Page 196 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 196
CHaPTEr 11 Lymphocyte Adhesion and Trafficking 177
modify adhesive interactions and modulate the microenvironment. INTRAORGAN LYMPHOCYTE LOCALIZATION
VAP-1 is a homodimeric sialoglycoprotein, which, under condi-
tions of inflammation, is rapidly translocated onto the endothelial Following its extravasation from the blood vessels, a lymphocyte
cell surface. It mediates early phases of leukocyte interaction needs to interact with several matrix molecules, such as fibro-
with the endothelium, as well as transmigration. Besides its nectin, laminin, and collagens. Adhesive interactions between a
adhesive function, it also possesses an amine oxidase activity lymphocyte and the extracellular matrix molecules are largely
that can produce potent immunomodulators, such as hydrogen mediated by β 1 integrins, although lymphocytes can also use
peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) and aldehyde as end products. CD44 to interact with fibronectin and collagens. The directional
CD73 is present both on a subpopulation of lymphocytes movement and the final localization of a lymphocyte within the
24
and on the endothelium. It is an ecto-nucleotidase. The main tissues are controlled by chemokines. Modern two-photon
product of its enzymatic activity in dephosphorylation of adenos- imaging has provided detailed information about the kinetics
ine monophosphate (AMP) is adenosine, which is highly anti- and directionality of lymphocyte movement in living tissues. 7
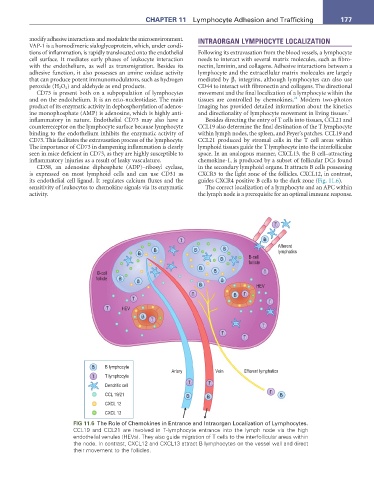
inflammatory in nature. Endothelial CD73 may also have a Besides directing the entry of T cells into tissues, CCL21 and
counterreceptor on the lymphocyte surface because lymphocyte CCL19 also determine the final destination of the T lymphocyte
binding to the endothelium inhibits the enzymatic activity of within lymph nodes, the spleen, and Peyer’s patches. CCL19 and
CD73. This facilitates the extravasation process of the lymphocyte. CCL21 produced by stromal cells in the T cell areas within
The importance of CD73 in dampening inflammation is clearly lymphoid tissues guide the T lymphocyte into the interfollicular
seen in mice deficient in CD73, as they are highly susceptible to space. In an analogous manner, CXCL13, the B cell–attracting
inflammatory injuries as a result of leaky vasculature. chemokine-1, is produced by a subset of follicular DCs found
CD38, an adenosine diphosphate (ADP)–ribosyl cyclase, in the secondary lymphoid organs. It attracts B cells possessing
is expressed on most lymphoid cells and can use CD31 as CXCR5 to the light zone of the follicles. CXCL12, in contrast,
its endothelial cell ligand. It regulates calcium fluxes and the guides CXCR4 positive B cells to the dark zone (Fig. 11.6).
sensitivity of leukocytes to chemokine signals via its enzymatic The correct localization of a lymphocyte and an APC within
activity. the lymph node is a prerequisite for an optimal immune response.
T
T B
Afferent
B B B
B lymphatics
B B-cell
follicle
B
B-cell B T
follicle B B
B
B HEV
T B T
T
T
T HEV
B
T
T
T
T
B B lymphocyte
Artery Vein Efferent lymphatics
T T lymphocyte
T T
Dendritic cell
T
CCL 19/21 B B B
CXCL 12
CXCL 13
FIG 11.6 The Role of Chemokines in Entrance and Intraorgan Localization of Lymphocytes.
CCL19 and CCL21 are involved in Tlymphocyte entrance into the lymph node via the high
endothelial venules (HEVs). They also guide migration of T cells to the interfollicular areas within
the node. In contrast, CXCL12 and CXCL13 attract B lymphocytes on the vessel wall and direct
their movement to the follicles.