Page 197 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 197
178 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
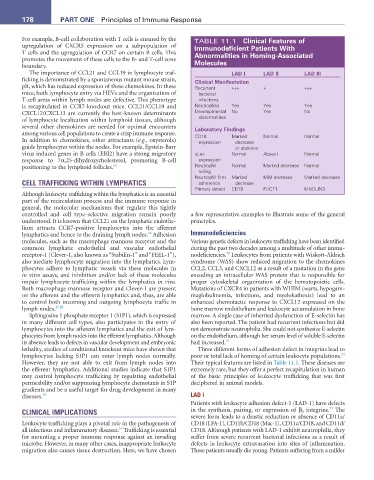
For example, B-cell collaboration with T cells is ensured by the TABLE 11.1 Clinical Features of
upregulation of CXCR5 expression on a subpopulation of Immunodeficient Patients With
T cells and the upregulation of CCR7 on certain B cells. This abnormalities in Homing-associated
promotes the movement of these cells to the B- and T-cell zone
boundary. Molecules
The importance of CCL21 and CCL19 in lymphocyte traf- LaD I LaD II LaD III
ficking is demonstrated by a spontaneous mutant mouse strain, Clinical Manifestation
plt, which has reduced expression of these chemokines. In these Recurrent +++ + +++
mice, both lymphocyte entry via HEVs and the organization of bacterial
T-cell areas within lymph nodes are defective. This phenotype infections
is recapitulated in CCR7-knockout mice. CCL21/CCL19 and Neutrophilia Yes Yes Yes
CXCL12/CXCL13 are currently the best-known determinants Developmental No Yes No
of lymphocyte localization within lymphoid tissues, although abnormalities
several other chemokines are needed for optimal encounters Laboratory Findings
among various cell populations to create a crisp immune response. CD18 Marked Normal Normal
In addition to chemokines, other attractants (e.g., oxysterols) expression decrease
guide lymphocytes within the nodes. For example, Epstein-Barr or absence
virus induced genes in B cells (EBI2) have a strong migratory sLex Normal Absent Normal
response to 7α,25-dihydroxycholesterol, promoting B-cell expression
positioning to the lymphoid follicles. 25 Neutrophil Normal Marked decrease Normal
rolling
Neutrophil firm Marked Mild decrease Marked decrease
CELL TRAFFICKING WITHIN LYMPHATICS adherence decrease
Primary detect CD18 FUCT1 KINDLIN3
Although leukocyte trafficking within the lymphatics is an essential
part of the recirculation process and the immune response in
general, the molecular mechanisms that regulate this tightly
controlled and cell type–selective migration remain poorly a few representative examples to illustrate some of the general
understood. It is known that CCL21 on the lymphatic endothe- principles.
lium attracts CCR7-positive lymphocytes into the afferent
26
lymphatics and hence to the draining lymph nodes. Adhesion Immunodeficiencies
molecules, such as the macrophage mannose receptor and the Various genetic defects in leukocyte trafficking have been identified
common lymphatic endothelial and vascular endothelial during the past two decades among a multitude of other immu-
30
receptor-1 (Clever-1, also known as “Stabilin-1” and “FEEL-1”), nodeficiencies. Leukocytes from patients with Wiskott-Aldrich
also mediate lymphocyte migration into the lymphatics. Lym- syndrome (WAS) show reduced migration to the chemokines
phocytes adhere to lymphatic vessels via these molecules in CCL2, CCL3, and CXCL12 as a result of a mutation in the gene
in vitro assays, and inhibition and/or lack of these molecules encoding an intracellular WAS protein that is responsible for
impair lymphocyte trafficking within the lymphatics in vivo. proper cytoskeletal organization of the hematopoietic cells.
Both macrophage mannose receptor and Clever-1 are present Mutations of CXCR4 in patients with WHIM (warts, hypogam-
on the afferent and the efferent lymphatics and, thus, are able maglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis) lead to an
to control both incoming and outgoing lymphocyte traffic in enhanced chemotactic response to CXCL12 expressed on the
lymph nodes. 27,28 bone marrow endothelium and leukocyte accumulation in bone
Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1), which is expressed marrow. A single case of inherited dysfunction of E-selectin has
in many different cell types, also participates in the entry of also been reported. The patient had recurrent infections but did
lymphocytes into the afferent lymphatics and the exit of lym- not demonstrate neutrophilia. She could not synthesize E-selectin
phocytes from lymph nodes into the efferent lymphatics. Although on the endothelium, although her serum level of soluble E-selectin
its absence leads to defects in vascular development and embryonic had increased. 31
lethality, studies of conditional knockout mice have shown that Three different forms of adhesion defect in integrins lead to
32
lymphocytes lacking S1P1 can enter lymph nodes normally. poor or total lack of homing of certain leukocyte populations.
However, they are not able to exit from lymph nodes into Their typical features are listed in Table 11.1. These diseases are
the efferent lymphatics. Additional studies indicate that S1P1 extremely rare, but they offer a perfect recapitulation in human
may control lymphocyte trafficking by regulating endothelial of the basic principles of leukocyte trafficking that was first
permeability and/or suppressing lymphocyte chemotaxis in S1P deciphered in animal models.
gradients and be a useful target for drug development in many
diseases. 29 LAD I
Patients with leukocyte adhesion defect-1 (LAD-1) have defects
33
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS in the synthesis, pairing, or expression of β 2 integrins. The
severe form leads to a drastic reduction or absence of CD11a/
Leukocyte trafficking plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of CD18 (LFA-1), CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1), CD11c/CD18, and CD11d/
16
all infectious and inflammatory diseases. Trafficking is essential CD18. Although patients with LAD-1 exhibit neutrophilia, they
for mounting a proper immune response against an invading suffer from severe recurrent bacterial infections as a result of
microbe. However, in many other cases, inappropriate leukocyte defects in leukocyte extravasation into sites of inflammation.
migration also causes tissue destruction. Here, we have chosen These patients usually die young. Patients suffering from a milder