Page 511 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 511
CHaPTEr 35 Primary T-Cell Immunodeficiencies 491
ADA, γc, JAK3
deficiency
NK cell
DN γδ T cell
Pro/Pre-T
Thymus CD3δ, CD3ε
RAG, Artemis
deficiencies
pTα b α β ZAP 70 αβ T cell
+
deficiency CD8
DP
Stem Lymphoid DN DN CD4+
cell progenitor Pro/Pre-T Pre-T
CD8+
ADA, γc, CD45, PNP IL2Rα, CD3γ
JAK3. IL-7Rα deficiency deficiency αβ T cell
deficiencies CD4 +
HLA
Class II deficiency
B cell
ADA, RAG, Artemis
deficiency
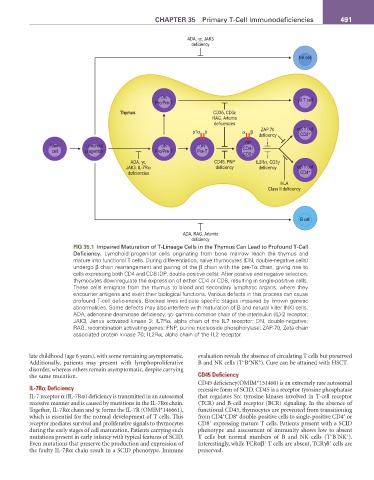
fIG 35.1 Impaired Maturation of T-Lineage Cells in the Thymus Can Lead to Profound T-Cell
Deficiency. Lymphoid progenitor cells originating from bone marrow reach the thymus and
mature into functional T cells. During differentiation, naïve thymocytes (DN, double-negative cells)
undergo β chain rearrangement and pairing of the β chain with the pre-Tα chain, giving rise to
cells expressing both CD4 and CD8 (DP, double-positive cells). After positive and negative selection,
thymocytes downregulate the expression of either CD4 or CD8, resulting in single-positive cells.
These cells emigrate from the thymus to blood and secondary lymphatic organs, where they
encounter antigens and exert their biological functions. Various defects in this process can cause
profound T-cell deficiencies. Blocked lines indicate specific stages impaired by known genetic
abnormalities. Some defects may also interfere with maturation of B and natural killer (NK) cells.
ADA, adenosine deaminase deficiency; γc- gamma common chain of the interleukin (IL)-2 receptor;
JAK3, Janus activated kinase 3; IL7Rα, alpha chain of the IL7 receptor; DN, double-negative;
RAG, recombination activating genes; PNP, purine nucleoside phosphorylase; ZAP-70, Zeta chain
associated protein kinase 70; IL2Rα, alpha chain of the IL2 receptor.
late childhood (age 6 years), with some remaining asymptomatic. evaluation reveals the absence of circulating T cells but preserved
+
− +
Additionally, patients may present with lymphoproliferative B and NK cells (T B NK ). Cure can be attained with HSCT.
disorder, whereas others remain asymptomatic, despite carrying
the same mutation. CD45 Deficiency
CD45 deficiency(OMIM*151460) is an extremely rare autosomal
IL-7Rα Deficiency recessive form of SCID. CD45 is a receptor tyrosine phosphatase
IL-7 receptor α (IL-7Rα) deficiency is transmitted in an autosomal that regulates Src tyrosine kinases involved in T-cell receptor
recessive manner and is caused by mutations in the IL-7Rα chain. (TCR) and B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling. In the absence of
Together, IL-7Rα chain and γc forms the IL-7R (OMIM*146661), functional CD45, thymocytes are prevented from transitioning
+
+
+
which is essential for the normal development of T cells. This from CD4 CD8 double-positive cells to single-positive CD4 or
+
receptor mediates survival and proliferative signals to thymocytes CD8 expressing mature T cells. Patients present with a SCID
during the early stages of cell maturation. Patients carrying such phenotype and assessment of immunity shows low to absent
− +
+
mutations present in early infancy with typical features of SCID. T cells but normal numbers of B and NK cells (T B NK ).
+
+
Even mutations that preserve the production and expression of Interestingly, while TCRαβ T cells are absent, TCRγδ cells are
the faulty IL-7Rα chain result in a SCID phenotype. Immune preserved.