Page 245 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 245
226 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
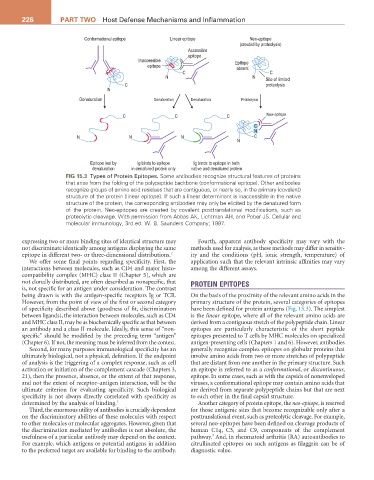
Conformational epitope Linear epitope Neo-epitope
(created by proteolysis)
Accessible
epitope
Inaccessible Epitope
epitope absent
C C
N N
Site of limited
C proteolysis
N
Denaturation Denaturation Denaturation Proteolysis
C C C New epitope
C
N
N N N C
N
Epitope lost by Ig binds to epitope Ig binds to epitope in both
denaturation in denatured protein only native and denatured protein
FIG 15.3 Types of Protein Epitopes. Some antibodies recognize structural features of proteins
that arise from the folding of the polypeptide backbone (conformational epitope). Other antibodies
recognize groups of amino acid residues that are contiguous, or nearly so, in the primary (covalent)
structure of the protein (linear epitope). If such a linear determinant is inaccessible in the native
structure of the protein, the corresponding antibodies may only be elicited by the denatured form
of the protein. Neo-epitopes are created by covalent posttranslational modifications, such as
proteolytic cleavage. With permission from Abbas AK, Lichtman AH, and Pober JS. Cellular and
molecular immunology, 3rd ed. W. B. Saunders Company; 1997.
expressing two or more binding sites of identical structure may Fourth, apparent antibody specificity may vary with the
not discriminate identically among antigens displaying the same methods used for analysis, as these methods may differ in sensitiv-
epitope in different two- or three-dimensional distributions. 2 ity and the conditions (pH, ionic strength, temperature) of
We offer some final points regarding specificity. First, the application such that the relevant intrinsic affinities may vary
interactions between molecules, such as CD4 and major histo- among the different assays.
compatibility complex (MHC) class II (Chapter 5), which are
not clonally distributed, are often described as nonspecific, that PROTEIN EPITOPES
is, not specific for an antigen under consideration. The contrast
being drawn is with the antigen-specific receptors Ig or TCR. On the basis of the proximity of the relevant amino acids in the
However, from the point of view of the first or second category primary structure of the protein, several categories of epitopes
of specificity described above (goodness of fit, discrimination have been defined for protein antigens (Fig. 15.3). The simplest
between ligands), the interaction between molecules, such as CD4 is the linear epitope, where all of the relevant amino acids are
and MHC class II, may be as biochemically specific as that between derived from a contiguous stretch of the polypeptide chain. Linear
an antibody and a class II molecule. Ideally, this sense of “non- epitopes are particularly characteristic of the short peptide
specific” should be modified by the preceding term “antigen” epitopes presented to T cells by MHC molecules on specialized
(Chapter 6). If not, the meaning must be inferred from the context. antigen-presenting cells (Chapters 1 and 6). However, antibodies
Second, for many purposes immunological specificity has an generally recognize complex epitopes on globular proteins that
ultimately biological, not a physical, definition. If the endpoint involve amino acids from two or more stretches of polypeptide
of analysis is the triggering of a complex response, such as cell that are distant from one another in the primary structure. Such
activation or initiation of the complement cascade (Chapters 3, an epitope is referred to as a conformational, or discontinuous,
21), then the presence, absence, or the extent of that response, epitope. In some cases, such as with the capsids of nonenveloped
and not the extent of receptor–antigen interaction, will be the viruses, a conformational epitope may contain amino acids that
ultimate criterion for evaluating specificity. Such biological are derived from separate polypeptide chains but that are next
specificity is not always directly correlated with specificity as to each other in the final capsid structure.
determined by the analysis of binding. 2 Another category of protein epitope, the neo-epitope, is reserved
Third, the enormous utility of antibodies is crucially dependent for those antigenic sites that become recognizable only after a
on the discriminatory abilities of these molecules with respect posttranslational event, such as proteolytic cleavage. For example,
to other molecules or molecular aggregates. However, given that several neo-epitopes have been defined on cleavage products of
the discrimination mediated by antibodies is not absolute, the human C1q, C3, and C9, components of the complement
9
usefulness of a particular antibody may depend on the context. pathway. And, in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) autoantibodies to
For example, which antigens or potential antigens in addition citrullinated epitopes on such antigens as filaggrin can be of
to the preferred target are available for binding to the antibody. diagnostic value.