Page 1079 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1079
1044 ParT EighT Immunology of Neoplasia
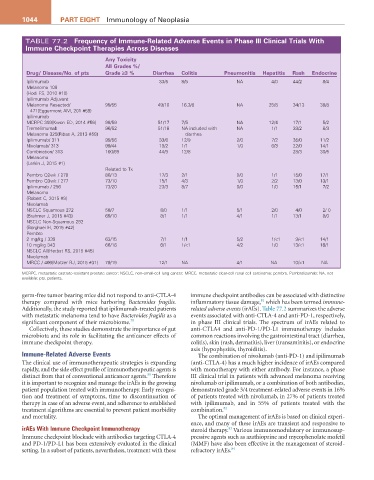
TABLE 77.2 Frequency of immune-related adverse Events in Phase iii Clinical Trials With
immune Checkpoint Therapies across Diseases
any Toxicity
all grades %/
Drug/ Disease/No. of pts grade ≥3 % Diarrhea Colitis Pneumonitis hepatitis rash Endocrine
Ipilimumab 33/5 8/5 NA 4/0 44/2 8/4
Melanoma 108
{Hodi FS, 2010 #10}
Ipilimumab Adjuvant
Melanoma Resected/ 99/55 49/10 16.3/8 NA 25/8 34/13 38/8
471{Eggermont AM, 201 #59}
Ipilimumab
MCRPC 393{Kwon ED, 2014 #56} 98/59 51/17 7/5 NA 12/4 17/1 5/2
Tremelimumab 96/52 51/18 NA included with NA 1/1 33/2 8/3
Melanoma 325{Ribas A, 2013 #58} diarrhea
Ipilimumab/ 311 99/56 33/6 12/9 2/0 7/2 35/0 11/2
Nivolumab/ 313 99/44 19/2 1/1 1/0 6/3 22/0 14/1
Combination/ 313 100/69 44/9 12/8 28/3 30/5
Melanoma
{Larkin J, 2015 #1}
Related to Tx
Pembro Q2wk / 278 80/13 17/3 2/1 0/0 1/1 15/0 17/1
Pembro Q3wk / 277 73/10 15/1 4/3 1/0 2/2 13/0 13/1
Ipilimumab / 256 73/20 23/3 8/7 0/0 1/0 15/1 7/2
Melanoma
{Robert C, 2015 #9}
Nivolumab
NSCLC Squamous 272 58/7 8/0 1/1 5/1 2/0 4/0 2/ 0
{Brahmer J, 2015 #43} 69/10 8/1 1/1 4/1 1/1 13/1 8/0
NSCLC Non-Squamous 292
{Borghaei H, 2015 #42}
Pembro
2 mg/kg / 339 63/15 7/1 1/1 5/2 1/<1 9/<1 14/1
10 mg/kg 343 66/16 6/1 1/<1 4/2 1/0 13/<1 16/1
NSCLC All{Herbst RS, 2015 #45}
Nivolumab
MRCC / 406{Motzer RJ, 2015 #31} 79/19 12/1 NA 4/1 NA 10/<1 NA
MCRPC, metastatic castrate-resistant prostate cancer; NSCLC, non–small-cell lung cancer; MRCC, metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma; pembro, Pembrolizumab; NA, not
available; pts, patients.
germ-free tumor bearing mice did not respond to anti-CTLA-4 immune checkpoint antibodies can be associated with distinctive
81
therapy compared with mice harboring Bacteroides fragilis. inflammatory tissue damage, which has been termed immune-
Additionally, the study reported that ipilimumab-treated patients related adverse events (irAEs). Table 77.2 summarizes the adverse
with metastatic melanoma tend to have Bacteroides fragilis as a events associated with anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1, respectively,
significant component of their microbiome. 79 in phase III clinical trials. The spectrum of irAEs related to
Collectively, these studies demonstrate the importance of gut anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy includes
microbiota and its role in facilitating the anticancer effects of common reactions involving the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea,
immune checkpoint therapy. colitis), skin (rash, dermatitis), liver (transaminitis), or endocrine
axis (hypophysitis, thyroiditis).
Immune-Related Adverse Events The combination of nivolumab (anti-PD-1) and ipilimumab
The clinical use of immunotherapeutic strategies is expanding (anti-CTLA-4) has a much higher incidence of irAEs compared
rapidly, and the side effect profile of immunotherapeutic agents is with monotherapy with either antibody. For instance, a phase
80
distinct from that of conventional anticancer agents. Therefore III clinical trial in patients with advanced melanoma receiving
it is important to recognize and manage the irAEs in the growing nivolumab or ipilimumab, or a combination of both antibodies,
patient population treated with immunotherapy. Early recogni- demonstrated grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events in 16%
tion and treatment of symptoms, time to discontinuation of of patients treated with nivolumab, in 27% of patients treated
therapy in case of an adverse event, and adherence to established with ipilimumab, and in 55% of patients treated with the
treatment algorithms are essential to prevent patient morbidity combination. 82
and mortality. The optimal management of irAEs is based on clinical experi-
ence, and many of these irAEs are transient and responsive to
irAEs With Immune Checkpoint Immunotherapy steroid therapy. Various immunomodulatory or immunosup-
83
Immune checkpoint blockade with antibodies targeting CTLA-4 pressive agents such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil
and PD-1/PD-L1 has been extensively evaluated in the clinical (MMF) have also been effective in the management of steroid-
setting. In a subset of patients, nevertheless, treatment with these refractory irAEs. 84