Page 182 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 182
164 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
Tissues Environment
CXCR4
N
CXCR2
Bone Marrow HSC CXCR4
B CXCR7 T em CCR7
Skin
B
N HSC CXCR4
Eo N CXCR4
Mo B CXCR4 CCR2
Thymus NK B CXCR4 Lymph Node MΦ
T n CCR7 Tp T cm CCR7 CCR7 TLR
T h1 CXCR3 GC DC T CCR7
T dp CCR9 T sp CCR4 Blood Th CCR4 T zone DC PAMPs
CCR7
2
T c1 CXCR3 fh CXCR5 iDC
T p
? B T T m CCR6 TLR
T cm
CXCR5 B T CXCR5 n CCR7 CCR5 T m Gut
CD8
em
CCR2 Mo CCR1 CCR7 CCR4 Eo CCR3
CCR3 CCR10 T m CCR9
CCR5 T h1
B CXCR3 T PC CCR9
h2
T B CXCR7 CCR4 T h17 N Eo Mo Mo NK
MZ
CCR2
Spleen CXCR3 CXCR2 CCR3 CX3CR1 CX3CR1 CX3CR1
CCR5
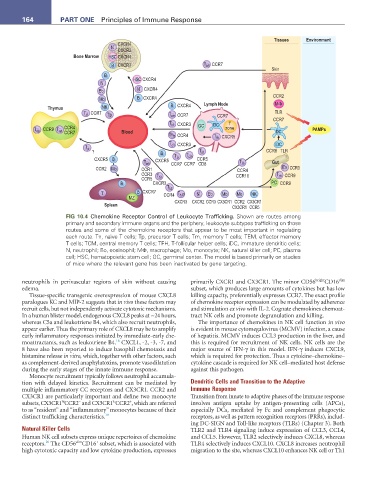
FIG 10.4 Chemokine Receptor Control of Leukocyte Trafficking. Shown are routes among
primary and secondary immune organs and the periphery, leukocyte subtypes trafficking on those
routes and some of the chemokine receptors that appear to be most important in regulating
each route. Tn, naïve T cells; Tp, precursor T cells; Tm, memory T cells; TEM, effector memory
T cells; TCM, central memory T cells; TFH, T-follicular helper cells; iDC, immature dendritic cells;
N, neutrophil; Eo, eosinophil; MΦ, macrophage; Mo, monocyte; NK, natural killer cell; PC, plasma
cell; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; GC, germinal center. The model is based primarily on studies
of mice where the relevant gene has been inactivated by gene targeting.
dim
neutrophils in perivascular regions of skin without causing primarily CXCR1 and CX3CR1. The minor CD56 bright CD16
edema. subset, which produces large amounts of cytokines but has low
Tissue-specific transgenic overexpression of mouse CXCL8 killing capacity, preferentially expresses CCR7. The exact profile
paralogues KC and MIP-2 suggests that in vivo these factors may of chemokine receptor expression can be modulated by adherence
recruit cells, but not independently activate cytotoxic mechanisms. and stimulation ex vivo with IL-2. Cognate chemokines chemoat-
In a human blister model, endogenous CXCL8 peaks at ~24 hours, tract NK cells and promote degranulation and killing.
whereas C5a and leukotriene B4, which also recruit neutrophils, The importance of chemokines in NK cell function in vivo
appear earlier. Thus the primary role of CXCL8 may be to amplify is evident in mouse cytomegalovirus (MCMV) infection, a cause
early inflammatory responses initiated by immediate-early che- of hepatitis. MCMV induces CCL3 production in the liver, and
18
moattractants, such as leukotriene B4. CXCL1, -2, -3, -7, and this is required for recruitment of NK cells. NK cells are the
8 have also been reported to induce basophil chemotaxis and major source of IFN-γ in this model. IFN-γ induces CXCL9,
histamine release in vitro, which, together with other factors, such which is required for protection. Thus a cytokine–chemokine–
as complement-derived anaphylatoxins, promote vasodilatation cytokine cascade is required for NK cell–mediated host defense
during the early stages of the innate immune response. against this pathogen.
Monocyte recruitment typically follows neutrophil accumula-
tion with delayed kinetics. Recruitment can be mediated by Dendritic Cells and Transition to the Adaptive
multiple inflammatory CC receptors and CX3CR1. CCR2 and Immune Response
CX3CR1 are particularly important and define two monocyte Transition from innate to adaptive phases of the immune response
−
+
hi
lo
subsets, CX3CR1 CCR2 and CX3CR1 CCR2 , which are referred involves antigen uptake by antigen-presenting cells (APCs),
to as “resident” and “inflammatory” monocytes because of their especially DCs, mediated by Fc and complement phagocytic
distinct trafficking characteristics. 19 receptors, as well as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), includ-
ing DC-SIGN and Toll-like receptors (TLRs) (Chapter 3). Both
Natural Killer Cells TLR2 and TLR4 signaling induce expression of CCL3, CCL4,
Human NK cell subsets express unique repertoires of chemokine and CCL5. However, TLR2 selectively induces CXCL8, whereas
+
dim
20
receptors. The CD56 CD16 subset, which is associated with TLR4 selectively induces CXCL10. CXCL8 increases neutrophil
high cytotoxic capacity and low cytokine production, expresses migration to the site, whereas CXCL10 enhances NK cell or Th1