Page 251 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 251
232 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
exclusively, on mAbs. By definition, a mAb population is derived
from a clonal population of B-lineage cells (Chapter 7). Therefore
all of the molecules express identical variable domains and scFv-toxin
identical antigen specificities. It is the homogeneity of V-domain scFv
structure associated with mAbs that most crucially distinguishes
them from polyclonal antibodies, such as those conventionally
derived from the serum. Homogeneous antibodies give more Fv
reproducible and more easily interpreted results for many kinds dAb
of assays.
Fab
KEY CoNCEPtS m.r.u
Monoclonal Antibodies From Hybridomas
Mouse antibody
• Hybridomas are created by fusing normal lymphocytes from immunized Fab enzyme
animals or immune humans with transformed cells of B-lymphocyte
lineage (myeloma cells). Fc
• Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) produced by a hybridoma are generally
homogeneous, expressing a single amino acid sequence.
• Hybridomas can be grown indefinitely in tissue culture.
• Hybridomas can be selected on the basis of the antigenic specificity
or functional properties of the mAb secreted by the hybridoma.
CD4
Chimeric immunoadhesin
mAbs of selected specificity were first produced by cells referred mouse antibody
26
to as hybridomas. In contrast, a myeloma protein would be an
example of an mAb of unselected specificity. Hybridomas are
hybrid transformed cells that are created by the fusion of two
'Reshaped'
types of cells, with each parental cell endowing the hybridoma human antibody
with desirable properties. One parent of a hybridoma (the fusion
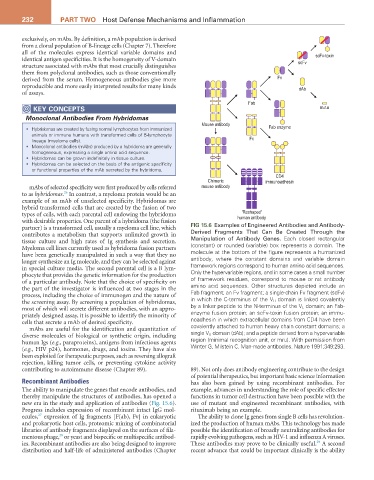
partner) is a transformed cell, usually a myeloma cell line, which FIG 15.6 Examples of Engineered Antibodies and Antibody-
contributes a metabolism that supports unlimited growth in Derived Fragments That Can Be Created Through the
tissue culture and high rates of Ig synthesis and secretion. Manipulation of Antibody Genes. Each closed rectangular
Myeloma cell lines currently used as hybridoma fusion partners (constant) or rounded (variable) box represents a domain. The
have been genetically manipulated in such a way that they no molecule at the bottom of the figure represents a humanized
longer synthesize an Ig molecule, and they can be selected against antibody, where the constant domains and variable domain
in special culture media. The second parental cell is a B lym- framework regions correspond to human amino acid sequences.
phocyte that provides the genetic information for the production Only the hypervariable regions, and in some cases a small number
of a particular antibody. Note that the choice of specificity on of framework residues, correspond to mouse or rat antibody
the part of the investigator is influenced at two stages in the amino acid sequences. Other structures depicted include an
process, including the choice of immunogen and the nature of Fab fragment; an Fv fragment; a single-chain Fv fragment (scFv)
the screening assay. By screening a population of hybridomas, in which the C-terminus of the V H domain is linked covalently
most of which will secrete different antibodies, with an appro- by a linker peptide to the N-terminus of the V L domain; an Fab-
priately designed assay, it is possible to identify the minority of enzyme fusion protein; an scFv-toxin fusion protein; an immu-
cells that secrete a mAb of desired specificity. noadhesin in which extracellular domains from CD4 have been
mAbs are useful for the identification and quantitation of covalently attached to human heavy chain constant domains; a
diverse molecules of biological or synthetic origin, including single V H domain (dAb); and a peptide derived from a hypervariable
human Igs (e.g., paraproteins), antigens from infectious agents region (minimal recognition unit, or mru). With permission from
(e.g., HIV p24), hormones, drugs, and toxins. They have also Winter G, Milstein C. Man-made antibodies. Nature 1991;349:293.
been exploited for therapeutic purposes, such as reversing allograft
rejection, killing tumor cells, or preventing cytokine activity
contributing to autoimmune disease (Chapter 89). 89). Not only does antibody engineering contribute to the design
of potential therapeutics, but important basic science information
Recombinant Antibodies has also been gained by using recombinant antibodies. For
The ability to manipulate the genes that encode antibodies, and example, advances in understanding the role of specific effector
thereby manipulate the structures of antibodies, has opened a functions in tumor cell destruction have been possible with the
new era in the study and application of antibodies (Fig. 15.6). use of mutant and engineered recombinant antibodies, with
Progress includes expression of recombinant intact IgG mol- rituximab being an example.
27
ecules, expression of Ig fragments [F(ab), Fv] in eukaryotic The ability to clone Ig genes from single B cells has revolution-
and prokaryotic host cells, proteomic mining of combinatorial ized the production of human mAbs. This technology has made
libraries of antibody fragments displayed on the surfaces of fila- possible the identification of broadly neutralizing antibodies for
28
mentous phage, or yeast and bispecific or multispecific antibod- rapidly evolving pathogens, such as HIV-1 and influenza A viruses.
29
ies. Recombinant antibodies are also being designed to improve These antibodies may prove to be clinically useful. A second
distribution and half-life of administered antibodies (Chapter recent advance that could be important clinically is the ability