Page 214 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 214
194 PART ONE Principles of Immune Response
CD28 CD28 CD28
TCR/CD3 TCR/CD3 TCR/CD3
Ca Ionophore
NFAT + AP-1 NFAT > AP-1 NFAT
↑IL-2 + Anergy Anergy
Transcription
A activation
TCR signaling for activation TCR signaling in anergy
TCR/CD3 b E3 ubiquitin ligases
TCR/CD3
GRAIL
LAT LAT a Palmitoylation
PTK
PTK Cbl-b
PLCγ1 PLCγ1
c DGK
IP3 DAG IP3 DAG PA
d
RAS PKCθ RAP1 RAS PKCθ
2+
Ca 2+ flux RAF IKK Ca flux RAF IKK
NFAT ERK NF-κB NFAT ERK NF-κB
Activation factors AP-1 NF-κB Anergy factors
NFAT AP-1 NF-κB NFAT
B
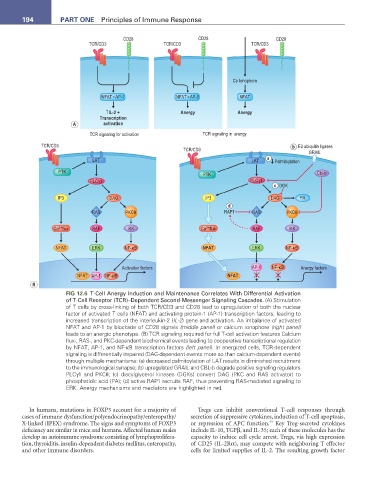
FIG 12.6 T-Cell Anergy Induction and Maintenance Correlates With Differential Activation
of T-Cell Receptor (TCR)–Dependent Second-Messenger Signaling Cascades. (A) Stimulation
of T cells by cross-linking of both TCR/CD3 and CD28 lead to upregulation of both the nuclear
factor of activated T cells (NFAT) and activating protein-1 (AP-1) transcription factors, leading to
increased transcription of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) gene and activation. An imbalance of activated
NFAT and AP-1 by blockade of CD28 signals (middle panel) or calcium ionophore (right panel)
leads to an anergic phenotype. (B) TCR signaling required for full T-cell activation features Calcium
flux-, RAS-, and PKC-dependent biochemical events leading to cooperative transcriptional regulation
by NFAT, AP-1, and NF-κB transcription factors (left panel). In anergized cells, TCR-dependent
signaling is differentially impaired (DAG-dependent events more so than calcium-dependent events)
through multiple mechanisms: (a) decreased palmitoylation of LAT results in diminished recruitment
to the immunological synapse; (b) upregulated GRAIL and CBL-b degrade positive signaling regulators
PLCγ1 and PKCθ; (c) diacylglycerol kinases (DGKs) convert DAG (PKC and RAS activator) to
phosphatidic acid (PA); (d) active RAP1 recruits RAF, thus preventing RAS-mediated signaling to
ERK. Anergy mechanisms and mediators are highlighted in red.
In humans, mutations in FOXP3 account for a majority of Tregs can inhibit conventional T-cell responses through
cases of immune dysfunction/polyendocrinopathy/enteropathy/ secretion of suppressive cytokines, induction of T-cell apoptosis,
49
X-linked (IPEX) syndrome. The signs and symptoms of FOXP3 or repression of APC function. Key Treg-secreted cytokines
deficiency are similar in mice and humans. Affected human males include IL-10, TGFβ, and IL-35; each of these molecules has the
develop an autoimmune syndrome consisting of lymphoprolifera- capacity to induce cell cycle arrest. Tregs, via high expression
tion, thyroiditis, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, enteropathy, of CD25 (IL-2Rα), may compete with neighboring T effector
and other immune disorders. cells for limited supplies of IL-2. The resulting growth factor