Page 81 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 81
56 Part II: The Organization of the Lymphohematopoietic Tissues Chapter 5: Structure of the Marrow and the Hematopoietic Microenvironment 57
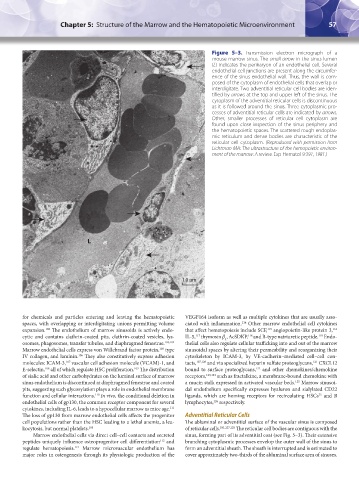
Figure 5–3. Transmission electron micrograph of a
mouse marrow sinus. The small arrow in the sinus lumen
(L) indicates the perikaryon of an endothelial cell. Several
endothelial cell junctions are present along the circumfer-
ence of the sinus endothelial wall. Thus, the wall is com-
posed of the cytoplasm of endothelial cells that overlap or
interdigitate. Two adventitial reticular cell bodies are iden-
tified by arrows at the top and upper left of the sinus. The
cytoplasm of the adventitial reticular cells is discontinuous
as it is followed around the sinus. Three cytoplasmic pro-
cesses of adventitial reticular cells are indicated by arrows.
Other, smaller processes of reticular cell cytoplasm are
found upon close inspection of the sinus periphery and
the hematopoietic spaces. The scattered rough endoplas-
mic reticulum and dense bodies are characteristic of the
reticular cell cytoplasm. (Reproduced with permission from
Lichtman MA: The ultrastructure of the hemopoietic environ-
ment of the marrow: A review. Exp Hematol 9:391, 1981.)
L
1.0 µm
for chemicals and particles entering and leaving the hematopoietic VEGF164 isoform as well as multiple cytokines that are usually asso-
spaces, with overlapping or interdigitating unions permitting volume ciated with inflammation. Other marrow endothelial cell cytokines
114
expansion. The endothelium of marrow sinusoids is actively endo- that affect hematopoiesis include SCF, angiopoietin-like protein 3,
116
115
102
cytic and contains clathrin-coated pits, clathrin-coated vesicles, lys- IL-5, thymosin β , AcSDKP, and B-type natriuretic peptide. Endo-
119
118
117
4
osomes, phagosomes, transfer tubules, and diaphragmed fenestrae. 103,104 thelial cells also regulate cellular trafficking into and out of the marrow
Marrow endothelial cells express von Willebrand factor protein, type sinusoidal spaces by altering their permeability and reorganizing their
105
IV collagen, and laminin. They also constitutively express adhesion cytoskeleton by ICAM-3, by VE-cadherin–mediated cell–cell con-
106
molecules: ICAM-3, vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, and tacts, 107,120 and via specialized heparin sulfate proteoglycans, CXCL12
107
121
E-selectin, all of which regulate HSC proliferation. The distribution bound to surface proteoglycans, and other chemokines/chemokine
122
109
108
of sialic acid and other carbohydrates on the luminal surface of marrow receptors, 123,124 such as fractalkine, a membrane-bound chemokine with
sinus endothelium is discontinued at diaphragmed fenestrae and coated a mucin stalk expressed in activated vascular beds. Marrow sinusoi-
125
pits, suggesting such glycosylation plays a role in endothelial membrane dal endothelium specifically expresses hyaluron and sialylated CD22
function and cellular interactions. In vivo, the conditional deletion in ligands, which are homing receptors for recirculating HSCs and B
110
75
endothelial cells of gp130, the common receptor component for several lymphocytes, respectively.
126
cytokines, including IL-6, leads to a hypocellular marrow as mice age.
111
The loss of gp130 from marrow endothelial cells affects the progenitor Adventitial Reticular Cells
cell populations rather than the HSC leading to a lethal anemia, a leu- The abluminal or adventitial surface of the vascular sinus is composed
kocytosis, but normal platelets. 108 of reticular cells. 101,127,128 The reticular cell bodies are contiguous with the
Marrow endothelial cells via direct cell–cell contacts and secreted sinus, forming part of its adventitial coat (see Fig. 5–3). Their extensive
peptides uniquely influence osteoprogenitor cell differentiation and branching cytoplasmic processes envelop the outer wall of the sinus to
112
regulate hematopoiesis. Marrow microvascular endothelium has form an adventitial sheath. The sheath is interrupted and is estimated to
113
major roles in osteogenesis through its physiologic production of the cover approximately two-thirds of the abluminal surface area of sinuses.
Kaushansky_chapter 05_p0051-0084.indd 57 9/19/15 12:10 AM