Page 485 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 485
466 ParT FOUr Immunological Deficiencies
and other cytokines, caused by mutations in the X-linked gene are highly prone to developing autoimmunity, while others such
IL2RG have SCID in which T and NK cells are absent but as C57BL/6 (B6) are resistant. 18
nonfunctional B cells are present in normal to high numbers,
− +
−
T B NK SCID. Mice with the orthologous gene Il2rg mutated FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS
or removed can make T cells but have no B cells, which gives
−
+ −
them a T B NK phenotype. 17 Immediately after the Human Genome Project was declared to
Genes other than IL2RG alone must be responsible for this have been completed in 2003, an important follow-on project
difference between species. Such genes, known as modifiers, have was launched to identify the functional segments of DNA,
not yet been identified. Notably, different strains of mice can particularly portions in the 98–99% lying outside of the coding
also have important phenotypic differences in the presence of exons of genes, for which there was no simple sequence code
a single gene mutation under study; some strains, for example, that could be understood the way the triplet codon code can be
nonobese diabetic (NOD) and Murphy Roths Large (MRL) mice read. This project, termed ENCODE (for “encyclopedia of DNA
elements”), began as a pilot project to identify functional elements
in 1% of the genome, but it was quickly expanded to include
100% the entire human genome as well as the genomes of model
90% 19
80% organisms. Before ENCODE, estimates were that 3–8% of the
70% human genome had some role in function, given that this fraction
60% of the genome appeared to be highly conserved among species
50% with only very limited variation. This estimate was clearly too
40% low, as it did not take into account rapidly evolving functional
30% elements or those restricted to particular evolutionary lineages.
20% This estimate also did not include segments of DNA that were
10% too small to show conservation with statistical significance, nor
0% did it include the functional elements in repetitive DNA that
Chimp Dog Mouse Rat Chicken Pufferfish Zebrafish Fruitfly Mosquito C. elegans Rice Amoebae E. coli are not reliably scored as being evolutionarily conserved.
Bee
C. cerevisiae
Mustard weed
Since the same genome is present but functions differently
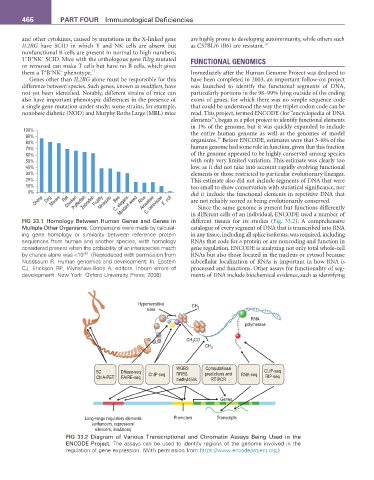
FIG 33.1 Homology Between Human Genes and Genes in in different cells of an individual, ENCODE used a number of
different tissues for its studies (Fig. 33.2). A comprehensive
Multiple Other Organisms. Comparisons were made by calculat- catalogue of every segment of DNA that is transcribed into RNA
ing gene homology or similarity between reference protein in any tissue, including all splice isoforms, was required, including
sequences from human and another species, with homology RNAs that code for a protein or are noncoding and function in
considered present when the probability of an interspecies match gene regulation. ENCODE is analyzing not only total whole-cell
-30
by chance alone was <10 . (Reproduced with permission from RNAs but also those located in the nucleus or cytosol because
Nussbaum R. Human genomics and development. In: Epstein subcellular localization of RNAs is important in how RNA is
CJ, Erickson RP, Wynshaw-Boris A, editors. Inborn errors of processed and functions. Other assays for functionality of seg-
development. New York: Oxford University Press; 2008). ments of DNA include biochemical evidence, such as identifying
Hypersensitive CH
sites 3
RNA
polymerase
CH CO
3
CH 3
WGBS Computational
5C DNase-seq ChIP-seq RRBS predictions and RNA-seq CLIP-seq
ChIA-PET FAIRE-seq methyl450k RT-PCR RIP-seq
Genes
Long-range regulatory elements Promoters Transcripts
(enhancers, repressors/
silencers, insulators)
FIG 33.2 Diagram of Various Transcriptional and Chromatin Assays Being Used in the
ENCODE Project. The assays can be used to identify regions of the genome involved in the
regulation of gene expression. (With permission from https://www.encodeproject.org.)