Page 698 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 698
CHaPTEr 49 Occupational Respiratory Allergies 671
Therefore, and not surprisingly, atopy is also a risk factor for
developing OA to HMW agents, since subjects who develop OA
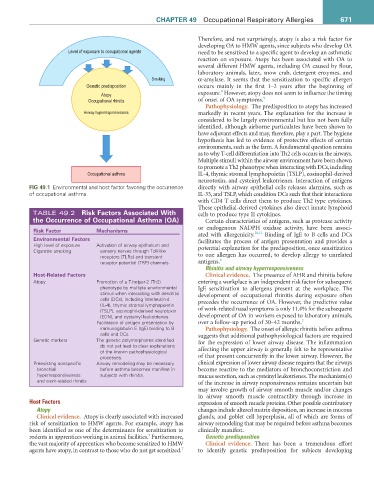
Level of exposure to occupational agents need to be sensitized to a specific agent to develop an asthmatic
reaction on exposure. Atopy has been associated with OA to
several different HMW agents, including OA caused by flour,
laboratory animals, latex, snow crab, detergent enzymes, and
Smoking α-amylase. It seems that the sensitization to specific allergen
Genetic predisposition occurs mainly in the first 1–2 years after the beginning of
8
Atopy exposure. However, atopy does not seem to influence the timing
Occupational rhinitis of onset of OA symptoms. 9
Pathophysiology. The predisposition to atopy has increased
Airway hyperresponsiveness markedly in recent years. The explanation for the increase is
considered to be largely environmental but has not been fully
identified, although airborne particulates have been shown to
have adjuvant effects and may, therefore, play a part. The hygiene
hypothesis has led to evidence of protective effects of certain
environments, such as the farm. A fundamental question remains
as to why T-cell differentiation into Th2 cells occurs in the airways.
Multiple stimuli within the airway environment have been shown
to promote a Th2 phenotype when interacting with DCs, including
Occupational asthma IL-4, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), eosinophil-derived
neurotoxin, and cysteinyl leukotrienes. Interaction of antigens
fiG 49.1 Environmental and host factor favoring the occurrence directly with airway epithelial cells releases alarmins, such as
of occupational asthma. IL-33, and TSLP, which condition DCs such that their interactions
with CD4 T cells direct them to produce Th2 type cytokines.
These epithelial-derived cytokines also direct innate lymphoid
TABLE 49.2 risk factors associated With cells to produce type II cytokines.
the Occurrence of Occupational asthma (Oa) Certain characteristics of antigens, such as protease activity
risk factor Mechanisms or endogenous NADPH oxidase activity, have been associ-
ated with allergenicity. 10,11 Binding of IgE to B cells and DCs
Environmental factors facilitates the process of antigen presentation and provides a
High level of exposure Activation of airway epithelium and potential explanation for the predisposition, once sensitization
Cigarette smoking sensory nerves through Toll-like
receptors (TLRs) and transient to one allergen has occurred, to develop allergy to unrelated
6
receptor potential (TRP) channels. antigens.
Rhinitis and airway hyperresponsiveness
Host-related factors Clinical evidence. The presence of AHR and rhinitis before
Atopy Promotion of a T-helper-2 (Th2) entering a workplace is an independent risk factor for subsequent
phenotype by multiple environmental IgE sensitization to allergens present at the workplace. The
stimuli when interacting with dendritic development of occupational rhinitis during exposure often
cells (DCs), including interleukin-4 precedes the occurrence of OA. However, the predictive value
(IL-4), thymic stromal lymphopoietin
(TSLP), eosinophil-derived neurotoxin of work-related nasal symptoms is only 11.4% for the subsequent
(EDN), and cysteinyl leukotrienes. development of OA in workers exposed to laboratory animals,
Facilitation of antigen presentation by over a follow-up period of 30–42 months. 2
immunoglobulin E (IgE) binding to B Pathophysiology. The onset of allergic rhinitis before asthma
cells and DCs suggests that additional pathophysiological factors are required
Genetic markers The genetic polymorphisms identified for the expression of lower airway disease. The inflammation
do not yet lead to clear explanations
of the known pathophysiological affecting the upper airway is generally felt to be representative
processes. of that present concurrently in the lower airway. However, the
Preexisting nonspecific Airway remodeling may be necessary clinical expression of lower airway disease requires that the airways
bronchial before asthma becomes manifest in become reactive to the mediators of bronchoconstriction and
hyperresponsiveness subjects with rhinitis. mucus secretion, such as cysteinyl leukotrienes. The mechanism(s)
and work-related rhinitis of the increase in airway responsiveness remains uncertain but
may involve growth of airway smooth muscle and/or changes
in airway smooth muscle contractility through increase in
Host Factors expression of smooth muscle proteins. Other possible contributory
Atopy changes include altered matrix deposition, an increase in mucous
Clinical evidence. Atopy is clearly associated with increased glands, and goblet cell hyperplasia, all of which are forms of
risk of sensitization to HMW agents. For example, atopy has airway remodeling that may be required before asthma becomes
been identified as one of the determinants for sensitization to clinically manifest.
7
rodents in apprentices working in animal facilities. Furthermore, Genetic predisposition
the vast majority of apprentices who become sensitized to HMW Clinical evidence. There has been a tremendous effort
7
agents have atopy, in contrast to those who do not get sensitized. to identify genetic predisposition for subjects developing