Page 1076 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1076
ChaPTEr 77 Immunotherapy of Cancer 1041
CAR T Cells development of phage/yeasts or ribosome display technology helped
generate mAbs from any species and facilitated selection based
1st 2nd 3rd on specificity, stability, and affinity.
generation generation generation Armored The mounting success of a mAb as a therapeutic agent is based
V L V L V L V L on three characteristics, including (i) an Fc moiety that mediates
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-
dependent cytotoxicity (CDC); (ii) an Fab moiety that promotes
high specificity and affinity for antigen binding; and (iii) a molecular
V H
V H
V H
V H
mass of about 150 kDa, which extends the circulatory half-life of
the mAb up to 21 days. Importantly, the mechanism of tumor
cell killing by mAbs involves (i) binding to specific receptors on
tumor cells via the Fab portion of the antibody and triggering
cytotoxicity via the Fc portion of the antibody or (ii) binding to
specific receptors on tumor cells via the Fab portion of the antibody
Cytokine and blocking important signaling pathways via the Fab portion
transgene
CD3ζ of the antibody or a combination of both mechanisms.
CD28 CD28 CD28 Over the past 15 years, antibody-based immunotherapy has
been established as a successful strategy for treating patients
Additional with hematological malignancies and some solid tumors. To
Linker costimulators enhance the effector functions, mAbs have been conjugated to
Spacer CD3ζ (ICOS, 4-1BB, radioisotopes, chemotherapeutic agents, bacterial toxins, cytokines,
OX40)
60
Intracellular and enzymes ; therefore mAbs are classified as follows:
domain
Single chain Naked mAbs
variable fragments CD3ζ CD3ζ
Cytokine transgene These mAbs are not attached to any drug or radioactive material
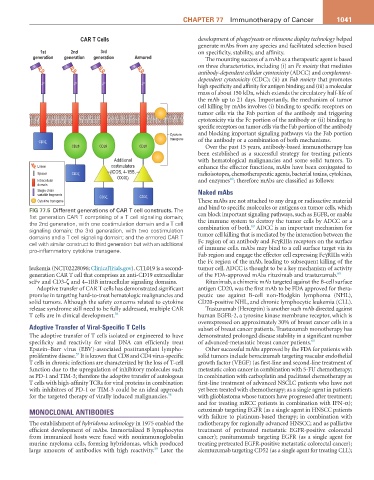
Fig 77.5 Different generations of CAR T cell constructs. The and bind to specific molecules or antigens on tumor cells, which
1st generation CAR T comprising of a T cell signaling domain; can block important signaling pathways, such as EGFR, or enable
the 2nd generation, with one costimulation domain and a T cell the immune system to destroy the tumor cells by ADCC or a
60
signaling domain; the 3rd generation, with two costimulation combination of both. ADCC is an important mechanism for
domains and a T cell signaling domain; and the armored CAR T tumor cell killing that is mediated by the interaction between the
cell with similar construct to third generation but with an additional Fc region of an antibody and FcγRIIIa receptors on the surface
pro-inflammatory cytokine transgene. of immune cells. mAbs may bind to a cell surface target via its
Fab region and engage the effector cell expressing FcγRIIIa with
the Fc region of the mAb, leading to subsequent killing of the
leukemia (NCT02228096; ClinicalTrials.gov). CTL019 is a second- tumor cell. ADCC is thought to be a key mechanism of activity
generation CAR T cell that comprises an anti-CD19 extracellular of the FDA-approved mAbs rituximab and trastuzumab. 60
scFv and CD3-ζ and 4–1BB intracellular signaling domains. Rituximab, a chimeric mAb targeted against the B-cell surface
Adoptive transfer of CAR T cells has demonstrated significant antigen CD20, was the first mAb to be FDA approved for thera-
promise in targeting hard-to-treat hematologic malignancies and peutic use against B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL),
solid tumors. Although the safety concerns related to cytokine CD20-positive NHL, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
release syndrome still need to be fully addressed, multiple CAR Trastuzumab (Herceptin) is another such mAb directed against
T cells are in clinical development. 56 human EGFR-2, a tyrosine kinase membrane receptor, which is
overexpressed on approximately 30% of breast cancer cells in a
Adoptive Transfer of Viral-Specific T Cells subset of breast cancer patients. Trastuzumab monotherapy has
The adoptive transfer of T cells isolated or engineered to have demonstrated prolonged disease stability in a significant number
specificity and reactivity for viral DNA can efficiently treat of advanced-metastatic breast cancer patients. 61
Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-associated posttransplant lympho- Other successful mAbs approved by the FDA for patients with
57
proliferative disease. It is known that CD8 and CD4 virus-specific solid tumors include bevacizumab targeting vascular endothelial
T cells in chronic infections are characterized by the loss of T-cell growth factor (VEGF) (as first-line and second-line treatment of
function due to the upregulation of inhibitory molecules such metastatic colon cancer in combination with 5-FU chemotherapy;
as PD-1 and TIM-3; therefore the adoptive transfer of autologous in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy as
T cells with high-affinity TCRs for viral proteins in combination first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC patients who have not
with inhibitors of PD-1 or TIM-3 could be an ideal approach yet been treated with chemotherapy; as a single agent in patients
for the targeted therapy of virally induced malignancies. 58 with glioblastoma whose tumors have progressed after treatment;
and for treating mRCC patients in combination with IFN-α);
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES cetuximab targeting EGFR (as a single agent in HNSCC patients
with failure to platinum-based therapy; in combination with
The establishment of hybridoma technology in 1975 enabled the radiotherapy for regionally advanced HNSCC; and as palliative
efficient development of mAbs. Immortalized B lymphocytes treatment of pretreated metastatic EGFR-positive colorectal
from immunized hosts were fused with nonimmunoglobulin cancer); panitumumab targeting EGFR (as a single agent for
murine myeloma cells, forming hybridomas, which produced treating pretreated EGFR-positive metastatic colorectal cancer);
59
large amounts of antibodies with high reactivity. Later the alemtuzumab targeting CD52 (as a single agent for treating CLL);