Page 344 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 344
324 Part two Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
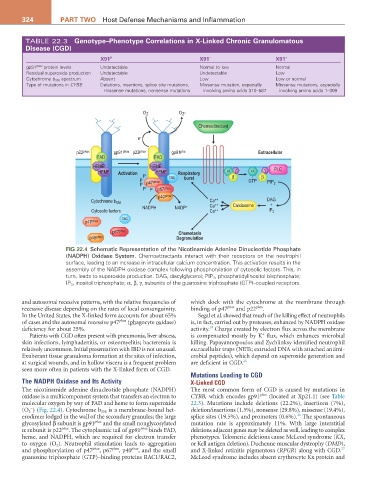
TABLE 22.3 Genotype–Phenotype Correlations in X-Linked Chronic Granulomatous
Disease (CGD)
X91 0 X91 − X91 +
gp91 phox protein levels Undetectable Normal to low Normal
Residual superoxide production Undetectable Undetectable Low
Cytochrome b 558 spectrum Absent Low Low or normal
Type of mutations in CYBB Deletions, insertions, splice site mutations, Missense mutation, especially Missense mutations, especially
missense mutations, nonsense mutations involving amino acids 310–587 involving amino acids 1–309
O 2 O -
2
Chemoattractant
e -
p22 phox gp91 phox p22 phox gp91 pho Extracellular
FAD FAD
HEME HEME PLC
HEME Activation P HEME Respiratory α γ α γ
P rac burst β GTP β
P p47 phox PIP 2
P P p67 phox
p40 phox
Cytochrome b 558 Ca ++ DAG
NADPH NADP + Ca ++ Calciosome +
Cytosolic factors Ca ++ IP 3
rac
p47 phox
p67 phox Chemotaxis
p40 phox Degranulation
FIG 22.4 Schematic Representation of the Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
(NADPH) Oxidase System. Chemoattractants interact with their receptors on the neutrophil
surface, leading to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration. This activation results in the
assembly of the NADPH oxidase complex following phosphorylation of cytosolic factors. This, in
turn, leads to superoxide production. DAG, diacylglycerol; PIP 2 , phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate;
IP 3 , inositol triphosphate; α, β, γ, subunits of the guanosine triphosphate (GTP)–coupled receptors.
and autosomal recessive patterns, with the relative frequencies of which dock with the cytochrome at the membrane through
recessive disease depending on the rates of local consanguinity. binding of p47 phox and p22 phox .
In the United States, the X-linked form accounts for about 65% Segal et al. showed that much of the killing effect of neutrophils
of cases and the autosomal recessive p47 phox (phagocyte oxidase) is, in fact, carried out by proteases, enhanced by NADPH oxidase
24
deficiency for about 25%. activity. Charge created by electron flux across the membrane
+
Patients with CGD often present with pneumonia, liver abscess, is compensated mostly by K flux, which enhances microbial
skin infections, lymphadenitis, or osteomyelitis; bacteremia is killing. Papayannopoulos and Zychlinksy identified neutrophil
relatively uncommon. Initial presentation with IBD is not unusual. extracellular traps (NETs; extruded DNA with attached antimi-
Exuberant tissue granuloma formation at the sites of infection, crobial peptides), which depend on superoxide generation and
at surgical wounds, and in hollow viscera is a frequent problem are deficient in CGD. 25
seen more often in patients with the X-linked form of CGD.
Mutations Leading to CGD
The NADPH Oxidase and Its Activity X-Linked CGD
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) The most common form of CGD is caused by mutations in
oxidase is a multicomponent system that transfers an electron to CYBB, which encodes gp91 phox (located at Xp21.1) (see Table
molecular oxygen by way of FAD and heme to form superoxide 22.3). Mutations include deletions (22.2%), insertions (7%),
−
(O 2 ) (Fig. 22.4). Cytochrome b 558 is a membrane-bound het- deletion/insertions (1.5%), nonsense (29.8%), missense (19.4%),
26
erodimer lodged in the wall of the secondary granules; the large splice sites (19.5%), and promoters (0.6%). The spontaneous
glycosylated β subunit is gp91 phox and the small nonglycosylated mutation rate is approximately 11%. With large interstitial
α subunit is p22 phox . The cytoplasmic tail of gp91 phox binds FAD, deletions adjacent genes may be deleted as well, leading to complex
heme, and NADPH, which are required for electron transfer phenotypes. Telomeric deletions cause McLeod syndrome (KX,
to oxygen (O 2). Neutrophil stimulation leads to aggregation or Kell antigen deletion), Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD),
27
and phosphorylation of p47 phox , p67 phox , p40 phox , and the small and X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (RPGR) along with CGD.
guanosine triphosphate (GTP)–binding proteins RAC1/RAC2, McLeod syndrome includes absent erythrocyte Kx protein and