Page 437 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 437
ChaPTEr 29 Host Defenses to Fungal Pathogens 417
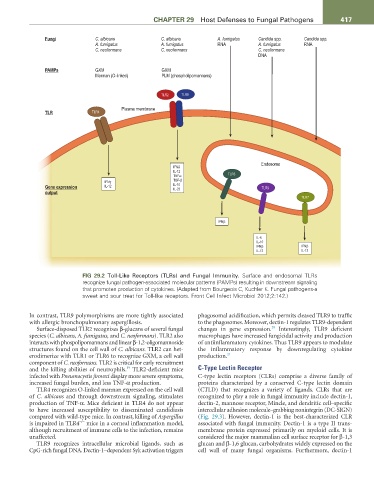
Fungi C. albicans C. albicans A. fumigatus Candida spp. Candida spp.
A. fumigatus A. fumigatus RNA A. fumigatus RNA
C. neoformans C. neoformans C. neoformans
DNA
PAMPs GXM GXM
Mannan (O-linked) PLM (phospholipomannans)
TLR2 TLR6
Plasma membrane
TLR TLR4
Endosome
IFNδ
IL-12
TNFα TLR3
IFNγ TGF-β
Gene expression IL-12 IL-10 TLR9
IL-23
output
TLR7
IFNβ
IL-6
IL-10
IFNβ IFNβ
IL-12 IL-12
FIG 29.2 Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and Fungal Immunity. Surface and endosomal TLRs
recognize fungal pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) resulting in downstream signaling
that promotes production of cytokines. (Adapted from Bourgeois C, Kuchler K. Fungal pathogens-a
sweet and sour treat for Toll-like receptors. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2012;2:142.)
In contrast, TLR9 polymorphisms are more tightly associated phagosomal acidification, which permits cleaved TLR9 to traffic
with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. to the phagosomes. Moreover, dectin-1 regulates TLR9-dependent
20
Surface-disposed TLR2 recognizes β-glucans of several fungal changes in gene expression. Interestingly, TLR9 deficient
species (C. albicans, A. fumigatus, and C. neoformans). TLR2 also macrophages have increased fungicidal activity and production
interacts with phospolipomannans and linear β-1,2-oligomannoside of antiinflammatory cytokines. Thus TLR9 appears to modulate
structures found on the cell wall of C. albicans. TLR2 can het- the inflammatory response by downregulating cytokine
erodimerize with TLR1 or TLR6 to recognize GXM, a cell wall production. 21
component of C. neoformans. TLR2 is critical for early recruitment
19
and the killing abilities of neutrophils. TLR2-deficient mice C-Type Lectin Receptor
infected with Pneumocystis jiroveci display more severe symptoms, C-type lectin receptors (CLRs) comprise a diverse family of
increased fungal burden, and less TNF-α production. proteins characterized by a conserved C-type lectin domain
TLR4 recognizes O-linked mannan expressed on the cell wall (CTLD) that recognizes a variety of ligands. CLRs that are
of C. albicans and through downstream signaling, stimulates recognized to play a role in fungal immunity include dectin-1,
production of TNF-α. Mice deficient in TLR4 do not appear dectin-2, mannose receptor, Mincle, and dendritic cell–specific
to have increased susceptibility to disseminated candidiasis intercellular adhesion molecule–grabbing nonintegrin (DC-SIGN)
compared with wild-type mice. In contrast, killing of Aspergillus (Fig. 29.3). However, dectin-1 is the best-characterized CLR
−/−
is impaired in TLR4 mice in a corneal inflammation model, associated with fungal immunity. Dectin-1 is a type II trans-
although recruitment of immune cells to the infection, remains membrane protein expressed primarily on myeloid cells. It is
unaffected. considered the major mammalian cell surface receptor for β-1,3
TLR9 recognizes intracellular microbial ligands, such as glucan and β-1,6 glucan, carbohydrates widely expressed on the
CpG-rich fungal DNA. Dectin-1–dependent Syk activation triggers cell wall of many fungal organisms. Furthermore, dectin-1