Page 250 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 250
CHaPtEr 15 Immunoglobulin Function 231
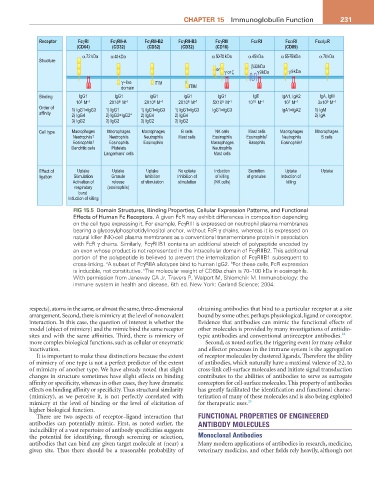
Receptor FcγRI FcγRII-A FcγRII-B2 FcγRII-B3 FcγRIII FcεRI FcαRI Fcα/µR
(CD64) (CD32) (CD32) (CD32) (CD16) (CD89)
α 72 kDa α 40 kDa α 50-70 kDa α 45 kDa α 55-75 kDa α 70 kDa
Structure
β 33 kDa
or γ or ζ γ 9 kDa γ 9 kDa
γ ~like ITIM
domain ITIM
Binding IgG1 IgG1 IgG1 IgG1 IgG1 IgE IgA1, IgA2 IgA, IgM
10 M 2X10 M 2X10 M 2X10 M 5X10 M 10 10 -1 10 M 3x10 M
8 -1
5 -1
7 -1
M
6 -1
9 -1
6 -1
6 -1
Order of 1) IgG1=IgG3 1) IgG1 1) IgG1=IgG3 1) IgG1=IgG3 IgG1=IgG3 IgA1=IgA2 1) IgM
affinity 2) IgG4 2) IgG3=IgG2* 2) IgG4 2) IgG4 2) IgA
3) IgG2 3) IgG2 3) IgG2 3) IgG2
Cell type Macrophages Macrophages Macrophages B cells NK cells Mast cells Macrophages Macrophages
Neutrophils † Neutrophils Neutrophils Mast cells Eosinophils Eosinophils † Neutrophils B cells
Eosinophils † Eosinophils Eosinophils Macrophages Basophils Eosinophils ‡
Dendritic cells Platelets Neutrophils
Langerhans’ cells Mast cells
Effect of Uptake Uptake Uptake No uptake Induction Secretion Uptake Uptake
ligation Stimulation Granule Inhibition Inhibition of of killing of granules Induction of
Activation of release of stimulation stimulation (NK cells) killing
respiratory (eosinophils)
burst
Induction of killing
FIG 15.5 Domain Structures, Binding Properties, Cellular Expression Patterns, and Functional
Effects of Human Fc Receptors. A given FcR may exhibit differences in composition depending
on the cell type expressing it. For example, FcγRIII is expressed on neutrophil plasma membranes
bearing a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor, without FcR γ chains, whereas it is expressed on
natural killer (NK)-cell plasma membranes as a conventional transmembrane protein in association
with FcR γ chains. Similarly, FcγRIIB1 contains an additional stretch of polypeptide encoded by
an exon whose product is not represented in the intracellular domain of FcγRIIB2. This additional
portion of the polypeptide is believed to prevent the internalization of FcγRIIB1 subsequent to
cross-linking. A subset of FcγRIIA allotypes bind to human IgG2. For these cells, FcR expression
b
a
is inducible, not constitutive. The molecular weight of CD89α chain is 70–100 kDa in eosinophils.
c
With permission from Janeway CA Jr, Travers P, Walport M, Shlomchik M. Immunobiology: the
immune system in health and disease, 6th ed. New York: Garland Science; 2004.
respects), atoms in the same, or almost the same, three-dimensional obtaining antibodies that bind to a particular receptor at a site
arrangement. Second, there is mimicry at the level of noncovalent bound by some other, perhaps physiological, ligand or coreceptor.
interaction. In this case, the question of interest is whether the Evidence that antibodies can mimic the functional effects of
model (object of mimicry) and the mimic bind the same receptor other molecules is provided by many investigations of antiidio-
sites and with the same affinities. Third, there is mimicry of typic antibodies and conventional antireceptor antibodies. 24
more complex biological functions, such as cellular or enzymatic Second, as noted earlier, the triggering event for many cellular
inactivation. and effector processes in the immune system is the aggregation
It is important to make these distinctions because the extent of receptor molecules by clustered ligands. Therefore the ability
of mimicry of one type is not a perfect predictor of the extent of antibodies, which naturally have a maximal valence of ≥2, to
of mimicry of another type. We have already noted that slight cross-link cell-surface molecules and initiate signal transduction
changes in structure sometimes have slight effects on binding contributes to the abilities of antibodies to serve as surrogate
affinity or specificity, whereas in other cases, they have dramatic coreceptors for cell-surface molecules. This property of antibodies
effects on binding affinity or specificity. Thus structural similarity has greatly facilitated the identification and functional charac-
(mimicry), as we perceive it, is not perfectly correlated with terization of many of these molecules and is also being exploited
mimicry at the level of binding or the level of elicitation of for therapeutic uses. 25
higher biological function.
There are two aspects of receptor–ligand interaction that FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES OF ENGINEERED
antibodies can potentially mimic. First, as noted earlier, the ANTIBODY MOLECULES
inducibility of a vast repertoire of antibody specificities suggests
the potential for identifying, through screening or selection, Monoclonal Antibodies
antibodies that can bind any given target molecule at (near) a Many modern applications of antibodies in research, medicine,
given site. Thus there should be a reasonable probability of veterinary medicine, and other fields rely heavily, although not