Page 237 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 237
216 Part One Principles of Immune Response
KINGDOM BACTERIA FUNGI
KINGDOM BACTERIA FUNGI
Bacteria Propionibacterium Malassezia
Glabella
Eukaryota Corynebacterium
Front Back Viruses Staphylococcus
SITE CHARACTERISTICS
External auditory canal Oily Moist Dry
KINGDOMKINGDOM BACTERIA FUNGI
Nare
Retroauricular crease
Manubrium
Occiput
Antecubital fossa
Back
Volar forearm
Hypothenar palm
KINGDOM BACTERIA FUNGI
KINGDOM
Inguinal crease Toenail
Toe web space Plantar heel
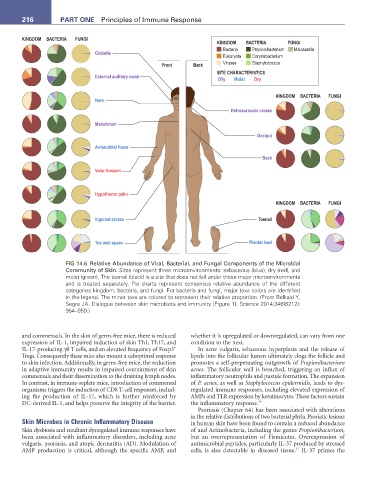
FIG 14.6 Relative Abundance of Viral, Bacterial, and Fungal Components of the Microbial
Community of Skin. Sites represent three microenvironments: sebaceous (blue), dry (red), and
moist (green). The toenail (black) is a site that does not fall under these major microenvironments
and is treated separately. Pie charts represent consensus relative abundance of the different
categories kingdom, bacteria, and fungi. For bacteria and fungi, major taxa colors are identified
in the legend. The minor taxa are colored to represent their relative proportion. (From Belkaid Y,
Segre JA. Dialogue between skin microbiota and immunity [Figure 1]. Science 2014;346(6212):
954–959.)
and commensals. In the skin of germ-free mice, there is reduced whether it is upregulated or downregulated, can vary from one
expression of IL-1, impaired induction of skin Th1, Th17, and condition to the next.
+
IL-17-producing γδ T cells, and an elevated frequency of Foxp3 In acne vulgaris, sebaceous hyperplasia and the release of
Tregs. Consequently these mice also mount a suboptimal response lipids into the follicular lumen ultimately clogs the follicle and
to skin infection. Additionally, in germ-free mice, the reduction promotes a self-perpetuating outgrowth of Propionibacterium
in adaptive immunity results in impaired containment of skin acnes. The follicular wall is breached, triggering an influx of
commensals and their dissemination to the draining lymph nodes. inflammatory neutrophils and pustule formation. The expansion
In contrast, in immune-replete mice, introduction of commensal of P. acnes, as well as Staphylococcus epidermidis, leads to dys-
organisms triggers the induction of CD8 T-cell responses, includ- regulated immune responses, including elevated expression of
ing the production of IL-17, which is further reinforced by AMPs and TLR expression by keratinocytes. These factors sustain
DC-derived IL-1, and helps preserve the integrity of the barrier. the inflammatory response. 46
Psoriasis (Chapter 64) has been associated with alterations
in the relative distributions of two bacterial phyla. Psoriatic lesions
Skin Microbes in Chronic Inflammatory Disease in human skin have been found to contain a reduced abundance
Skin dysbiosis and resultant dysregulated immune responses have of and Actinobacteria, including the genus Propionibacterium,
been associated with inflammatory disorders, including acne but an overrepresentation of Firmicutes. Overexpression of
vulgaris, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis (AD). Modulation of antimicrobial peptides, particularly IL-37 produced by stressed
47
AMP production is critical, although the specific AMP, and cells, is also detectable in diseased tissue. IL-37 primes the