Page 356 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 356
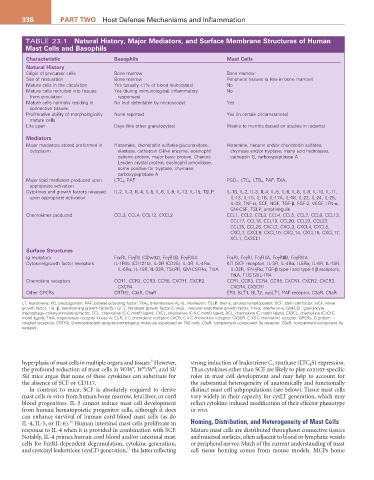
336 ParT TwO Host Defense Mechanisms and Inflammation
TABLE 23.1 Natural History, Major Mediators, and Surface Membrane Structures of Human
Mast Cells and Basophils
Characteristic Basophils Mast Cells
Natural History
Origin of precursor cells Bone marrow Bone marrow
Site of maturation Bone marrow Peripheral tissues (a few in bone marrow)
Mature cells in the circulation Yes (usually <1% of blood leukocytes) No
Mature cells recruited into tissues Yes (during immunological, inflammatory No
from circulation responses)
Mature cells normally residing in No (not detectable by microscopy) Yes
connective tissues
Proliferative ability of morphologically None reported Yes (in certain circumstances)
mature cells
Life span Days (like other granulocytes) Weeks to months (based on studies in rodents)
Mediators
Major mediators stored preformed in Histamine, chondroitin sulfates-glucuronidase, Histamine, heparin and/or chondroitin sulfates,
cytoplasm elastase, cathepsin G-like enzyme, eosinophil chymase and/or tryptase, many acid hydrolases,
cationic protein, major basic protein, Charcot- cathepsin G, carboxypeptidase A
Leyden crystal protein, eosinophil peroxidase,
some positive for tryptase, chymase,
carboxypeptidase A
Major lipid mediators produced upon LTC 4 , PAF PGD 2 , LTC 4 , LTB 4 , PAF, TXA 2
appropriate activation
Cytokines and growth factors released IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-9, IL-13, IL-15, TSLP IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8, IL-9, IL-10, IL-11,
upon appropriate activation IL-13, IL-15, IL-16, IL-17A, IL-18, IL-22, IL-24, IL-25,
IL-33, TNF-α, SCF, NGF, TGF-β, FGF-2, VEGF, IFN-α,
GM-CSF, TSLP, amphiregulin
Chemokines produced CCL3, CCL4, CCL12, CXCL2 CCL1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL13,
CCL17, CCL18, CCL19, CCL20, CCL22, CCL23,
CCL25, CCL28, CXCL2, CXCL3, CXCL4, CXCL5,
CXCL7, CXCL8, CXCL10, CXCL14, CXCL16, CXCL17,
XCL1, CX3CL1
Surface Structures
Ig receptors FcεRI, FcγRII (CDw32), FcγRIIB, FcγRIIIA FcεRI, FcγRI, FcγRIIA, FcγRIIB, FcγRIIIA
Cytokine/growth factor receptors IL-1RIIb (CD121b), IL-2R (CD25), IL-3R, IL-4Rα, KIT (SCF receptor), IL-3R, IL-4Rα, IL5Rα, IL-6R, IL-18R,
IL-5Rα, IL-18R, IL-33R, TSLPR, GM-CSFRα, TrkA IL-33R, IFN-γRα, TGF-β type-I and type-II β receptors,
TrkA, T1/ST2/IL-1R4
Chemokine receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, CCR5, CXCR1, CXCR2, CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CXCR1, CXCR2, CXCR3,
CXCR4 CXCR4, CX3CR1
Other GPCRs CRTH2, C3aR, C5aR EP3, BLT1, BLT2, cysLT1, PAF receptor, C3aR, C5aR
LT, leukotriene; PG, prostaglandin; PAF, platelet-activating factor; TXA 2, thromboxane A 2; IL, interleukin; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; SCF, stem cell factor; NGF, nerve
growth factor; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; FGF-2, fibroblast growth factor-2; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IFN-α, interferon-α; GM-CSF, granulocyte
macrophage–colony-stimulating factor; CCL, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; XCL, chemokine (C motif) ligand; CX3CL, chemokine (C-X3-C
motif) ligand; TrkA, tropomyosin receptor kinase A; CCR, C-C chemokine receptor; CXCR, C-X-C chemokine receptor; CX3CR, C-X3-C chemokine receptor; GPCRs, G protein–
coupled receptors; CRTH2, chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells; C3aR, complement component 3a receptor; C5aR, complement component 5a
receptor.
9
hyperplasia of mast cells in multiple organs and tissues. However, strong induction of leukotriene C 4 synthase (LTC 4 S) expression.
v
sh
sh
the profound reduction of mast cells in W/W , W /W , and Sl/ Thus cytokines other than SCF are likely to play context-specific
Sld mice argue that none of these cytokines can substitute for roles in mast cell development and may help to account for
the absence of SCF or CD117. the substantial heterogeneity of anatomically and functionally
In contrast to mice, SCF is absolutely required to derive distinct mast cell subpopulations (see below). Tissue mast cells
mast cells in vitro from human bone marrow, fetal liver, or cord vary widely in their capacity for cysLT generation, which may
blood progenitors. IL-3 cannot induce mast cell development reflect cytokine-induced modification of their effector phenotype
from human hematopoietic progenitor cells, although it does in vivo.
can enhance survival of human cord blood mast cells (as do
10
IL-4, IL-5, or IL-6). Human intestinal mast cells proliferate in Homing, Distribution, and Heterogeneity of Mast Cells
response to IL-4 when it is provided in combination with SCF. Mature mast cells are distributed throughout connective tissues
Notably, IL-4 primes human cord blood and/or intestinal mast and mucosal surfaces, often adjacent to blood or lymphatic vessels
cells for FcεRI-dependent degranulation, cytokine generation, or peripheral nerves. Much of the current understanding of mast
11
and cysteinyl leukotriene (cysLT) generation, the latter reflecting cell tissue homing comes from mouse models. MCPs home