Page 179 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 179
CHaPTEr 10 Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors 161
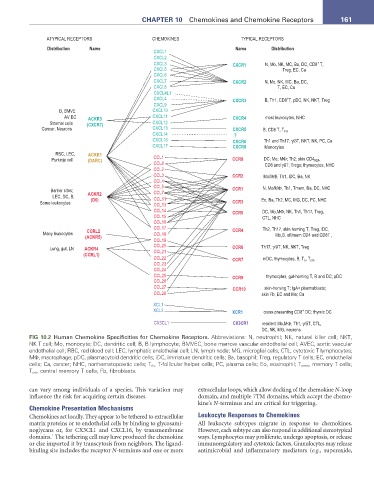
ATYPICAL RECEPTORS CHEMOKINES TYPICAL RECEPTORS
Distribution Name Name Distribution
CXCL1
CXCL2
CXCL3 CXCR1 N, Mo, NK, MC, Ba, DC, CD8 T,
+
CXCL5 Treg, EC, Ca
CXCL6
CXCL7 CXCR2 N, Mo, NK, MC, Ba, DC,
CXCL8 T, EC, Ca
CXCL4L1
CXCL4 CXCR3 B, Th1, CD8 T, pDC, NK, NKT, Treg
+
CXCL9
B, BMVE CXCL10
AV EC ACKR3 CXCL11 CXCR4 most leukocytes, NHC
Stromal cells (CXCR7) CXCL12
Cancer, Neurons CXCL13 CXCR5 B, CD8 T, T FH
CXCL14 ?
CXCL16 CXCR6 Th1 and Th17, γ/δT, NKT, NK, PC, Ca
CXCL17 CXCR8 Monocytes
RBC, LEC, ACKR1
Purkinje cell (DARC) CCL1 CCR8 DC; Mo; MΦ; Th2; skin CD4 ,
RM
CCL8 CD8 and γδT; Tregs; thymocytes, NHC
CCL2
CCL3 CCR2 Mo/MΦ, Th1, iDC, Ba, NK
CCL4
CCL5 N, Mo/MΦ, Th1, Tmem, Ba, DC, NHC
Barrier sites; CCL7 CCR1
LEC, DC, B; ACKR2 CCL11
Some leukocytes (D6) CCL13 CCR3 Eo, Ba, Th2, MC, MG, DC, PC, NHC
CCL14 CCR5 DC, Mo,MΦ, NK, Th1, Th17, Treg,
CCL15 CTL, NHC
CCL16
CCL17 CCR4 Th2, Th17, skin-homing T, Treg, iDC,
Many leukocytes CCRL2 CCL18 Mo,B, eff/mem CD4 and CD8T ,
(ACKR5)
CCL19
CCL20 Th17, γ/δT, NK, NKT, Treg
Lung, gut, LN ACKR4 CCL21 CCR6
(CCRL1)
CCL22 CCR7 mDC, thymocytes, B, T , T cm
n
CCL23
CCL24
CCL25 CCR9 thymocytes, gut-homing T, B and DC; pDC
CCL26
CCL27 CCR10 skin-homing T; IgA+ plasmablasts;
CCL28 skin Fb, EC and Me; Ca
XCL1
XCL2 XCR1 cross-presenting CD8 DC; thymic DC
+
CX3CL1 CX3CR1 resident Mo,MΦ, Th1, γ/δT, CTL,
DC, NK, MG, neurons
FIG 10.2 Human Chemokine Specificities for Chemokine Receptors. Abbreviations: N, neutrophil; NK, natural killer cell; NKT,
NK T cell; Mo, monocyte; DC, dendritic cell; B, B lymphocyte; BMVEC, bone marrow vascular endothelial cell; AVEC, aortic vascular
endothelial cell; RBC, red blood cell; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; LN, lymph node; MG, microglial cells; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocytes;
MΦ, macrophage; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; iDC, immature dendritic cells; Ba, basophil; Treg, regulatory T cells; EC, endothelial
cells; Ca, cancer; NHC, nonhematopoietic cells; T fh , T-follicular helper cells; PC, plasma cells; Eo, eosinophil; T mem , memory T cells;
T cm , central memory T cells; Fb, fibroblasts.
can vary among individuals of a species. This variation may extracellular loops, which allow docking of the chemokine N-loop
influence the risk for acquiring certain diseases. domain, and multiple 7TM domains, which accept the chemo-
kine’s N-terminus and are critical for triggering.
Chemokine Presentation Mechanisms
Chemokines act locally. They appear to be tethered to extracellular Leukocyte Responses to Chemokines
matrix proteins or to endothelial cells by binding to glycosami- All leukocyte subtypes migrate in response to chemokines.
noglycans or, for CX3CL1 and CXCL16, by transmembrane However, each subtype can also respond in additional stereotypical
1
domains. The tethering cell may have produced the chemokine ways. Lymphocytes may proliferate, undergo apoptosis, or release
or else imported it by transcytosis from neighbors. The ligand- immunoregulatory and cytotoxic factors. Granulocytes may release
binding site includes the receptor N-terminus and one or more antimicrobial and inflammatory mediators (e.g., superoxide,