adhesion of CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors to hyaluronan. Lym-
254
c-KIT ligand Granulocyte-macrophage colony- phocyte CD44 has a binding site on the carboxy-terminal heparin-
stimulating factor binding domain of FN, and neutralizing antibodies to CD44 inhibit
255
256
Tumor necrosis factor-α Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) hematopoiesis in long-term marrow cultures. Chondroitin sulfates A
(TNF-α) and B mediate monocyte and B-cell activation via a CD44-dependent
pathway. Hyaluronate binding enhances hematopoiesis by releasing
257
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)
IL-1 in a CD44-dependent manner and IL-6 by a CD44-independent
Macrophage colony- Interleukins (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, pathway. In humans, a specific CD44 isoform displayed on hemato-
258
stimulating factor IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-12) poietic cells is a ligand for E- and L-selectins and plays a role in HSC
(M-CSF) homing and integrin-mediated transendothelial migration in the
Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) marrow. 259
235
Transforming growth Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) Heparan sulfate mediates IL-7–dependent lymphopoiesis and
260
factor-α (TGF-α) modulates hematopoiesis and stromal cell–matrix remodeling by
anchoring HGF 236,261 and bFGF. 260,262,263 On the surface of marrow
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF- stromal cells, the main heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycans are
β; binding to endoglin and heparan
sulfate) syndecan-3, syndecan-4, and glypican-1. In the ECM, the most prev-
alent form is perlecan. Syndecan-3 is expressed by marrow stromal
264
IP-10, interferon-inducible protein 10; PF-4, platelet factor 4; RANTES, cells as a variant form with a core protein of 50 to 55 kDa, suggesting
regulated upon activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted. syndecan-3 plays a role in hematopoiesis. Perlecan promotes bFGF
264
receptor binding and mitogenesis, and can bind GM-CSF. 257,265 Hepa-
ran sulfate expression is induced on the cell surface in early erythroid
266
In addition to its supply of hematopoietic growth factors, the ECM differentiation of multipotential HSC. Glypican-4, another member
267
provides noncellular binding partners for surface adhesion molecules of this family, is found on marrow stromal cells and progenitor cells.
of the hematopoietic and mesenchymal cells. The marrow microelastic- Syndecan-1 expression in B lymphoid cells is reduced by IL-6, which
268
ity, which is a function of cellular density and ECM composition, var- implies similar regulatory pathways in other cell types. Biglycan, a
ies more than 100-fold from the soft central areas to the much stiffer matrix glycoprotein, with homology to osteonectin, and the molecule
endosteal areas. This microelasticity determines the differentiation of SIM, a transmembrane protein, selectively increase IL-7–dependent
239
269
MSCs, and the fate of HSCs and committed hematopoietic cells. In proliferation of B cells. Interactions of B cells with other components
240
241
HSCs and HPCs, the activities of two nonmuscle myosin isozymes are of the immune system are mediated by syndecan-4, which facilitates the
270
regulated in response to the elasticity of the ECM. The increased relative formation of dendritic processes and regulates focal adhesion, stress
activity of nonmuscle myosin II B that mediates asymmetric cell divi- fiber formation, and cell migration. 271
sion and self-renewal is greatest in the stiffer ECM of endosteal areas,
whereas increased relative activity of non-muscle myosin IIA in the areas Fibronectin
of softer ECM mediates symmetric cell division and differentiation. 239 FN localizes at sites of attachment of hematopoietic cells and marrow
stromal cells in vitro 219,272 and at sites of interaction between these cells
Proteoglycans and developing granulocytes or monocytes. Early erythroid pro-
273
Proteoglycans are polyanionic macromolecules (heparan sulfate, der- genitors bind FN through their integrin receptors α β and α β . 274,275
4 1
matan, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronic acid) that are distributed on the Adhesion of HPCs to stroma is partly mediated by FN. 5 1 The alterna-
248,276
surface of adventitial reticular cells and within the ECM. 218,242 Heparan tively spliced form of FN (type III connecting segment [IIICS]), which
sulfate is the main cell-surface GAG in long-term marrow cultures, is expressed uniquely within the marrow microenvironment, associates
and chondroitin sulfate is the major secreted species. D-xylosides, with the α β -integrin receptor on HSC. Additional IIICS FN variants
243
277
4 1
which stimulate artificial sulfated GAG synthesis, increase chondroitin have been detected in marrow stroma, providing for finely controlled
sulfate synthesis and hematopoietic cell production. Hyaluronic progenitor–stem cell interactions based on messenger RNA splicing.
278
243
acid and chondroitin sulfate-containing proteoglycans are prominent FN adhesion to peptide domains, such as the CS1 domain (which acti-
in the adherent and nonadherent compartments of long-term mar- vates α integrins) or stromal cells, can have dual effects of stimulation
4
row cultures. Heparin-containing and heparan sulfate-containing and inhibition of hematopoietic progenitor growth. 279–282
242
proteoglycans interact with laminin and type IV collagen and may The very-late antigens (VLA)-4 and VLA-5 (α β and α β ) and
244
5 1
play a role in cell–cell interactions, cytokine presentation, and cell CD44 cooperate to promote FN adhesive interactions. 4 1 Cytokines
279,282–284
Kaushansky_chapter 05_p0051-0084.indd 62 9/19/15 12:10 AM