Page 693 - Clinical Immunology_ Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 693
666 ParT FivE Allergic diseases
ON THE HOriZON
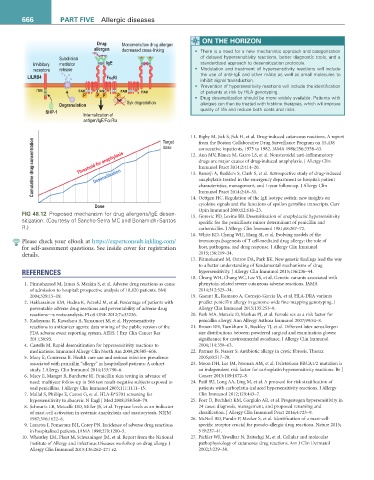
Drug Monomeric/low drug allergen
allergen decreased cross-linking • There is a need for a new mechanistic approach and categorization
Subclinical of delayed hypersensitivity reactions, better diagnostic tools, and a
Inhibitory mediator IgE standardized approach to desensitization protocols.
receptors release • Modulation and treatment of hypersensitivity reactions will include
LILRB4 FcεRI the use of anti–IgE and other mAbs as well as small molecules to
inhibit signal transduction.
• Prevention of hypersensitivity reactions will include the identification
ITIM ITAM ITAM ITAM ITAM of patients at risk by HLA genotyping.
P P P P
Syk • Drug desensitization should be more widely available. Patients with
Degranulation Syk degradation allergies can then be treated with first-line therapies, which will improve
SHP-1 quality of life and reduce both costs and risks.
Internalization of
antigen/IgE/FcεRla
11. Bigby M, Jick S, Jick H, et al. Drug-induced cutaneous reactions. A report
Cumulative drug concentration Threshold for anaphylaxis 12. Aun MV, Blanca M, Garro LS, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
Target
from the Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program on 15,438
dose
consecutive inpatients, 1975 to 1982. JAMA 1986;256:3358–63.
drugs are major causes of drug-induced anaphylaxis. J Allergy Clin
Immunol Pract 2014;2:414–20.
Desensitization
13. Banerji A, Rudders S, Clark S, et al. Retrospective study of drug-induced
anaphylaxis treated in the emergency department or hospital: patient
characteristics, management, and 1-year follow-up. J Allergy Clin
Immunol Pract 2014;2:46–51.
cytokine signals and the functions of epsilon germline transcripts. Curr
Dose 14. Oettgen HC. Regulation of the IgE isotype switch: new insights on
Opin Immunol 2000;12:618–23.
FiG 48.12 Proposed mechanism for drug allergens/IgE desen- 15. Gorevic PD, Levine BB. Desensitization of anaphylactic hypersensitivity
sitization. (Courtesy of Sancho-Serra MC and Bonamichi-Santos specific for the penicilloate minor determinant of penicillin and
R.) carbenicillin. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1981;68:267–72.
16. White KD, Chung WH, Hung SI, et al. Evolving models of the
Please check your eBook at https://expertconsult.inkling.com/ immunopathogenesis of T cell-mediated drug allergy: the role of
for self-assessment questions. See inside cover for registration host, pathogens, and drug response. J Allergy Clin Immunol
details. 2015;136:219–34.
17. Pirmohamed M, Ostrov DA, Park BK. New genetic findings lead the way
to a better understanding of fundamental mechanisms of drug
REFERENCES hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;136:236–44.
18. Chung WH, Chang WC, Lee YS, et al. Genetic variants associated with
1. Pirmohamed M, James S, Meakin S, et al. Adverse drug reactions as cause phenytoin-related severe cutaneous adverse reactions. JAMA
of admission to hospital: prospective analysis of 18,820 patients. BMJ 2014;312:525–34.
2004;329:15–19. 19. Gueant JL, Romano A, Cornejo-Garcia JA, et al. HLA-DRA variants
2. Hakkarainen KM, Hedna K, Petzold M, et al. Percentage of patients with predict penicillin allergy in genome-wide fine-mapping genotyping. J
preventable adverse drug reactions and preventability of adverse drug Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;135:253–9.
reactions—a meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012;7:e33236. 20. Park MA, Matesic D, Markus PJ, et al. Female sex as a risk factor for
3. Kadoyama K, Kuwahara A, Yamamori M, et al. Hypersensitivity penicillin allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2007;99:54–8.
reactions to anticancer agents: data mining of the public version of the 21. Brown RH, Taenkhum K, Buckley TJ, et al. Different latex aeroallergen
FDA adverse event reporting system, AERS. J Exp Clin Cancer Res size distributions between powdered surgical and examination gloves:
2011;30:93. significance for environmental avoidance. J Allergy Clin Immunol
4. Castells M. Rapid desensitization for hypersensitivity reactions to 2004;114:358–63.
medications. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 2009;29:585–606. 22. Parmar JS, Nasser S. Antibiotic allergy in cystic fibrosis. Thorax
5. Macy E, Contreras R. Health care use and serious infection prevalence 2005;60:517–20.
associated with penicillin “allergy” in hospitalized patients: A cohort 23. Moon DH, Lee JM, Noonan AM, et al. Deleterious BRCA1/2 mutation is
study. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2014;133:790–6. an independent risk factor for carboplatin hypersensitivity reactions. Br J
6. Macy E, Mangat R, Burchette RJ. Penicillin skin testing in advance of Cancer 2013;109:1072–8.
need: multiyear follow-up in 568 test result-negative subjects exposed to 24. Patil SU, Long AA, Ling M, et al. A protocol for risk stratification of
oral penicillins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111:1111–15. patients with carboplatin-induced hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy
7. Mallal S, Phillips E, Carosi G, et al. HLA-B*5701 screening for Clin Immunol 2012;129:443–7.
hypersensitivity to abacavir. N Engl J Med 2008;358:568–79. 25. Foer D, Buchheit KM, Gargiulo AR, et al. Progestogen hypersensitivity in
8. Schwartz LB, Metcalfe DD, Miller JS, et al. Tryptase levels as an indicator 24 cases: diagnosis, management, and proposed renaming and
of mast-cell activation in systemic anaphylaxis and mastocytosis. NEJM classification. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2016;4:723–9.
1987;316:1622–6. 26. McNeil BD, Pundir P, Meeker S, et al. Identification of a mast-cell-
9. Lazarou J, Pomeranz BH, Corey PN. Incidence of adverse drug reactions specific receptor crucial for pseudo-allergic drug reactions. Nature 2015;
in hospitalized patients. JAMA 1998;279:1200–5. 519:237–41.
10. Wheatley LM, Plaut M, Schwaninger JM, et al. Report from the National 27. Pichler WJ, Yawalkar N, Britschgi M, et al. Cellular and molecular
Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases workshop on drug allergy. J pathophysiology of cutaneous drug reactions. Am J Clin Dermatol
Allergy Clin Immunol 2015;136:262–271 e2. 2002;3:229–38.