Page 513 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 513
CHaPTEr 35 Primary T-Cell Immunodeficiencies 493
−
+
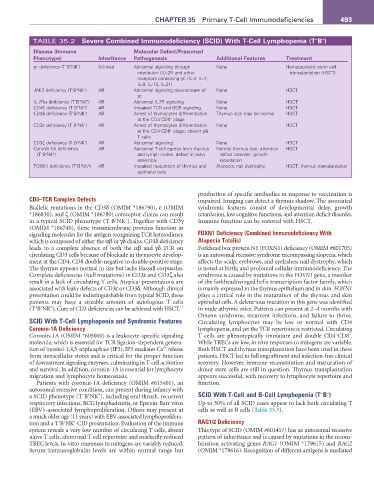
TABLE 35.2 Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) With T-Cell Lymphopenia (T B )
Disease (Immune Molecular Defect/Presumed
Phenotype) Inheritance Pathogenesis additional features Treatment
−
+
γc deficiency (T B NK ) − X-linked Abnormal signaling through None Hematopoietic stem cell
interleukin (IL)-2R and other transplantation (HSCT)
receptors containing γC (IL-4, IL-7,
IL-9, IL-15, IL-21)
+
−
−
JAK3 deficiency (T B NK ) AR Abnormal signaling downstream of None HSCT
γc
+
−
+
IL-7Rα deficiency (T B NK ) AR Abnormal IL7R signaling None HSCT
CD45 deficiency (T B NK ) + AR Impaired TCR and BCR signaling None HSCT
−
+
+
+
−
CD3δ deficiency (T B NK ) AR Arrest of thymocytes differentiation Thymus size may be normal HSCT
at the CD4 CD8 stage
−
−
+
−
CD3ε deficiency (T B NK ) + AR Arrest of thymocytes differentiation None HSCT
−
−
at the CD4 CD8 stage; absent γ/δ
T cells
+
−
CD3ζ deficiency (T B NK ) AR Abnormal signaling None HSCT
+
Coronin-1A deficiency AR Abnormal T-cell egress from thymus Normal thymus size; attention HSCT
−
+
(T B NK ) and lymph nodes; defect in actin deficit disorder; growth
+
assembly retardation
+
−
+
FOXN1 deficiency (T B NK ) AR Impaired maturation of thymus and Alopecia; nail dystrophy HSCT, thymus transplantation
epithelial cells
production of specific antibodies in response to vaccination is
CD3–TCR Complex Defects impaired. Imaging can detect a thymus shadow. The associated
Biallelic mutations in the CD3δ (OMIM *186790), ε (OMIM syndromic features consist of developmental delay, growth
*186830), and ζ (OMIM *186780) coreceptor chains can result retardation, low cognitive functions, and attention deficit disorder.
+
− +
in a typical SCID phenotype (T B NK ). Together with CD3γ Immune function can be restored with HSCT.
(OMIM *186740), these transmembrane proteins function as
signaling molecules for the antigen recognizing TCR heterodimer, FOXN1 Deficiency (Combined Immunodeficiency With
which is composed of either the αβ or γδ chains. CD3δ deficiency Alopecia Totalis)
leads to a complete absence of both the αβ and γδ TCR on Forkhead box protein N1 (FOXN1) deficiency (OMIM #601705)
circulating CD3 cells because of blockade in thymocyte develop- is an autosomal recessive syndrome encompassing alopecia, which
ment at the CD4, CD8 double-negative to double-positive stage. affects the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes; nail dystrophy, which
The thymus appears normal in size but lacks Hassall corpuscles. is noted at birth; and profound cellular immunodeficiency. The
Complete deficiencies (null mutations) in CD3ε and CD3ζ also syndrome is caused by mutations in the FOXN1 gene, a member
result in a lack of circulating T cells. Atypical presentations are of the forkhead/winged helix transcription factor family, which
associated with leaky defects of CD3ε or CD3δ. Although clinical is mainly expressed in the thymus epithelium and in skin. FOXN1
presentation could be indistinguishable from typical SCID, these plays a critical role in the maturation of the thymus and skin
patients may have a sizeable amount of autologous T cells epithelial cells. A deleterious mutation in this gene was identified
+ +
+
(T B NK ). Cure of CD3 deficiencies can be achieved with HSCT. 13 in nude athymic mice. Patients can present at 2–4 months with
Omenn syndrome, recurrent infections, and failure to thrive.
SCID With T-Cell Lymphopenia and Syndromic Features Circulating lymphocytes may be low or normal with CD4
Coronin-1A Deficiency lymphopenia, and yet the TCR repertoire is restricted. Circulating
−
−
Coronin-1A (OMIM *605000) is a leukocyte-specific signaling T cells are phenotypically immature and double CD4 CD8 .
molecule, which is essential for TCR ligation–dependent genera- While TRECs are low, in vitro responses to mitogens are variable.
2+
tion of inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3). IP3 mediates Ca release Both HSCT and thymus transplantation have been tried in these
from intracellular stores and is critical for the proper function patients. HSCT led to full engraftment and infection-free clinical
of downstream signaling enzymes, culminating in T-cell activation recovery. However, immune reconstitution and maturation of
and survival. In addition, coronin-1A is essential for lymphocyte donor stem cells are still in question. Thymus transplantation
migration and lymphocyte homeostasis. appears successful, with recovery to lymphocyte repertoire and
Patients with coronin-1A deficiency (OMIM #615401), an function.
autosomal recessive condition, can present during infancy with − −
− +
+
a SCID phenotype (T B NK ), including oral thrush, recurrent SCID With T-Cell and B-Cell Lymphopenia (T B )
respiratory infections, BCG lymphadenitis, or Epstein-Barr virus Up to 30% of all SCID cases appear to lack both circulating T
(EBV)–associated lymphoproliferation. Others may present at cells as well as B cells (Table 35.3).
a much older age (11 years) with EBV-associated lymphoprolifera-
+
+ +
tion and a T B NK CID presentation. Evaluation of the immune RAG1/2 Deficiency
system reveals a very low number of circulating T cells, absent This type of SCID (OMIM #601457) has an autosomal recessive
naïve T cells, abnormal T cell repertoire and markedly reduced pattern of inheritance and is caused by mutations in the recom-
TREC levels. In-vitro responses to mitogens are variably reduced. bination activating genes RAG1 (OMIM *179615) and RAG2
Serum immunoglobulin levels are within normal range but (OMIM *179616). Recognition of different antigens is mediated