Page 209 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 209
CHAPTER 12 T-Cell Activation and Tolerance 189
1 233
LAT TM P-Y sites
1 322
GADS SH3 SH2 SH3
1 533
A SLP-76 P-Y sites Prorich SH2
TCR/CD3
PIP2
LCK P PLCγ1 P VAV RAC
ZAP-70 P SLP-76 P NCK PAK
GRB2 P GADs P ITK WASP DAG IP3
SOS
HPK1 ADAP
RAS
ERK Integrin Cytoskeletal
activation rearrangements
Nucleus
Transcription
B
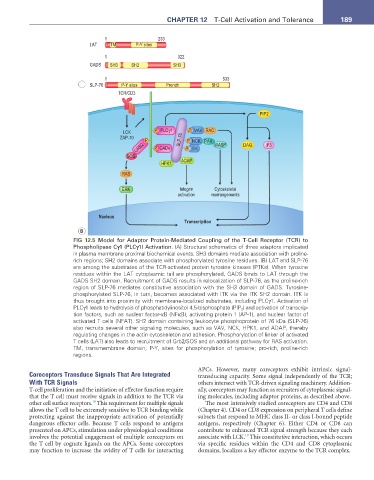
FIG 12.5 Model for Adaptor Protein-Mediated Coupling of the T-Cell Receptor (TCR) to
Phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) Activation. (A) Structural schematics of three adaptors implicated
in plasma membrane proximal biochemical events. SH3 domains mediate association with proline-
rich regions; SH2 domains associate with phosphorylated tyrosine residues. (B) LAT and SLP-76
are among the substrates of the TCR-activated protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). When tyrosine
residues within the LAT cytoplasmic tail are phosphorylated, GADS binds to LAT through the
GADS SH2 domain. Recruitment of GADS results in relocalization of SLP-76, as the proline-rich
region of SLP-76 mediates constitutive association with the SH3 domain of GADS. Tyrosine-
phosphorylated SLP-76, in turn, becomes associated with ITK via the ITK SH2 domain. ITK is
thus brought into proximity with membrane-localized substrates, including PLCγ1. Activation of
PLCγ1 leads to hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP 2 ) and activation of transcrip-
tion factors, such as nuclear factor-κB (NFκB), activating protein 1 (AP-1), and nuclear factor of
activated T cells (NFAT). SH2 domain containing leukocyte phosphoprotein of 76 kDa (SLP-76)
also recruits several other signaling molecules, such as VAV, NCK, HPK1, and ADAP, thereby
regulating changes in the actin cytoskeleton and adhesion. Phosphorylation of linker of activated
T cells (LAT) also leads to recruitment of Grb2/SOS and an additional pathway for RAS activation.
TM, transmembrane domain; P-Y, sites for phosphorylation of tyrosine; pro-rich, proline-rich
regions.
APCs. However, many coreceptors exhibit intrinsic signal-
Coreceptors Transduce Signals That Are Integrated transducing capacity. Some signal independently of the TCR;
With TCR Signals others intersect with TCR-driven signaling machinery. Addition-
T-cell proliferation and the initiation of effector function require ally, coreceptors may function as recruiters of cytoplasmic signal-
that the T cell must receive signals in addition to the TCR via ing molecules, including adaptor proteins, as described above.
18
other cell surface receptors. This requirement for multiple signals The most intensively studied coreceptors are CD4 and CD8
allows the T cell to be extremely sensitive to TCR binding while (Chapter 4). CD4 or CD8 expression on peripheral T cells define
protecting against the inappropriate activation of potentially subsets that respond to MHC class II- or class I-bound peptide
dangerous effector cells. Because T cells respond to antigens antigens, respectively (Chapter 6). Either CD4 or CD8 can
presented on APCs, stimulation under physiological conditions contribute to enhanced TCR signal strength because they each
19
involves the potential engagement of multiple coreceptors on associate with LCK. This constitutive interaction, which occurs
the T cell by cognate ligands on the APCs. Some coreceptors via specific residues within the CD4 and CD8 cytoplasmic
may function to increase the avidity of T cells for interacting domains, localizes a key effector enzyme to the TCR complex.