Page 305 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 305
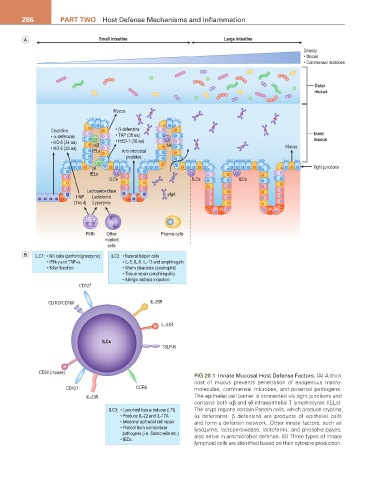
286 ParT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
A Small intestine Large intestine
Density
• Mucus
• Commensal microbes
Outer
mucus
Mucus
Cryptdins: • β-defensins Inner
• α-defensins • TAP (38 aa)
• HD-5 (34 aa) αβ • HBD-1 (36 aa) NK mucus
• HD-6 (35 aa) IELs Anti-microbial Mucus
peptides
γδ Tight junctions
IELs
ILCs ILCs ILCs
Lactoperoxidase
HNP Lactoferrin plgA
(1 to 4) Lysozyme
PMN Other Plasma cells
myeloid
cells
B ILC1: • NK cells (perforin/granzyme) ILC2: • Natural helper cells
• IFN-γ and TNF-α • IL-5, IL-9, IL-13 and amphiregulin
• Killer function • Worm clearance (eosinophil)
• Tissue repair (amphiregulin)
• Allergic asthma induction
CD127
CD103/CD160 IL-25R
IL-33R
ILCs
TSLP-R
CD90 (mouse)
FIG 20.1 Innate Mucosal Host Defense Factors. (A) A thick
coat of mucus prevents penetration of exogenous macro-
CD127 CCR6 molecules, commensal microbes, and potential pathogens.
IL-23R The epithelial cell barrier is connected via tight junctions and
contains both αβ and γδ intraepithelial T lymphocytes (IELs).
ILC3: • Lymphoid tissue inducer (LTi) The crypt regions contain Paneth cells, which produce cryptins
• Produce IL-22 and IL-17A (α defensins). β defensins are products of epithelial cells
• Intestinal epithelial cell repair and form a defensin network. Other innate factors, such as
• Protect from extracellular lysozyme, lactoperoxidase, lactoferrin, and phospholipases,
pathogens (i.e. Salmonella etc.) also serve in antimicrobial defense. (B) Three types of innate
• IBDs
lymphoid cells are identified based on their cytokine production.