Page 255 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 255
236 PArT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
mature DCs readily elicit T-cell activation. DC maturation is
regulated by external stimuli, such as Toll-like receptor (TLR)
stimulation. T cells also stimulate DC maturation by expressing
T cell DC-bearing Tissue DC CD40 ligand (CD40L or CD154). Mature DCs instruct T cells
antigen through expression of MHC, costimulatory ligands, and cytokines.
The expression of these molecules provides context to the T-cell
activation process and helps tailor the immune response. For
Lymph node
instance, TLR stimulation may elicit the expression of specific
types or levels of costimulation and cytokine allowing mature
Th1 Th2
Th22 DCs to promote antibacterial T-effector responses. Tissue-specific
factors, such as vitamin D, transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)
Th1 Treg and interleukin-10 (IL-10), alter costimulatory ligand and cytokine
Th9 expression by the DC and reduce T-cell activation. Thus DCs
Th17 Tcm transmit information from tissues to either promote specific
immunity or suppress potentially damaging T-cell responses. 8
Proliferation
Differentiation T-cell activation defects contribute to several immunodefi-
ciency diseases. T cells from patients with Wiskott-Aldrich
syndrome, for instance, have defects in the formation of stable
DC Activated TCR signaling complexes. T cells in leukocyte adhesion deficiency
T cell Apoptosis
1 have a reduced capacity to become activated in response to
stimulation due to defects in integrin β 2 . Similarly, patients with
T cell mutations in the TCR signaling components lck and Zap70 show
Activation Expansion differentiation defective T-cell activation. In contrast, mutations in inhibitory
receptors, including CTLA-4 and PD-1, are thought to contribute
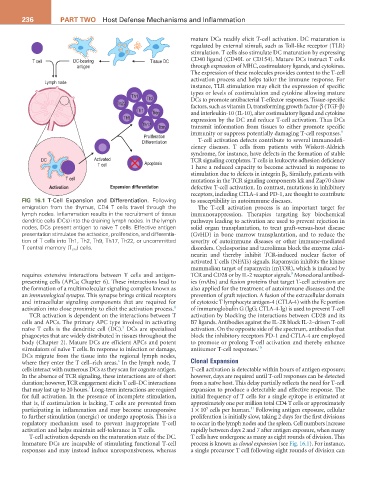
FIG 16.1 T-Cell Expansion and Differentiation. Following to susceptibility in autoimmune diseases.
emigration from the thymus, CD4 T cells travel through the The T-cell activation process is an important target for
lymph nodes. Inflammation results in the recruitment of tissue immunosuppression. Therapies targeting key biochemical
dendritic cells (DCs) into the draining lymph nodes. In the lymph pathways leading to activation are used to prevent rejection in
nodes, DCs present antigen to naïve T cells. Effective antigen solid organ transplantation, to treat graft-versus-host disease
presentation stimulates the activation, proliferation, and differentia- (GvHD) in bone marrow transplantation, and to reduce the
tion of T cells into Th1, Th2, Th9, Th17, Th22, or uncommitted severity of autoimmune diseases or other immune-mediated
T central memory (T cm ) cells. disorders. Cyclosporine and tacrolimus block the enzyme calci-
neurin and thereby inhibit TCR-induced nuclear factor of
activated T cells (NFATs) signals. Rapamycin inhibits the kinase
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which is induced by
9
requires extensive interactions between T cells and antigen- TCR and CD28 or by IL-2 receptor signals. Monoclonal antibod-
presenting cells (APCs; Chapter 6). These interactions lead to ies (mAbs) and fusion proteins that target T-cell activation are
the formation of a multimolecular signaling complex known as also applied for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and the
an immunological synapse. This synapse brings critical receptors prevention of graft rejection. A fusion of the extracellular domain
and intracellular signaling components that are required for of cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 (CTLA-4) with the Fc portion
activation into close proximity to elicit the activation process. 4 of immunoglobulin G (IgG; CTLA-4-Ig) is used to prevent T-cell
TCR activation is dependent on the interactions between T activation by blocking the interactions between CD28 and its
cells and APCs. The primary APC type involved in activating B7 ligands. Antibodies against the IL-2R block IL-2–driven T-cell
5
naïve T cells is the dendritic cell (DC). DCs are specialized activation. On the opposite side of the spectrum, antibodies that
phagocytes that are widely distributed in tissues throughout the block the inhibitory receptors PD-1 and CTLA-4 are employed
body (Chapter 2). Mature DCs are efficient APCs and potent to promote or prolong T-cell activation and thereby enhance
stimulators of naïve T cells. In response to infection or damage, antitumor T-cell responses. 10
DCs migrate from the tissue into the regional lymph nodes,
6
where they enter the T cell–rich areas. In the lymph node, T Clonal Expansion
cells interact with numerous DCs as they scan for cognate antigen. T-cell activation is detectable within hours of antigen exposure;
In the absence of TCR signaling, these interactions are of short however, days are required until T-cell responses can be detected
duration; however, TCR engagement elicits T cell–DC interactions from a naïve host. This delay partially reflects the need for T-cell
7
that may last up to 20 hours. Long-term interactions are required expansion to produce a detectable and effective response. The
for full activation. In the presence of incomplete stimulation, initial frequency of T cells for a single epitope is estimated at
that is, if costimulation is lacking, T cells are prevented from approximately one per million total CD4 T cells or approximately
5
11
participating in inflammation and may become unresponsive 1 × 10 cells per human. Following antigen exposure, cellular
to further stimulation (anergic) or undergo apoptosis. This is a proliferation is initially slow, taking 2 days for the first divisions
regulatory mechanism used to prevent inappropriate T-cell to occur in the lymph nodes and the spleen. Cell numbers increase
activation and helps maintain self-tolerance in T cells. rapidly between days 2 and 7 after antigen exposure, when many
T-cell activation depends on the maturation state of the DC. T cells have undergone as many as eight rounds of division. This
Immature DCs are incapable of stimulating functional T-cell process is known as clonal expansion (see Fig. 16.1). For instance,
responses and may instead induce unresponsiveness, whereas a single precursor T cell following eight rounds of division can