Page 340 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 340
320 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
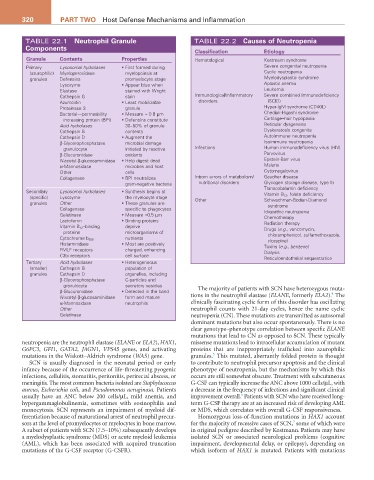
TABLE 22.1 Neutrophil Granule TABLE 22.2 Causes of Neutropenia
Components Classification Etiology
Granule Contents Properties Hematological Kostmann syndrome
Primary Lysosomal hydrolases • First formed during Severe congenital neutropenia
(azurophilic) Myeloperoxidase myelopoiesis at Cyclic neutropenia
granules Defensins promyelocyte stage Myelodysplastic syndrome
Lysozyme • Appear blue when Aplastic anemia
Elastase stained with Wright Leukemia
Cathepsin G stain Immunological/inflammatory Severe combined immunodeficiency
Azurocidin • Least mobilizable disorders (SCID)
Proteinase 3 granule Hyper-IgM syndrome (CD40L)
Bacterial—permeability • Measure ≈ 0.8 µm Chediak-Higashi syndrome
increasing protein (BPI) • Defensins constitute Cartilage–hair hypoplasia
Acid hydrolases 30–50% of granule Reticular dysgenesis
Cathepsin B contents Dyskeratosis congenita
Cathepsin D • Augment the Autoimmune neutropenia
β-Glycerophosphatase microbial damage Isoimmune neutropenia
granulocyte initiated by reactive Infections Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
β-Glucuronidase oxidants Parvovirus
N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase • Help digest dead Epstein-Barr virus
α-Mannosidase microbes and host Malaria
Other cells Cytomegalovirus
Collagenase • BPI neutralizes Inborn errors of metabolism/ Gaucher disease
gram-negative bacteria nutritional disorders Glycogen storage disease, type lb
Transcobalamin deficiency
Secondary Lysosomal hydrolases • Synthesis begins at Vitamin B 12 , folate deficiency
(specific) Lysozyme the myelocyte stage Other Schwachman-Bodian-Diamond
granules Other • These granules are syndrome
Collagenase specific to phagocytes Idiopathic neutropenia
Gelatinase • Measure ≈0.5 µm Chemotherapy
Lactoferrin • Binding proteins Radiation therapy
Vitamin B 12 –binding deprive Drugs (e.g., vancomycin,
proteins microorganisms of chloramphenicol, sulfamethoxazole,
nutrients
Cytochrome b 558 clozapine)
Histaminidase • Most are positively Toxins (e.g., benzene)
FMLF receptors charged, enhancing Dialysis
C3bi receptors cell surface Reticuloendothelial sequestration
Tertiary Acid hydrolases • Heterogeneous
(smaller) Cathepsin B population of
granules Cathepsin D organelles, including
β-Glycerophosphatase C-particles and
granulocyte secretory vesicles
β-Glucuronidase • Detected in the band The majority of patients with SCN have heterozygous muta-
4
N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase form and mature tions in the neutrophil elastase (ELANE, formerly ELA2). The
α-Mannosidase neutrophils clinically fascinating cyclic form of this disorder has oscillating
Other neutrophil counts with 21-day cycles, hence the name cyclic
Gelatinase neutropenia (CN). These mutations are transmitted as autosomal
dominant mutations but also occur spontaneously. There is no
clear genotype–phenotype correlation between specific ELANE
mutations that lead to CN as opposed to SCN. These typically
neutropenia are the neutrophil elastase (ELANE or ELA2), HAX1, missense mutations lead to intracellular accumulation of mutant
G6PC3, GFI1, GATA2, JAGN1, VPS45 genes, and activating proteins that are inappropriately trafficked into azurophilic
5
mutations in the Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (WAS) gene. granules. This mutated, aberrantly folded protein is thought
SCN is usually diagnosed in the neonatal period or early to contribute to neutrophil precursor apoptosis and the clinical
infancy because of the occurrence of life-threatening pyogenic phenotype of neutropenia, but the mechanisms by which this
infections, cellulitis, stomatitis, peritonitis, perirectal abscess, or occurs are still somewhat obscure. Treatment with subcutaneous
meningitis. The most common bacteria isolated are Staphylococcus G-CSF can typically increase the ANC above 1000 cells/µL, with
aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Patients a decrease in the frequency of infections and significant clinical
6
usually have an ANC below 200 cells/µL, mild anemia, and improvement overall. Patients with SCN who have received long-
hypergammaglobulinemia, sometimes with eosinophilia and term G-CSF therapy are at an increased risk of developing AML
monocytosis. SCN represents an impairment of myeloid dif- or MDS, which correlates with overall G-CSF responsiveness.
ferentiation because of maturational arrest of neutrophil precur- Homozygous loss-of-function mutations in HAX1 account
7
sors at the level of promyelocytes or myelocytes in bone marrow. for the majority of recessive cases of SCN, some of which were
A subset of patients with SCN (7.5–10%) subsequently develops in original pedigree described by Kostmann. Patients may have
a myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) or acute myeloid leukemia isolated SCN or associated neurological problems (cognitive
(AML), which has been associated with acquired truncation impairment, developmental delay, or epilepsy), depending on
mutations of the G-CSF receptor (G-CSFR). which isoform of HAX1 is mutated. Patients with mutations