Page 662 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 662
636 Part five Allergic Diseases
A B
C D
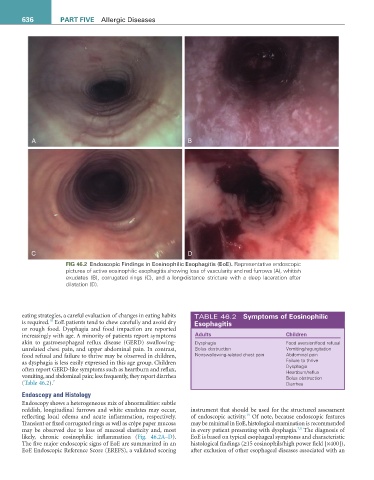
fiG 46.2 Endoscopic Findings in Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Representative endoscopic
pictures of active eosinophilic esophagitis showing loss of vascularity and red furrows (A), whitish
exudates (B), corrugated rings (C), and a long-distance stricture with a deep laceration after
dilatation (D).
eating strategies, a careful evaluation of changes in eating habits TABLE 46.2 Symptoms of eosinophilic
18
is required. EoE patients tend to chew carefully and avoid dry esophagitis
or rough food. Dysphagia and food impaction are reported
increasingly with age. A minority of patients report symptoms adults Children
akin to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) swallowing- Dysphagia Food aversion/food refusal
unrelated chest pain, and upper abdominal pain. In contrast, Bolus obstruction Vomiting/regurgitation
food refusal and failure to thrive may be observed in children, Nonswallowing-related chest pain Abdominal pain
as dysphagia is less easily expressed in this age group. Children Failure to thrive
often report GERD-like symptoms such as heartburn and reflux, Dysphagia
Heartburn/reflux
vomiting, and abdominal pain; less frequently, they report diarrhea Bolus obstruction
(Table 46.2). 7 Diarrhea
Endoscopy and Histology
Endoscopy shows a heterogeneous mix of abnormalities: subtle
reddish, longitudinal furrows and white exudates may occur, instrument that should be used for the structured assessment
19
reflecting local edema and acute inflammation, respectively. of endoscopic activity. Of note, because endoscopic features
Transient or fixed corrugated rings as well as crêpe paper mucosa may be minimal in EoE, histological examination is recommended
7,8
may be observed due to loss of mucosal elasticity and, most in every patient presenting with dysphagia. The diagnosis of
likely, chronic eosinophilic inflammation (Fig. 46.2A–D). EoE is based on typical esophageal symptoms and characteristic
The five major endoscopic signs of EoE are summarized in an histological findings (≥15 eosinophils/high power field [×400]),
EoE Endoscopic Reference Score (EREFS), a validated scoring after exclusion of other esophageal diseases associated with an