Page 427 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 427
CHaPtEr 28 Host Defenses to Spirochetes 407
Professional antigen-presenting cell Little is known about the molecular events or receptors that
mediate B. burgdorferi phagocytosis despite the importance of
Phagocytic receptor Endosomal PRRs this cardinal mechanism of pathogen clearance. MyD88-mediated
signals substantially mediate the phagocytosis of B. burgdorferi.
IL-1β IFNγ However, MyD88-mediated phagocytosis occurs independently
IL-12
TLR 1/2 IL-18 of any known B. burgdorferi-recognizing TLRs. The mechanism
MyD88 of MyD88-mediated phagocytic uptake is therefore unclear.
Furthermore, the analysis of MyD88-deficient macrophages shows
CD4 + that although reduced, phagocytosis is not absent in these cells.
TCR T cell Therefore the uptake of B. burgdorferi by phagocytic cells seems
Signaling to be mediated by more than one receptor with MyD88-dependent
and MyD88-independent components. Complement receptor 3
(CR3) is a β 2 integrin, which, in cooperation with the GPI-
anchored CD14, acts as a phagocytic receptor for B. burgdorferi
Type I IFN independently of TLR or MyD88-induced signals. Phagocytosis
10
Surface PRRs (i.e., integins) plays a major role in the pathogenesis of Lyme disease, not only
TNF
through the control of bacterial numbers but also through
Endothelial cell modulation of the potency and quality of proinflammatory
cytokine induction. Indeed, as opposed to MyD88-mediated
phagocytosis, which is proinflammatory, the internalization of
B. burgdorferi by CR3 tempers the inflammatory response of
macrophages. Therefore the presence of alternative phagocytic
IL-8, MCP-1, KC mechanisms has nonredundant physiological consequences during
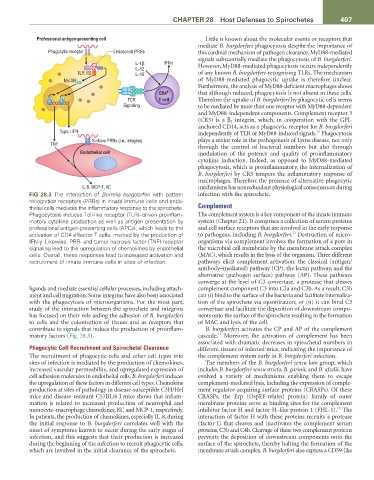
FIG 28.3 The interaction of Borrelia burgdorferi with pattern infection with the spirochete.
recognition receptors (PRRs) in innate immune cells and endo-
thelial cells mediates the inflammatory response to the spirochete. Complement
Phagocytosis induces Toll-like receptor (TLR)–driven proinflam- The complement system is a key component of the innate immune
matory cytokine production as well as antigen presentation by system (Chapter 21). It comprises a collection of serum proteins
professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which leads to the and cell surface receptors that are involved in the early response
11
activation of CD4 effector T cells, marked by the production of to pathogens, including B. burgdorferi. Destruction of micro-
IFN-γ. Likewise, PRR- and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor organisms via complement involves the formation of a pore in
signaling lead to the upregulation of chemokines by endothelial the microbial cell membrane by the membrane attack complex
cells. Overall, these responses lead to increased activation and (MAC), which results in the lysis of the organism. Three different
recruitment of innate immune cells in sites of infection. pathways elicit complement activation: the classical (antigen/
antibody–mediated) pathway (CP), the lectin pathway, and the
alternative (pathogen surface) pathway (AP). These pathways
converge at the level of C3 convertase, a protease that cleaves
ligands and mediate essential cellular processes, including attach- complement component C3 into C3a and C3b. As a result, C3b
ment and cell migration. Some integrins have also been associated can (i) bind to the surface of the bacteria and facilitate internaliza-
with the phagocytosis of microorganisms. For the most part, tion of the spirochete via opsonization; or (ii) it can bind C3
study of the interaction between the spirochete and integrins convertase and facilitate the deposition of downstream compo-
has focused on their role aiding the adhesion of B. burgdorferi nents onto the surface of the spirochete resulting in the formation
to cells and the colonization of tissues and as receptors that of MAC and lysis of the cell.
contribute to signals that induce the production of proinflam- B. burgdorferi activates the CP and AP of the complement
12
matory factors (Fig. 28.3). cascade. Moreover, the activation of complement has been
associated with dramatic decreases in spirochetal numbers in
Phagocytic Cell Recruitment and Spirochetal Clearance different tissues of infected mice, indicating the importance of
The recruitment of phagocytic cells and other cell types into the complement system early in B. burgdorferi infection.
sites of infection is mediated by the production of chemokines, The members of the B. burgdorferi sensu lato group, which
increased vascular permeability, and upregulated expression of includes B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, B. garinii, and B. afzelii, have
cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells. B. burgdorferi induces evolved a variety of mechanisms enabling them to escape
the upregulation of these factors in different cell types. Chemokine complement-mediated lysis, including the expression of comple-
production at sites of pathology in disease-susceptible C3H/HeJ ment regulator-acquiring surface proteins (CRASPs). Of these
mice and disease-resistant C57BL/6 J mice shows that inflam- CRASPs, the Erp (OspEF-related protein) family of outer
mation is related to increased production of neutrophil and membrane proteins serve as binding sites for the complement
13
monocyte–macrophage chemokines, KC and MCP-1, respectively. inhibitor factor H and factor H–like protein 1 (FHL-1). The
In patients, the production of chemokines, especially IL-8, during interaction of factor H with these proteins recruits a protease
the initial response to B. burgdorferi correlates well with the (factor I) that cleaves and inactivates the complement serum
onset of symptoms known to occur during the early stages of proteins, C3b and C4b. Cleavage of these two complement proteins
infection, and this suggests that their production is increased prevents the deposition of downstream components onto the
during the beginning of the infection to recruit phagocytic cells, surface of the spirochete, thereby halting the formation of the
which are involved in the initial clearance of the spirochete. membrane attack complex. B. burgdorferi also express a CD59-like