Page 219 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 219
198 ParT ONE Principles of Immune Response
class I interaction and CD4 T cells via MHC class II interaction When challenged with injurious conditions, such as ischemia–
(Chapter 5), thus shifting the immune response to an antigen reperfusion in solid-organ transplantations, options for cellular
specific response, as cytotoxic T cells and active B cells now fate are directly succumbing via accidental cell death (ACD),
specifically attack stressed cells (Fig. 13.2). However, in addition restoring cellular homeostasis, or dying by RCD. ACD happens
to these DAMPs, other intracellular content has the potential to passively under certain conditions, such as extreme heat, and
be sensed as a target as well, which could lead to the development occurs nearly immediately in an uncontrolled fashion. Because
of autoimmunity. of the direct loss of membrane integrity, huge amounts of DAMPs
are released. This leads to massive recruitment of innate immunity
and local inflammation. As this kind of stimulus is not given in
ischemia–reperfusion, this is not further discussed here. However,
Apoptosis Necrosis if these cells do not explode directly, they balance on the edge.
regulated cell death accidental or regulated The issue then becomes whether balance will be restored (e.g.,
by means of autophagy or unfolded protein response following
Regulated cell death endoplasmic reticulum [ER] stress) or, if the damage is too great,
RCD will balance be lost and RCD be induced?
Within the cells that succumb to cell death, the necroinflam-
matory loop starts with perturbation of intracellular homeostasis
Apoptosis Necrosis Necrosis (class V DAMPs), which triggers the heat shock response, a system
Regulated cell death Regulated cell death accidental of critical importance for correct protein folding. Secreted or
nonimmunogenic immunogenic cell death surface-exposed heat shock proteins (HSPs) can be sensed by
FIG 13.1 New Concept of Regulated Cell Death. When either classic (e.g., TLR2/4) or nonclassic (e.g., CD91) receptors
apoptosis was first identified, two models of regulated cell death on DCs. In parallel, ER stress (which is often result of reactive
were recognized: apoptosis and necrosis. More recently, however, oxygen species [ROS] generation) leads to secretion of calreticulin
cell death is divided into regulated cell death (including apoptosis (an ER chaperone referred to as “CALR”), which then acts
and regulated necrosis) and accidental cell death (instant necrosis). extracellularly as a class I DAMP by binding to CD91. This leads
A second parameter classifies cell death as either immunogenic inactive dendritic cells (iDCs) to be activated. For full activation,
or nonimmunogenic. however, an inflammatory milieu is required.
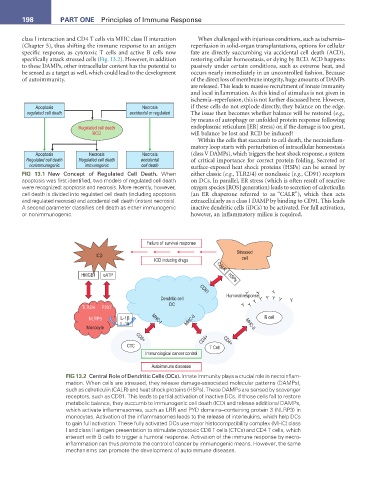
Failure of survival response
Stressed
ICD
ICD inducing drugs CALR cell
HMGB1 eATP HSPs
Y
CD91
Humoral response:
Y
Y
Dendritic cell Y Y Y Y Y Y
DC Y Y
TLR2/4 P2X7
NLRP3 IL-1β MHC-I MHC-II B cell
IL-18 MHC-II
Monocyte
CD4+ CD4+
CD8+
CTC T Cell
Immunological cancer control
Autoimmune diseases
FIG 13.2 Central Role of Dendritic Cells (DCs). Innate immunity plays a crucial role in necroinflam-
mation. When cells are stressed, they release damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs),
such as calreticulin (CALR) and heat shock proteins (HSPs). These DAMPs are sensed by scavenger
receptors, such as CD91. This leads to partial activation of inactive DCs. If those cells fail to restore
metabolic balance, they succumb to immunogenic cell death (ICD) and release additional DAMPs,
which activate inflammasomes, such as LRR and PYD domains–containing protein 3 (NLRP3) in
monocytes. Activation of the inflammasomes leads to the release of interleukins, which help DCs
to gain full activation. These fully activated DCs use major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class
I and class II antigen presentation to stimulate cytotoxic CD8 T cells (CTCs) and CD4 T cells, which
interact with B cells to trigger a humoral response. Activation of the immune response by necro-
inflammation can thus promote the control of cancer by immunogenic means. However, the same
mechanisms can promote the development of autoimmune diseases.