Page 483 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 483
464 ParT FOUr Immunological Deficiencies
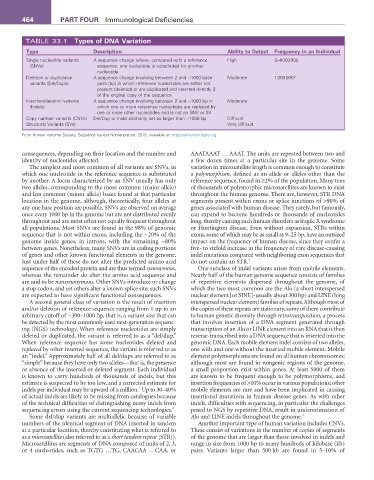
TABLE 33.1 Types of DNa Variation
Type Description ability to Detect Frequency in an Individual
Single nucleotide variants A sequence change where, compared with a reference High 3–4 000 000
(SNVs) sequence, one nucleotide is substituted for another
nucleotide
Deletion or duplication A sequence change involving between 2 and ~1000 base Moderate 1 000 000?
variants (Del/Dups) pairs (bp) in which reference nucleotides are either not
present (deleted) or are duplicated and inserted directly 3’
of the original copy of the sequence
Insertion/deletion variants A sequence change involving between 2 and ~1000 bp in Moderate
(Indels) which one or more reference nucleotides are replaced by
one or more other nucleotides and is not an SNV or SV
Copy number variants (CNVs) Del/Dup or Indel arbitrarily set as larger than ~1000 bp Difficult
Structural Variants (SVs) Very difficult
From Human Variome Society, Sequence Variant Nomenclature. 2016. Available at: http://varnomen.hgvs.org.
consequences, depending on their location and the number and AAATAAAT … AAAT. The units are repeated between two and
identity of nucleotides affected. a few dozen times at a particular site in the genome. Some
The simplest and most common of all variants are SNVs, in variation in microsatellite length is common enough to constitute
which one nucleotide in the reference sequence is substituted a polymorphism, defined as an allele or alleles other than the
by another. A locus characterized by an SNV usually has only reference sequence, found in ≥2% of the population. Many tens
two alleles, corresponding to the more common (major allele) of thousands of polymorphic microsatellites are known to exist
and less common (minor allele) bases found at that particular throughout the human genome. There are, however, STR DNA
location in the genome, although, theoretically, four alleles at segments present within exons or splice junctions of >90% of
any one base position are possible. SNVs are observed on average genes associated with human disease. They rarely, but famously,
once every 1000 bp in the genome but are not distributed evenly can expand to become hundreds or thousands of nucleotides
throughout and are most often not equally frequent throughout long, thereby causing such human disorders as fragile X syndrome
all populations. Most SNVs are found in the 98% of genomic or Huntington disease. Even without expansion, STRs within
sequence that is not within exons, including the ~20% of the exons, some of which may be as small as 9–25 bp, have an outsized
genome inside genes, in introns, with the remaining ~80% impact on the frequency of human disease, since they confer a
between genes. Nonetheless, many SNVs are in coding portions five- to sixfold increase in the frequency of rare disease-causing
of genes and other known functional elements in the genome. indel mutations compared with neighboring exon sequences that
Just under half of these do not alter the predicted amino acid do not contain an STR. 5
sequence of the encoded protein and are thus termed synonymous, One subclass of indel variants arises from mobile elements.
whereas the remainder do alter the amino acid sequence and Nearly half of the human genome sequence consists of families
are said to be nonsynonymous. Other SNVs introduce or change of repetitive elements dispersed throughout the genome, of
a stop codon, and yet others alter a known splice site; such SNVs which the two most common are the Alu (a short interspersed
are expected to have significant functional consequences. nuclear element [or SINE]-usually about 300 bp) and LINE (long
A second general class of variation is the result of insertion interspersed nuclear element) families of repeats. Although most of
and/or deletion of reference sequence ranging from 1 up to an the copies of these repeats are stationary, some of them contribute
arbitrary cutoff of ~300–1000 bp, that is, a variant size that can to human genetic diversity through retrotransposition, a process
be detected by the most commonly used next-generation sequenc- that involves insertion of a DNA segment generated through
ing (NGS) technology. When reference nucleotides are simply transcription of an Alu or LINE element into an RNA that is then
deleted or duplicated, the variant is referred to as a “del/dup.” reverse-transcribed into a DNA sequence that is inserted into the
When reference sequence has some nucleotides deleted and genomic DNA. Each mobile element indel consists of two alleles,
replaced by other inserted sequence, the variant is referred to as one with and one without the inserted mobile element. Mobile
an “indel.” Approximately half of all del/dups are referred to as element polymorphisms are found on all human chromosomes;
“simple” because they have only two alleles—that is, the presence although most are found in nongenic regions of the genome,
or absence of the inserted or deleted segment. Each individual a small proportion exist within genes. At least 5000 of them
is known to carry hundreds of thousands of indels, but this are known to be frequent enough to be polymorphisms, and
estimate is suspected to be too low, and a corrected estimate for insertion frequencies of >10% occur in various populations; other
3
indels per individual may be upward of a million. Up to 30–40% mobile elements are rare and have been implicated in causing
of actual indels are likely to be missing from catalogues because insertional mutations in human disease genes. As with other
of the technical difficulties of distinguishing many indels from indels, difficulties with sequencing, in particular the challenges
sequencing errors using the current sequencing technologies. 4 posed to NGS by repetitive DNA, result in underestimation of
Some del/dup variants are multiallelic because of variable Alu and LINE indels throughout the genome. 3
numbers of the identical segment of DNA inserted in tandem Another important type of human variation includes CNVs.
at a particular location, thereby constituting what is referred to These consist of variations in the number of copies of segments
as a microsatellite (also referred to as a short tandem repeat [STR]). of the genome that are larger than those involved in indels and
Microsatellites are segments of DNA composed of units of 2, 3, range in size from 1000 bp to many hundreds of kilobase (kb)
or 4 nucleotides, such as TGTG …TG, CAACAA …CAA, or pairs. Variants larger than 500 kb are found in 5–10% of