Page 514 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 514
494 ParT fOur Immunological Deficiencies
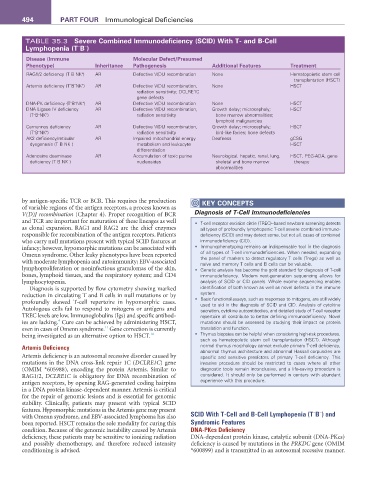
TABLE 35.3 Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) With T- and B-Cell
−
−
Lymphopenia (T B )
Disease (Immune Molecular Defect/Presumed
Phenotype) Inheritance Pathogenesis additional features Treatment
−
−
RAG1/2 deficiency (T B NK ) + AR Defective V(D)J recombination None Hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation (HSCT)
Artemis deficiency (T B NK ) AR Defective V(D)J recombination, None HSCT
+
−
−
radiation sensitivity; DCLRE1C
gene defects
+
−
DNA-PK deficiency (T B NK ) AR Defective V(D)J recombination None HSCT
−
DNA Ligase IV deficiency AR Defective V(D)J recombination, Growth delay; microcephaly; HSCT
(T B NK ) radiation sensitivity bone marrow abnormalities;
−
+
−
lymphoid malignancies
Cernunnos deficiency AR Defective V(D)J recombination, Growth delay; microcephaly; HSCT
−
+
−
(T B NK ) radiation sensitivity bird-like facies; bone defects
AK2 deficiency/reticular AR Impaired mitochondrial energy Deafness gCSG
−
−
−
dysgenesis (T B NK ) metabolism and leukocyte HSCT
differentiation
Adenosine deaminase AR Accumulation of toxic purine Neurological, hepatic, renal, lung, HSCT, PEG-ADA, gene
deficiency (T B NK ) nucleosides skeletal and bone marrow therapy
−
−
−
abnormalities
by antigen-specific TCR or BCR. This requires the production KEY CONCEPTS
of variable regions of the antigen receptors, a process known as
V(D)J recombination (Chapter 4). Proper recognition of BCR Diagnosis of T-Cell Immunodeficiencies
and TCR are important for maturation of these lineages as well • T-cell receptor excision circle (TREC)–based newborn screening detects
as clonal expansion. RAG1 and RAG2 are the chief enzymes all types of profoundly lymphopenic T-cell severe combined immuno-
responsible for recombination of the antigen receptors. Patients deficiency (SCID) and may detect some, but not all, cases of combined
who carry null mutations present with typical SCID features at immunodeficiency (CID).
infancy; however, hypomorphic mutations can be associated with • Immunophenotyping remains an indispensable tool in the diagnosis
Omenn syndrome. Other leaky phenotypes have been reported of all types of T-cell immunodeficiencies. When needed, expanding
with moderate lymphopenia and autoimmunity; EBV-associated the panel of markers to detect regulatory T cells (Tregs) as well as
naïve and memory T cells and B cells can be valuable.
lymphoproliferation or noninfectious granulomas of the skin, • Genetic analysis has become the gold standard for diagnosis of T-cell
bones, lymphoid tissues, and the respiratory system; and CD4 immunodeficiency. Modern next-generation sequencing allows for
lymphocytopenia. analysis of SCID or CID panels. Whole exome sequencing enables
Diagnosis is supported by flow cytometry showing marked identification of both known as well as novel defects in the immune
reduction in circulating T and B cells in null mutations or by system.
profoundly skewed T-cell repertoire in hypomorphic cases. • Basic functional assays, such as responses to mitogens, are still widely
used to aid in the diagnosis of SCID and CID. Analysis of cytokine
Autologous cells fail to respond to mitogens or antigens and secretion, cytokine autoantibodies, and detailed study of T-cell receptor
TREC levels are low. Immunoglobulins (Igs) and specific antibod- repertoire all contribute to better defining immunodeficiency. Novel
4
ies are lacking. Cure can be achieved by administering HSCT, mutations should be assessed by studying their impact on protein
11
even in cases of Omenn syndrome. Gene correction is currently translation and function.
being investigated as an alternative option to HSCT. 14 • Thymus biopsies can be helpful when considering high-risk procedures,
such as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Although
Artemis Deficiency normal thymus morphology cannot exclude primary T-cell deficiency,
abnormal thymus architecture and abnormal Hassall corpuscles are
Artemis deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by specific and sensitive predictors of primary T-cell deficiency. This
mutations in the DNA cross-link repair 1C (DCLRE1C) gene invasive procedure should be restricted to cases where all other
(OMIM *605988), encoding the protein Artemis. Similar to diagnostic tools remain inconclusive, and a life-saving procedure is
RAG1/2, DCLRE1C is obligatory for DNA recombination of considered. It should only be performed in centers with abundant
antigen receptors, by opening RAG-generated coding hairpins experience with this procedure.
in a DNA protein kinase-dependent manner. Artemis is critical
for the repair of genomic lesions and is essential for genomic
stability. Clinically, patients may present with typical SCID
features. Hypomorphic mutations in the Artemis gene may present − −
with Omenn syndrome, and EBV-associated lymphoma has also SCID With T-Cell and B-Cell Lymphopenia (T B ) and
been reported. HSCT remains the sole modality for curing this Syndromic Features
condition. Because of the genomic instability caused by Artemis DNA-PKcs Deficiency
deficiency, these patients may be sensitive to ionizing radiation DNA-dependent protein kinase, catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs)
and possibly chemotherapy, and therefore reduced intensity deficiency is caused by mutations in the PRKDC gene (OMIM
conditioning is advised. *600899) and is transmitted in an autosomal recessive manner.