Page 700 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 700
CHaPTEr 49 Occupational Respiratory Allergies 673
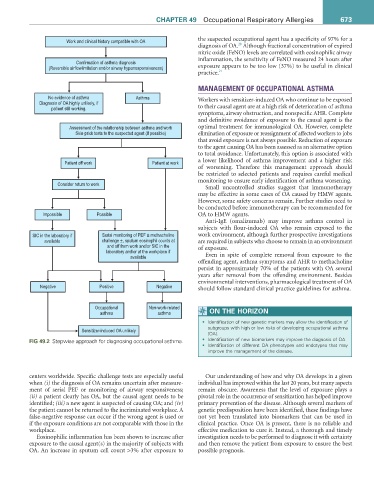
Work and clinical history compatible with OA the suspected occupational agent has a specificity of 97% for a
20
diagnosis of OA. Although fractional concentration of expired
nitric oxide (FeNO) levels are correlated with eosinophilic airway
Confirmation of asthma diagnosis inflammation, the sensitivity of FeNO measured 24 hours after
(Reversible airflowlimitation and/or airway hyperresponsiveness) exposure appears to be too low (37%) to be useful in clinical
practice. 21
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL ASTHMA
No evidence of asthma Asthma
Diagnosis of OA highly unlikely, if Workers with sensitizer-induced OA who continue to be exposed
patient still working. to their causal agent are at a high risk of deterioration of asthma
symptoms, airway obstruction, and nonspecific AHR. Complete
and definitive avoidance of exposure to the causal agent is the
Assessment of the relationship between asthma and work optimal treatment for immunological OA. However, complete
Skin-prick tests to the suspected agent (if possible) elimination of exposure or reassignment of affected workers to jobs
that avoid exposure is not always possible. Reduction of exposure
to the agent causing OA has been assessed as an alternative option
to total avoidance. Unfortunately, this option is associated with
Patient off work Patient at work a lower likelihood of asthma improvement and a higher risk
of worsening. Therefore this management approach should
be restricted to selected patients and requires careful medical
monitoring to ensure early identification of asthma worsening.
Consider return to work
Small uncontrolled studies suggest that immunotherapy
may be effective in some cases of OA caused by HMW agents.
However, some safety concerns remain. Further studies need to
be conducted before immunotherapy can be recommended for
Impossible Possible OA to HMW agents.
Anti-IgE (omalizumab) may improve asthma control in
subjects with flour-induced OA who remain exposed to the
SIC in the laboratory if Serial monitoring of PEF ± methacholine work environment, although further prospective investigations
available challenge ±, sputum eosinophil counts at are required in subjects who choose to remain in an environment
and off from work and/or SIC in the of exposure.
laboratory and/or at the workplace if
available Even in spite of complete removal from exposure to the
offending agent, asthma symptoms and AHR to methacholine
persist in approximately 70% of the patients with OA several
years after removal from the offending environment. Besides
environmental interventions, pharmacological treatment of OA
Negative Positive Negative should follow standard clinical practice guidelines for asthma.
Occupational Non-work-related
asthma asthma ON THE HOriZON
• Identification of new genetic markers may allow the identification of
Sensitizer-induced OA unlikely subgroups with high or low risks of developing occupational asthma
(OA).
fiG 49.2 Stepwise approach for diagnosing occupational asthma. • Identification of new biomarkers may improve the diagnosis of OA.
• Identification of different OA phenotypes and endotypes that may
improve the management of the disease.
centers worldwide. Specific challenge tests are especially useful Our understanding of how and why OA develops in a given
when (i) the diagnosis of OA remains uncertain after measure- individual has improved within the last 20 years, but many aspects
ment of serial PEF or monitoring of airway responsiveness; remain obscure. Awareness that the level of exposure plays a
(ii) a patient clearly has OA, but the causal agent needs to be pivotal role in the occurrence of sensitization has helped improve
identified; (iii) a new agent is suspected of causing OA; and (iv) primary prevention of the disease. Although several markers of
the patient cannot be returned to the incriminated workplace. A genetic predisposition have been identified, these findings have
false-negative response can occur if the wrong agent is used or not yet been translated into biomarkers that can be used in
if the exposure conditions are not comparable with those in the clinical practice. Once OA is present, there is no reliable and
workplace. effective medication to cure it. Instead, a thorough and timely
Eosinophilic inflammation has been shown to increase after investigation needs to be performed to diagnose it with certainty
exposure to the causal agent(s) in the majority of subjects with and then remove the patient from exposure to ensure the best
OA. An increase in sputum cell count >3% after exposure to possible prognosis.