Page 1063 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1063
1026 Part seven Organ-Specific Inflammatory Disease
e.g., cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) Ig (abatacept)
35
or the CD40-antagonist FFP104, are under investigation. When
the disease has already progressed and bile is accumulating,
obeticholic acid (OCA), an analog of CDCA with a much higher
affinity to the farnesoid X receptor, has been shown to decrease
bile synthesis, promote secretion, and induce liver regeneration
in animal models. In a phase III trial, OCA administered with
UDCA or as monotherapy for 12 months resulted in a decrease
in alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin levels that differed
significantly from the changes observed with placebo. 35
Ultimately, UDCA represents the cornerstone therapy of PBC.
Doses ranging from 13 to 15 mg/kg are currently used for
optimum bile enrichment and in 50% of patients normalize
alkaline phosphatase. Other immunosuppressive treatments
should be started only in combination with UDCA.
Liver transplantation is the ultimate treatment for end-stage
A
PBC, with survival rates of 92% and 85% at 1 and 5 years after
transplant, respectively. Recurrence is common, and its rates seem
to be influenced by certain immunosuppressive regimens. The
use of UDCA in cases of recurrence is safe and recommended.
KeY COnCePts
• Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic autoimmune cholestatic
disease affecting preferentially women in the fifth to sixth decades
of life.
• Genetics plays a strong role in PBC pathogenesis, as suggested by
familial clustering and the high concordance in monozygotic twins.
• Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) are highly specific for PBC and
can be detected in nearly 100% of patients.
CLInICaL PearLs
B
• Fatigue and pruritus represent the most frequently observed symptoms,
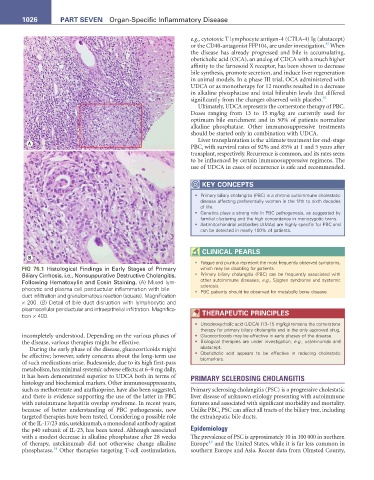
FIG 76.1 Histological Findings in Early Stages of Primary which may be disabling for patients.
Biliary Cirrhosis, i.e., Nonsuppurative Destructive Cholangitis, • Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) can be frequently associated with
Following Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining. (A) Mixed lym- other autoimmune diseases, e.g., Sjögren syndrome and systemic
sclerosis.
phocytic and plasma cell periductular inflammation with bile • PBC patients should be observed for metabolic bone disease.
duct infiltration and granulomatous reaction (square). Magnification
× 200. (B) Detail of bile duct disruption with lymphocytic and
plasmacellular periductular and intraepithelial infiltration. Magnifica-
tion × 400. tHeraPeUtIC PrInCIPLes
• Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) (13–15 mg/kg) remains the cornerstone
therapy for primary biliary cholangitis and is the only approved drug.
incompletely understood. Depending on the various phases of • Glucocorticoids may be effective in early phases of the disease.
the disease, various therapies might be effective. • Biological therapies are under investigation, e.g., ustekinumab and
During the early phase of the disease, glucocorticoids might abatacept.
be effective; however, safety concerns about the long-term use • Obeticholic acid appears to be effective in reducing cholestatic
biomarkers.
of such medications arise. Budesonide, due to its high first-pass
metabolism, has minimal systemic adverse effects; at 6–9 mg daily,
it has been demonstrated superior to UDCA both in terms of PRIMARY SCLEROSING CHOLANGITIS
histology and biochemical markers. Other immunosuppressants,
such as methotrexate and azathioprine, have also been suggested, Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a progressive cholestatic
and there is evidence supporting the use of the latter in PBC liver disease of unknown etiology presenting with autoimmune
with autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndrome. In recent years, features and associated with significant morbidity and mortality.
because of better understanding of PBC pathogenesis, new Unlike PBC, PSC can affect all tracts of the biliary tree, including
targeted therapies have been tested. Considering a possible role the extrahepatic bile ducts.
of the IL-17/23 axis, ustekinumab, a monoclonal antibody against
the p40 subunit of IL-23, has been tested. Although associated Epidemiology
with a modest decrease in alkaline phosphatase after 28 weeks The prevalence of PSC is approximately 10 in 100 000 in northern
4,5
of therapy, ustekinumab did not otherwise change alkaline Europe and the United States, while it is far less common in
34
phosphatase. Other therapies targeting T-cell costimulation, southern Europe and Asia. Recent data from Olmsted County,